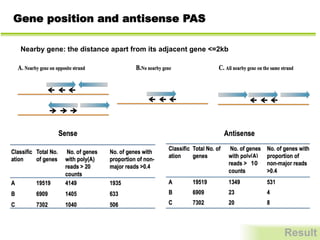
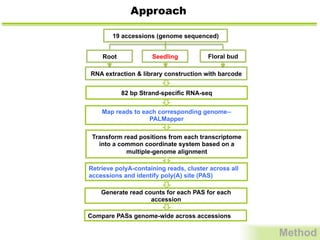
This study investigates alternative polyadenylation (APA) in Arabidopsis, revealing that approximately 70% of its genes utilize multiple polyadenylation sites, influencing gene expression significantly. The research employs a deep-sequencing method to establish a comprehensive landscape of APA, indicating that protein-coding regions and introns experience extensive alternative processing. Findings suggest that APA plays a crucial role in plant gene regulation, offering insights into potential genetic variations across different Arabidopsis accessions.

![Alternative polyadenylation (APA)
Background
thus allowing these transcripts to evade miRNA-
mediated degradation. Transcripts are also subject to
transcript degradation but also stability. In a genome-
wide computational analysis of sequence and stability
Figure 1
(a)
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex3Ex2
(b)
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex2
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
5′
5′ 3′
5′
5′
5′ 5′3′ 3′
3′
3′
3′
Current Opinion in Cell Biology
Major categories of APA. This model refers to a hypothetical gene with three exons and two PASs. (a) When both PASs are located in the 30
UTR, then
dentical proteins are produced. Because the 30
UTR often contains elements regulating transcript stability, degradation, or localization, the quantity of
protein produced may be altered depending upon PAS choice. (b) When one PAS is located in the coding region, a truncated protein is produced when
Mueller, et al. 2012
Tian, et al. 2013
differentiated cells are reprogrammed to ES cell-like in-
duced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells [41]. A notable excep-
tion, however, has been observed with spermatogonial
germ cells, whose reprogramming to ES cells involves 30
UTR lengthening [41]. Notably, this is in line with the fact
that germ cells are more proliferative than ES cells. Simi-
lar trends of 30
UTR length regulation have been reported
for comparisons of ES cells versus neural stem/progenitor
(NSP) cells or neurons [42]. Although these studies have all
pointed to a connection between 30
UTR length and cell
proliferation, cardiac hypertrophy, in which myocytes grow
in size rather than in number, has also been found to
involve 30
UTR shortening [43]. Thus, a general rule
may be that APA regulation is correlated with cell growth.
Cancer
Cancer cells are of co
with this, and consist
been found to express,
UTRs, as first shown
mouse B-cell leukem
recently in human colo
lung cancers [47]. In t
profile was found to
subtypes with differe
its relevance to cance
nostic marker. One ke
in cancer is whether p
major driver of APA. M
transformed and non
dicted proliferation ra
transformation has a
[44]. However, a recen
the same cells (BJ prim
lial cell line MCF10A)
formed states, pro
determinant of 30
UTR
of 30
UTR regulation i
that, compared to MC
and MB231 show sho
spectively. Notably, it
to the general trend,
adhesion genes, tend t
UTRs in cancer cells [4
delineated how APA o
different cancer types
APA is modulated by
miRNA
RBP
TranslaƟon DegradaƟonLocalizaƟon
AAAnCDS
CDS
cUTR aUTR
!!
