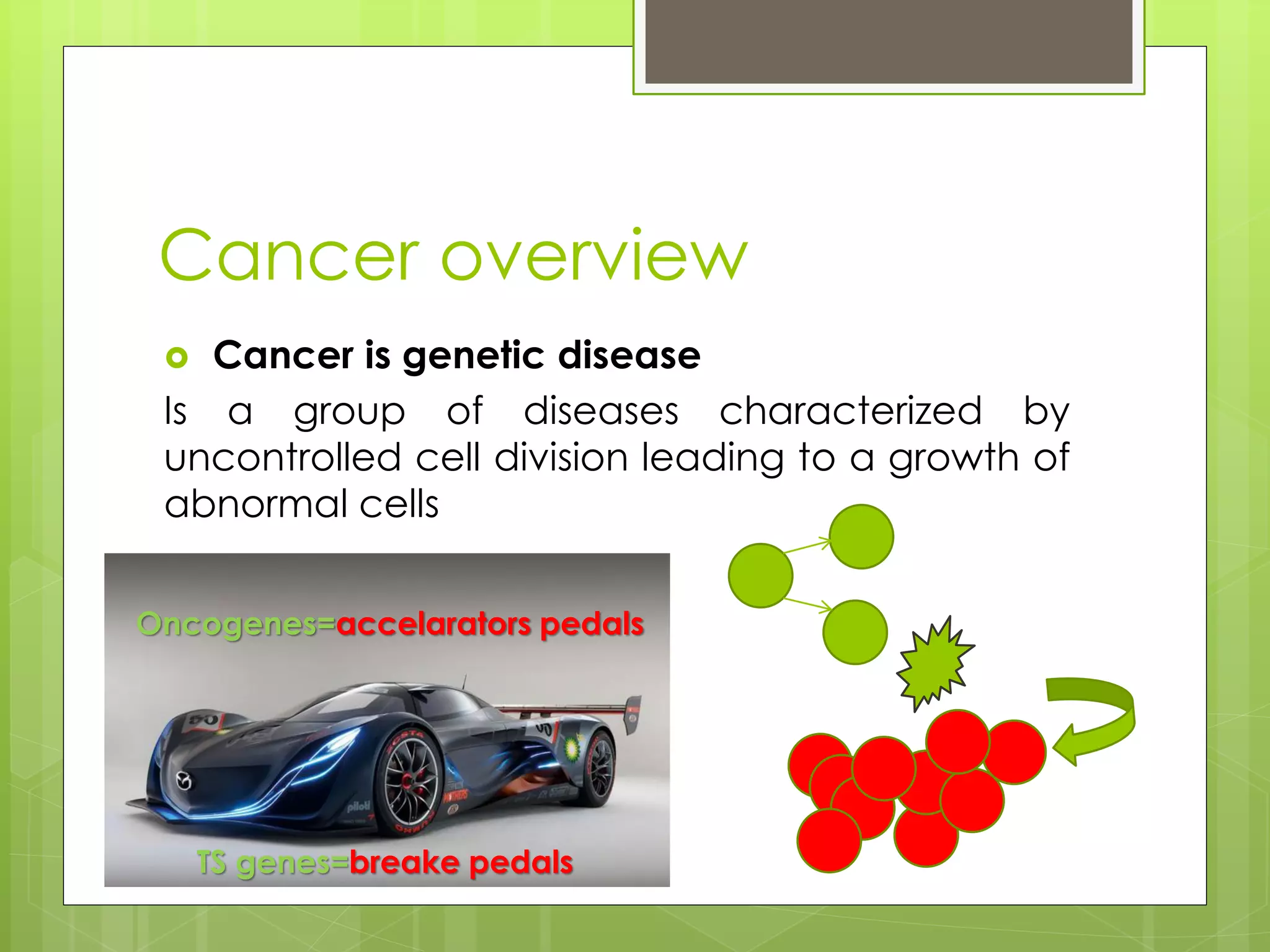
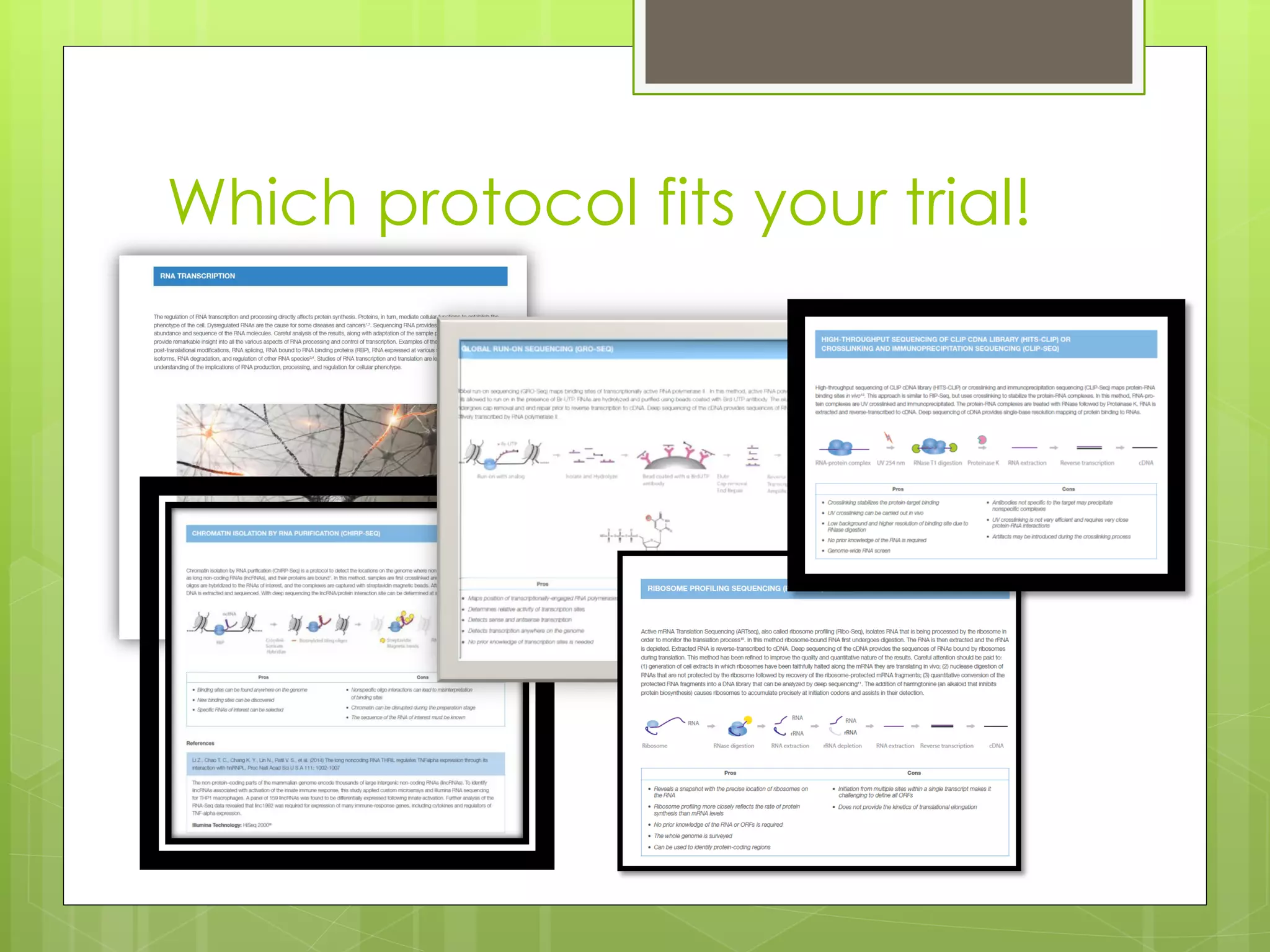
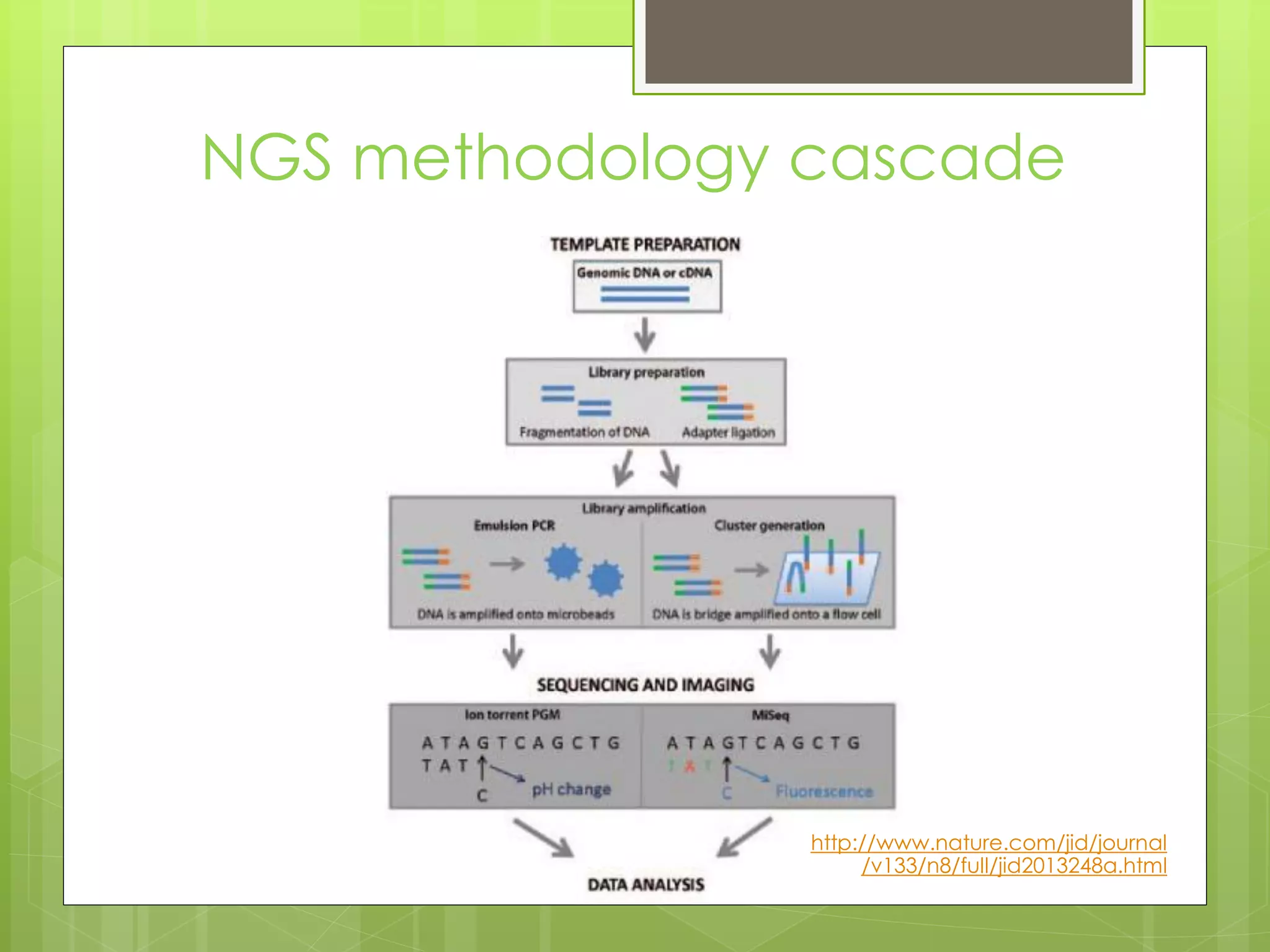