AAA
AAA
n
TiBS
Figure 2. Regulation of cis elements in 30
untranslated regions (UTRs) by
alternative cleavage and polyadenylation (APA). Two mRNA isoforms are
mediated degradation. Transcripts are also subject to wide computational analysis of sequence and stability
Figure 1
(a)
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex3Ex2
(b)
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex2
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
5′
5′ 3′
5′
5′
5′ 5′3′ 3′
3′
3′
3′
Current Opinion in Cell Biology
Major categories of APA. This model refers to a hypothetical gene with three exons and two PASs. (a) When both PASs are located in the 30
UTR, then
identical proteins are produced. Because the 30
UTR often contains elements regulating transcript stability, degradation, or localization, the quantity of
protein produced may be altered depending upon PAS choice. (b) When one PAS is located in the coding region, a truncated protein is produced when
the proximal PAS is chosen. Ex = exon, PAS = polyadenylation site; thick lines = UTR regions, thin lines = intronic regions.
www.sciencedirect.com Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2013, 25:222–232
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex3Ex2
(b)
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex2
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
5′ 3′
5′
5′
5′ 5′3′ 3′
3′
3′
Current Opinion in Cell Biology
Major categories of APA. This model refers to a hypothetical gene with three exons and two PASs. (a) When both PASs are located in the 30
UTR, then
identical proteins are produced. Because the 30
UTR often contains elements regulating transcript stability, degradation, or localization, the quantity of
protein produced may be altered depending upon PAS choice. (b) When one PAS is located in the coding region, a truncated protein is produced when
the proximal PAS is chosen. Ex = exon, PAS = polyadenylation site; thick lines = UTR regions, thin lines = intronic regions.
www.sciencedirect.com Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2013, 25:222–232
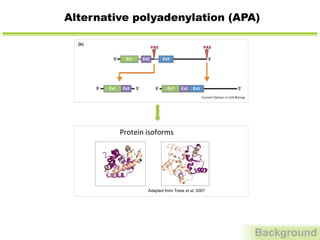
Adapted from Tress et al. 2007
Protein
isoforms
depletion at t
downstream
tioning migh
ing the rate o
these observ
mental studie
and to estab
nucleosome o
Anotherw
to affect APA
genetic effect
tissues, in tw
Napl15), whi
genes(namel
cases,thepro
are therefore
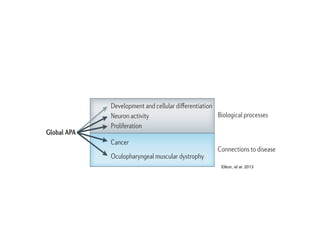
Nature Reviews | Genetics
Neuron activity
Proliferation
Cancer
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
Global APA
Biological processes
Connections to disease
Favour distal poly(A) site usage Favour proximal poly(A) site usage
Figure 3 | Biological processes that have been linked with broad APA modulation.
A schematic showing the biological processes and diseases that alternative
polyadenylation(APA)hasbeenlinkedwith.Inaddition,thetendencytowardsdistal
orproximalpoly(A)siteusageisshown.
Elkon, et al. 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioinformaticjc08142013formal-130905160158-/85/Bioinformatic-jc-08_14_2013_formal-4-320.jpg)
![APA in plants and unknown questions?
Background
Although genome-wide investigation of polyadenylation in single Arabidopsis
accession, we still do not know:
1. How much variation in the polyadenylation usage across Arabidopsis
accessions? What is the genetic basis for such variation? Cis regulation?
Trans?
2. Is Arabidopsis an outlier for any of the trends of polyadenylation site
usage compared with related species? How has APA evolved across
related species?
Genome-wide landscape of polyadenylation in
Arabidopsis provides evidence for extensive
alternative polyadenylation
Xiaohui Wua,b
, Man Liua
, Bruce Downiec
, Chun Lianga
, Guoli Jib
, Qingshun Q. Lia,b,1
, and Arthur G. Huntd,1
a
Department of Botany, Miami University, Oxford, OH 45056; b
Department of Automation, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian 361005, People’s Republic of
China; and c
Department of Horticulture and Seed Biology Group, and d
Department of Plant and Soil Sciences, University of Kentucky, Lexington,
KY 40546-0312.
Edited by David C. Baulcombe, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, and approved June 8, 2011 (received for review January 14, 2011)
Alternative polyadenylation (APA) has been shown to play an
important role in gene expression regulation in animals and
plants. However, the extent of sense and antisense APA at the
genome level is not known. We developed a deep-sequencing
protocol that queries the junctions of 3′UTR and poly(A) tails and
confidently maps the poly(A) tags to the annotated genome. The
results of this mapping show that 70% of Arabidopsis genes use
more than one poly(A) site, excluding microheterogeneity. Analy-
sis of the poly(A) tags reveal extensive APA in introns and coding
sequences, results of which can significantly alter transcript se-
quences and their encoding proteins. Although the interplay of
intron splicing and polyadenylation potentially defines poly(A)
site uses in introns, the polyadenylation signals leading to the
use of CDS protein-coding region poly(A) sites are distinct from
the rest of the genome. Interestingly, a large number of poly(A)
sites correspond to putative antisense transcripts that overlap
with the promoter of the associated sense transcript, a mode pre-
viously demonstrated to regulate sense gene expression. Our
results suggest that APA plays a far greater role in gene expres-
sion in plants than previously expected.
alternative processing | antisense transcription | nonstop mRNAs
The polyadenylation of mRNA in eukaryotes is an important
step in gene expression in eukaryotes. With few exceptions,
mature eukaryotic mRNAs possess a poly(A) tract, that in turn
functions to facilitate transport of the mRNA to the cytoplasm
and its subsequent stabilization and translation. The poly(A) tail
contributes regulatory information to each of these processes
through interactions with RNA processing factors and poly(A)-
binding proteins. The process of polyadenylation also contributes
to regulation by “determining” the composition of the mRNA
apart from the poly(A) tail. Thus, the position along the gene
where the pre-mRNA is processed and polyadenylated deter-
mines the sequence content in terms of exons and regulatory
motifs. If a gene possesses more than one polyadenylation site,
then the nature of the expressed mRNA can be altered via dif-
ferential choice of these sites, a process that is called alternative
polyadenylation, or APA. That APA may be important is sug-
gested by the observations that more than 50% of human and
plant genes have multiple poly(A) sites (1–5). APA may be an
important factor in the regulation of genes associated with can-
cer and with early embryo development in animals (6–8). APA
the FLC gene (15, 16); these antisense transcripts are involved in
transcriptional regulation of sense FLC mRNAs through chro-
matin modifications in the vicinity of the sense FLC promoter.
The regulation of these two genes thus provides examples of two
modes of APA, involving intronic polyadenylation and 3′ end
processing of antisense transcripts.
Plant poly(A) site datasets (3, 17) have been assembled from
the analysis and curation of the results of EST and full-length
cDNA sequencing projects. Unfortunately, these projects are not
specially targeted to the identification of poly(A) sites, nor are
they high-throughput. With this consideration in mind, a strategy
designed to specifically query the mRNA-poly(A) junction on
a transcriptome-wide basis was developed and used to study
poly(A) site choice in Arabidopsis leaves and seeds. The results
obtained using this strategy reveal an extensive network of po-
tential APA in Arabidopsis, including unanticipated and novel
modes of APA. In addition, the results corroborate other reports
suggestive of wide-spread antisense transcription in Arabidopsis,
and provide a dataset of poly(A) sites associated with antisense
transcripts. Finally, they provide evidence for tissue-specific
poly(A) site choice.