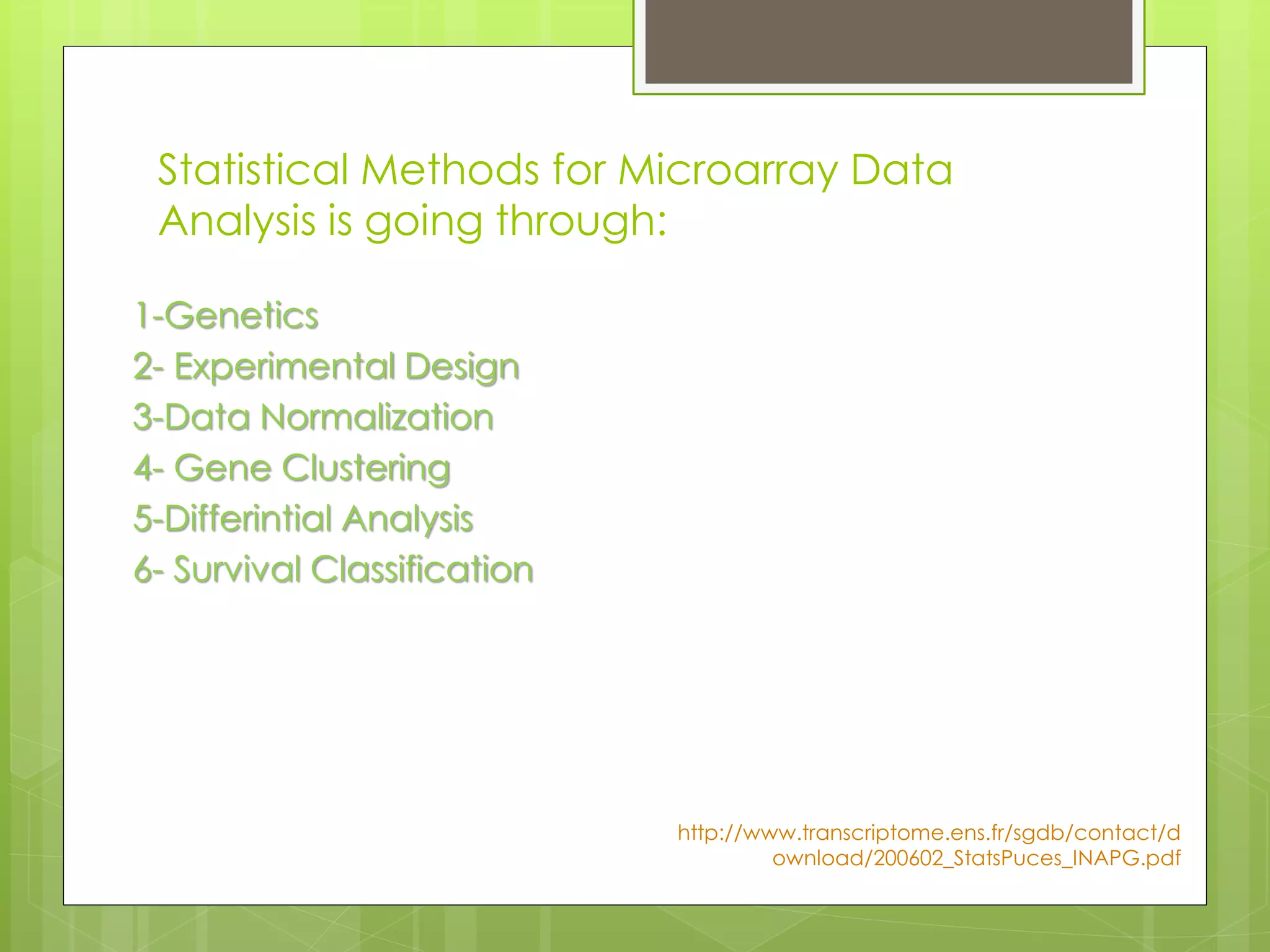
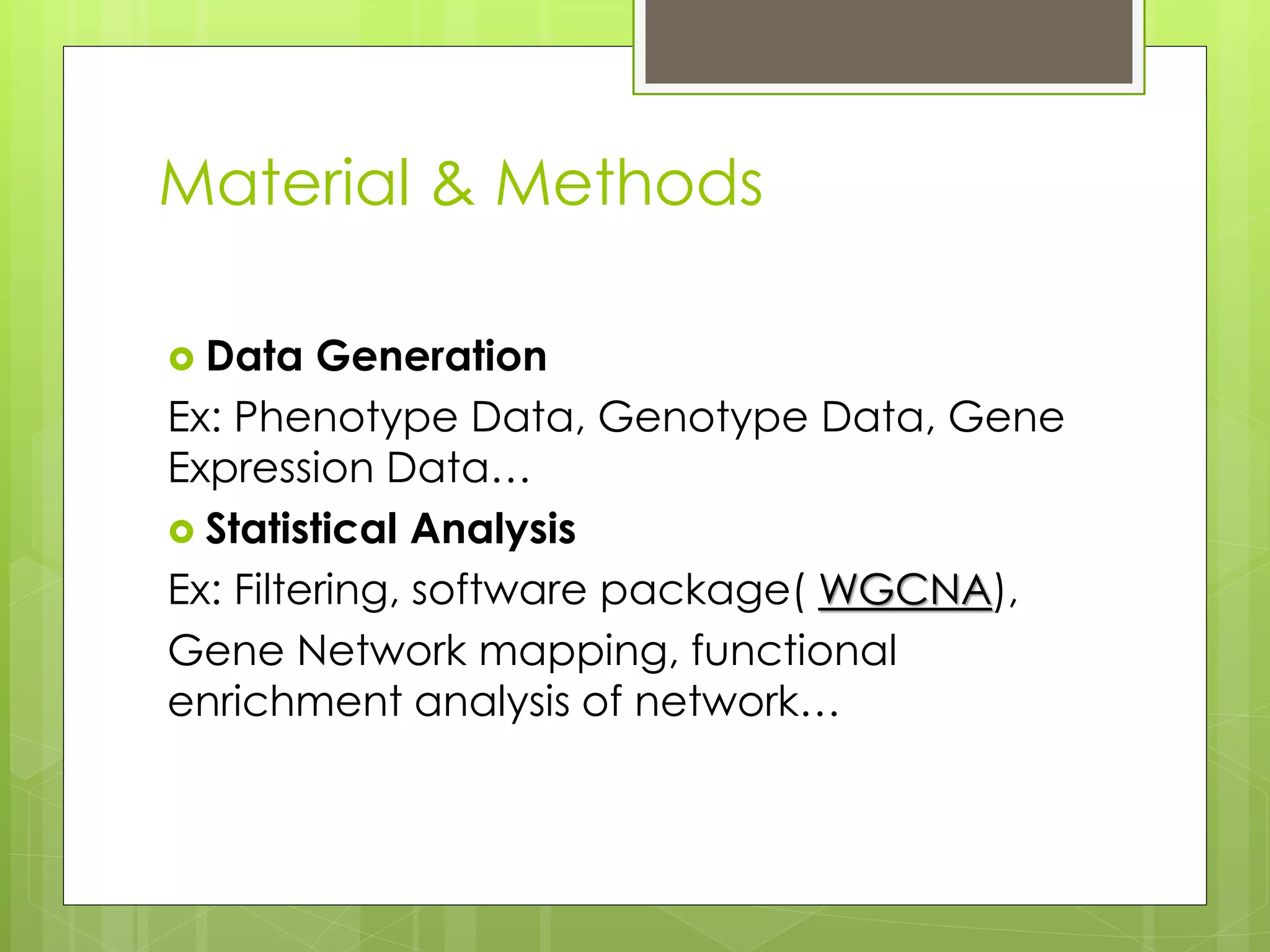
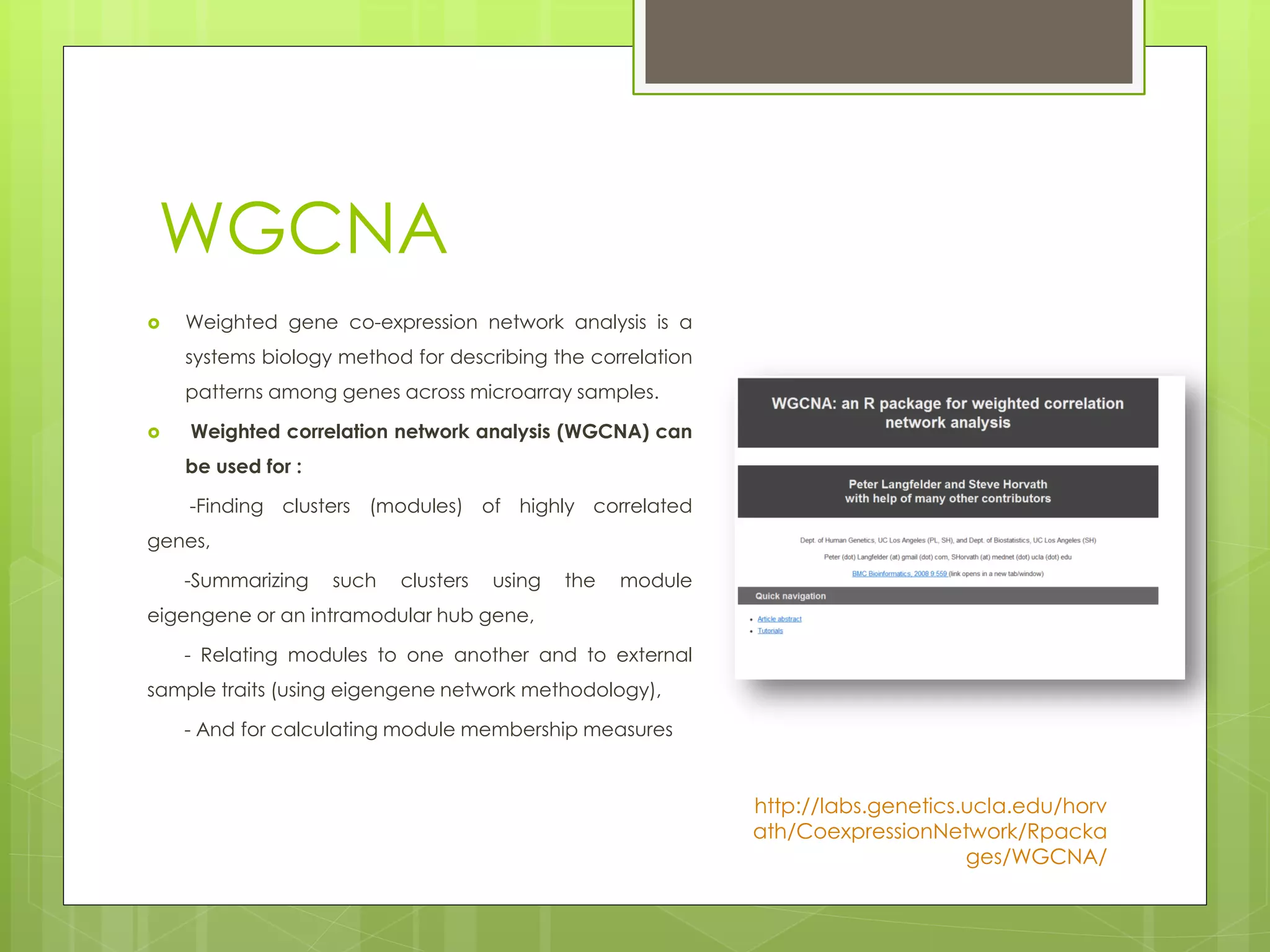