Results
Preparation and Characterization of cDNA Tags That Query Poly-
adenylation Sites. To study Arabidopsis poly(A) sites on a genome-
wide basis, short DNA tags that include the mRNA-poly(A) site
junction [called poly(A) tags, or PATs hereafter] were prepared
and sequenced; the starting materials for these samples were
RNA isolated from dry seeds and the leaves of young seed-
lings. The initial sequences were processed and mapped to the
Arabidopsis reference genome. After removing potential internal
priming candidates and eliminating tags that mapped to chlo-
roplast and mitochondria genomes and to miscellaneous RNAs
(primarily rRNAs), a collection of tags that defined more than
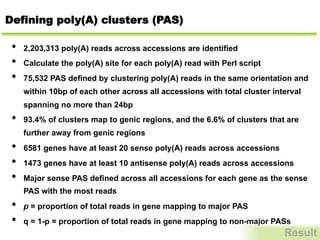
280,000 individual poly(A) sites were obtained (Table S1). Be-
cause poly(A) site microheterogeneity is ubiquitous in plants (3,
4), poly(A) sites in the same gene that are located within 24 nt of
each other were clustered so as to define a poly(A) site cluster
(PAC). The results of this process were more than 71,000 PACs
with an average of 54 PATs per PAC (Table S1). Of these PACs,
57,473 were in the “sense” orientation with respect to an anno-
Author contributions: X.W., M.L., G.J., Q.Q.L., and A.G.H. designed research; X.W., M.L.,
NATURE STRUCTURAL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY VOLUME 19 NUMBER 8 AUGUST 2012 845
R E S OU RC E
Arabidopsis thaliana is an important model system that has had a
critical role in discoveries essential to our understanding of plant
biology and of generically important processes such as RNA interfer-
ence (RNAi). Although the A. thaliana genome was sequenced more
than a decade ago, challenges remain in resolving the RNAs that it
encodes and determining their functional significance. Establishing
where transcripts end is essential in genome annotation and for
understanding gene function. Alternative cleavage and polyadenyla-
tion (APA) defines different 3 ends within pre-mRNA transcribed
from the same gene, and this can affect function by determining
coding potential or the inclusion of regulatory sequence elements1,2.
This regulation of RNA 3 -end formation is considerably more wide-
spread than previously thought1,2, and RNA-binding proteins that
enable A. thaliana flowering provide important examples of the
biological impact of this control3. Defective 3 -end formation and
transcription termination at tandem or convergent gene pairs can
result in transcription interference or RNAi4,5, revealing that these
processes normally partition the genome and maintain expression of
neighboring genes6. Accordingly, such consequences of uncontrolled
3 -end formation also emphasize the critical nature of gene arrange-
ment along a eukaryotic chromosome.
As a prelude to the analysis of regulators of 3 -end formation,
we set out to map A. thaliana RNA 3 ends genome-wide. Previous
high-throughput A. thaliana transcriptome studies have depended
on the copying of RNA into complementary DNA (cDNA) with
reverse transcriptase7–10. However, the intrinsic template switch-
ing11 and DNA-dependent DNA-polymerase12 activities of reverse
transcriptases, together with oligo(dT)-dependent internal priming13,
cause well-established artifacts that can affect the identification of
authentic antisense RNAs14,15, splicing events14 and RNA 3 ends13,16.
Different strategies have been developed to address these problems,
making strand-specific RNA sequencing an increasingly powerful
tool for the analysis of transcriptomes. However, a recent comparison
of several such methods showed marked differences not only in strand
specificity but also in a range of criteria that influence transcriptome
interpretation17. Therefore, as an alternative, we used direct RNA
sequencing (DRS) to identify polyadenylated A. thaliana RNAs18.
This approach is direct in the sense that native RNA is used as the
sequencing template, but the sequence is read by imaging comple-
mentary fluorescent nucleotides incorporated by a polymerase.
In this true single-molecule sequencing (tSMS) procedure, the site
of RNA cleavage and polyadenylation is defined with an accuracy
of 2 nucleotides (nt) in the absence of errors induced by reverse
transcriptase, ligation or amplification18.
RESULTS
Mapping A. thaliana RNA 3 ends
Total RNA purified from A. thaliana seedlings was subjected to DRS,
and a computational procedure to align reads uniquely to the most
recent A. thaliana genome release (currently TAIR10) was developed.
The initial mapping analysis revealed that the vast majority of reads
(89.60%) aligned to protein-coding genes, which is consistent with
the idea that this approach can identify authentic sites of mRNA
cleavage and polyadenylation (Fig. 1a). These data define extremely
heterogeneous patterns of RNA 3 -end formation (Fig. 1b) that
differ markedly from those of human mRNAs analyzed in the same
way (Supplementary Fig. 1a)18.
Although nontemplated base addition between cleavage sites and the
poly(A) tail has been reported from analysis of A. thaliana expressed-
sequence-tag (EST) data19, we found no evidence for this phenomenon
1College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, Dundee, UK. 2Department of Cell and Molecular Sciences, James Hutton Institute, Invergowrie, Dundee, UK. 3Helicos
BioSciences Corporation, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA. Correspondence should be addressed to G.G.S. (g.g.simpson@dundee.ac.uk) or G.J.B. (g.j.barton@dundee.ac.uk).
Received 16 February; accepted 19 June; published online 22 July 2012; doi:10.1038/nsmb.2345
Direct sequencing of Arabidopsis thaliana RNA reveals
patterns of cleavage and polyadenylation
Alexander Sherstnev1, Céline Duc1, Christian Cole1, Vasiliki Zacharaki1, Csaba Hornyik2, Fatih Ozsolak3,
Patrice M Milos3, Geoffrey J Barton1 & Gordon G Simpson1,2
It has recently been shown that RNA 3 -end formation plays a more widespread role in controlling gene expression than
previously thought. To examine the impact of regulated 3 -end formation genome-wide, we applied direct RNA sequencing to
A. thaliana. Here we show the authentic transcriptome in unprecedented detail and describe the effects of 3 -end formation on
genome organization. We reveal extreme heterogeneity in RNA 3 ends, discover previously unrecognized noncoding RNAs and
propose widespread reannotation of the genome. We explain the origin of most poly(A)+ antisense RNAs and identify cis elements
that control 3 -end formation in different registers. These findings are essential to understanding what the genome actually
encodes, how it is organized and how regulated 3 -end formation affects these processes.
npg©2012NatureAmerica,Inc.Allrightsreserved.
(AtCPSF30)
(AtCPSF30*-YT521B)
FLC
OXT6
D P
P D
a
a
a
b
c
b
b
c
c
FIGURE 2 | Schematic representation of alternative polyadenyla
Xing, et al. 2012PAS2 PAS1
Gene
Transcript1
Transcript2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioinformaticjc08142013formal-130905160158-/85/Bioinformatic-jc-08_14_2013_formal-5-320.jpg)









![Tian, et al. 2013
differentiated cells are reprogrammed to ES cell-like in-
duced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells [41]. A notable excep-
tion, however, has been observed with spermatogonial
germ cells, whose reprogramming to ES cells involves 30
UTR lengthening [41]. Notably, this is in line with the fact
that germ cells are more proliferative than ES cells. Simi-
lar trends of 30
UTR length regulation have been reported
for comparisons of ES cells versus neural stem/progenitor
(NSP) cells or neurons [42]. Although these studies have all
pointed to a connection between 30
UTR length and cell
proliferation, cardiac hypertrophy, in which myocytes grow
in size rather than in number, has also been found to
involve 30
UTR shortening [43]. Thus, a general rule
may be that APA regulation is correlated with cell growth.
Cancer
Cancer cells are of course hi
with this, and consistent with
been found to express, in gene
UTRs, as first shown in tran
mouse B-cell leukemia/lymp
recently in human colorectal c
lung cancers [47]. In the stud
profile was found to be info
subtypes with different surv
its relevance to cancer devel
nostic marker. One key questi
in cancer is whether prolifera
major driver of APA. Meta-an
transformed and nontransfo
dicted proliferation rates has
transformation has a signific
[44]. However, a recent study
the same cells (BJ primary fib
lial cell line MCF10A) in prol
formed states, proliferatio
determinant of 30
UTR length
of 30
UTR regulation in cance
that, compared to MCF10A,
and MB231 show shortened
spectively. Notably, it has als
to the general trend, some g
adhesion genes, tend to expre
UTRs in cancer cells [45,46]. T
delineated how APA of differe
different cancer types and at
APA is modulated by multi
Regulation of core C/P facto
miRNA
RBP
TranslaƟon DegradaƟonLocalizaƟon
AAAnCDS
CDS
cUTR aUTR
!!