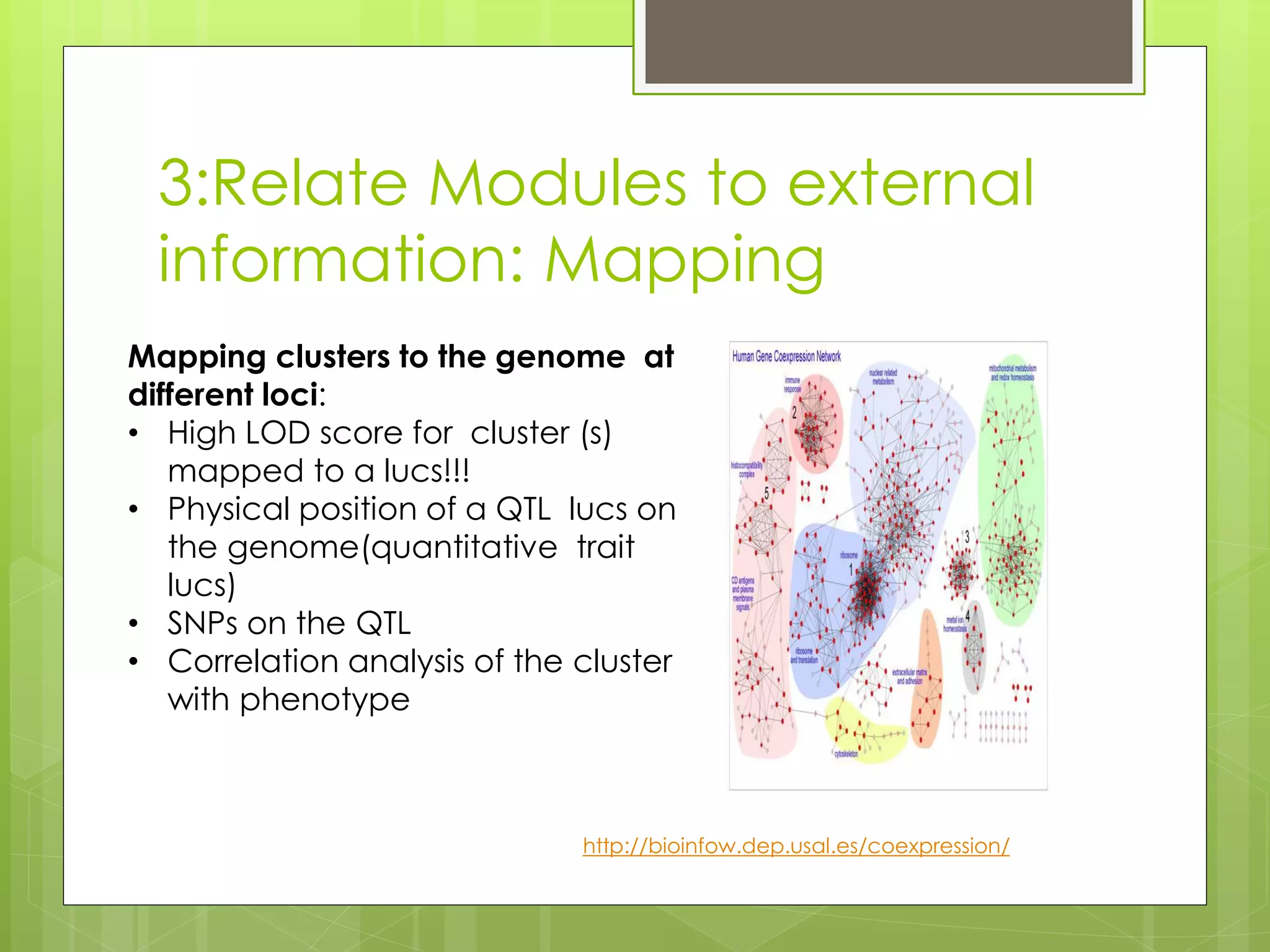
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) and its application to breast cancer research is discussed. NGS allows for comprehensive profiling of microRNA (miRNA) expression, which can provide insights into tumorigenesis pathways. The document outlines the NGS process, including template preparation, sequencing/imaging, and complex data analysis using statistical methods and software. Key applications are identifying miRNA involvement in cancer driver genes and exploring miRNA expression patterns to discover potential diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer subtypes.