AAA
AAA
n
TiBS
Figure 2. Regulation of cis elements in 30
untranslated regions (UTRs) by
alternative cleavage and polyadenylation (APA). Two mRNA isoforms are
shown. The 30
UTR region upstream of the proximal cleavage and
Figure 1
(a)
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex3Ex2
(b)
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex2
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
5′
5′ 3′
5′
5′
5′ 5′3′ 3′
3′
3′
3′
Current Opinion in Cell Biology
Major categories of APA. This model refers to a hypothetical gene with three exons and two PASs. (a) When both PASs are located in the 30
UTR, then
identical proteins are produced. Because the 30
UTR often contains elements regulating transcript stability, degradation, or localization, the quantity of
protein produced may be altered depending upon PAS choice. (b) When one PAS is located in the coding region, a truncated protein is produced when
the proximal PAS is chosen. Ex = exon, PAS = polyadenylation site; thick lines = UTR regions, thin lines = intronic regions.
www.sciencedirect.com Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2013, 25:222–232](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioinformaticjc08142013formal-130905160158-/85/Bioinformatic-jc-08_14_2013_formal-24-320.jpg)
![Alternative polyadenylation (APA)
Background
in abundance. One of the best-charac-
is that of microRNA (miR)-mediated
studies of myogenic [43,44
], hemato-
d cancer [45] cells, transcripts bearing
contained fewer miRNA-binding sites,
these transcripts to evade miRNA-
dation. Transcripts are also subject to
Upf1 binds to the 3 UTR in a length-dependent manner,
thus eliciting degradation of longer transcripts more
rapidly [48
].
The 30
UTR contains elements that affect not only
transcript degradation but also stability. In a genome-
wide computational analysis of sequence and stability
(a)
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex3Ex2
(b)
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex2
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
5′
5′ 3′
5′
5′
5′ 5′3′ 3′
3′
3′
3′
Current Opinion in Cell Biology
PA. This model refers to a hypothetical gene with three exons and two PASs. (a) When both PASs are located in the 30
UTR, then
produced. Because the 30
UTR often contains elements regulating transcript stability, degradation, or localization, the quantity of
be altered depending upon PAS choice. (b) When one PAS is located in the coding region, a truncated protein is produced when
hosen. Ex = exon, PAS = polyadenylation site; thick lines = UTR regions, thin lines = intronic regions.
om Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2013, 25:222–232
Mueller, et al. 2012
Tian, et al. 2013
lar trends of 30
UTR length regulation have been reported
for comparisons of ES cells versus neural stem/progenitor
(NSP) cells or neurons [42]. Although these studies have all
pointed to a connection between 30
UTR length and cell
proliferation, cardiac hypertrophy, in which myocytes grow
in size rather than in number, has also been found to
involve 30
UTR shortening [43]. Thus, a general rule
may be that APA regulation is correlated with cell growth.
recentl
lung ca
profile
subtyp
its rele
nostic m
in canc
major d
transfo
dicted
transfo
[44]. H
the sam
lial cel
formed
determ
of 30
U
that, co
and M
spectiv
to the
adhesi
UTRs i
delinea
differen
APA is
Regula
The co
include
subuni
miRNA
RBP
TranslaƟon DegradaƟonLocalizaƟon
AAAnCDS
CDS
cUTR aUTR
!!
AAA
AAA
n
Ti BS
Figure 2. Regulation of cis elements in 30
untranslated regions (UTRs) by
alternative cleavage and polyadenylation (APA). Two mRNA isoforms are
shown. The 30
UTR region upstream of the proximal cleavage and
polyadenylation site (pA) is called the constitutive UTR (cUTR), and the
downstream region is called the alternative UTR (aUTR). RNA-binding protein
(RBP) and miRNA targeting to the aUTR are shown. Impacts on mRNA localization,
translation, and degradation are indicated. CDS, coding sequence.
Adapted from Tress et al. 2007
Protein
isoforms
depletion at the site and more pron
downstream from it, suggesting th
tioning might influence PAS use by
ing the rate of polymerase elongat
these observations are only corr
mental studies are required in ord
and to establish a cause–effect re
nucleosome occupancy and poly(A
Neuron activity
Proliferation
Cancer
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
Global APA
Biological processes
Connections to disease
R
Elkon, et al. 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioinformaticjc08142013formal-130905160158-/85/Bioinformatic-jc-08_14_2013_formal-25-320.jpg)
![Alternative polyadenylation (APA)
Background
in abundance. One of the best-charac-
is that of microRNA (miR)-mediated
studies of myogenic [43,44
], hemato-
d cancer [45] cells, transcripts bearing
contained fewer miRNA-binding sites,
these transcripts to evade miRNA-
dation. Transcripts are also subject to
Upf1 binds to the 3 UTR in a length-dependent manner,
thus eliciting degradation of longer transcripts more
rapidly [48
].
The 30
UTR contains elements that affect not only
transcript degradation but also stability. In a genome-
wide computational analysis of sequence and stability
(a)
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex3Ex2
(b)
Ex1 Ex3Ex2Ex1 Ex2
Ex1 Ex3
PASPAS
Ex2
5′
5′ 3′
5′
5′
5′ 5′3′ 3′
3′
3′
3′
Current Opinion in Cell Biology
PA. This model refers to a hypothetical gene with three exons and two PASs. (a) When both PASs are located in the 30
UTR, then
produced. Because the 30
UTR often contains elements regulating transcript stability, degradation, or localization, the quantity of
be altered depending upon PAS choice. (b) When one PAS is located in the coding region, a truncated protein is produced when
hosen. Ex = exon, PAS = polyadenylation site; thick lines = UTR regions, thin lines = intronic regions.
om Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2013, 25:222–232
Mueller, et al. 2012
Tian, et al. 2013
lar trends of 30
UTR length regulation have been reported
for comparisons of ES cells versus neural stem/progenitor
(NSP) cells or neurons [42]. Although these studies have all
pointed to a connection between 30
UTR length and cell
proliferation, cardiac hypertrophy, in which myocytes grow
in size rather than in number, has also been found to
involve 30
UTR shortening [43]. Thus, a general rule
may be that APA regulation is correlated with cell growth.
recentl
lung ca
profile
subtyp
its rele
nostic m
in canc
major d
transfo
dicted
transfo
[44]. H
the sam
lial cel
formed
determ
of 30
U
that, co
and M
spectiv
to the
adhesi
UTRs i
delinea
differen
APA is
Regula
The co
include
subuni
miRNA
RBP
TranslaƟon DegradaƟonLocalizaƟon
AAAnCDS
CDS
cUTR aUTR
!!
AAA
AAA
n
Ti BS
Figure 2. Regulation of cis elements in 30
untranslated regions (UTRs) by
alternative cleavage and polyadenylation (APA). Two mRNA isoforms are
shown. The 30
UTR region upstream of the proximal cleavage and
polyadenylation site (pA) is called the constitutive UTR (cUTR), and the
downstream region is called the alternative UTR (aUTR). RNA-binding protein
(RBP) and miRNA targeting to the aUTR are shown. Impacts on mRNA localization,
translation, and degradation are indicated. CDS, coding sequence.
Adapted from Tress et al. 2007
Protein
isoforms
depletion at the site and more pron
downstream from it, suggesting th
tioning might influence PAS use by
ing the rate of polymerase elongat
these observations are only corr
mental studies are required in ord
and to establish a cause–effect re
nucleosome occupancy and poly(A
Neuron activity
Proliferation
Cancer
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
Global APA
Biological processes
Connections to disease
R
Elkon, et al. 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioinformaticjc08142013formal-130905160158-/85/Bioinformatic-jc-08_14_2013_formal-26-320.jpg)