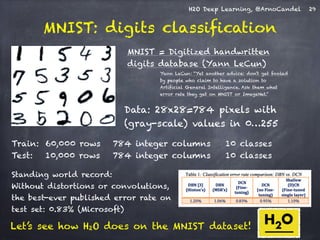
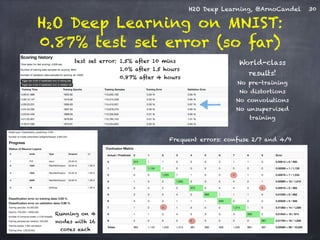
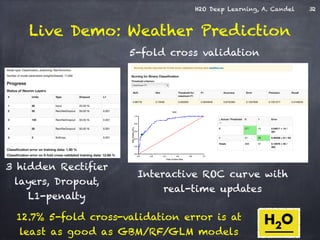
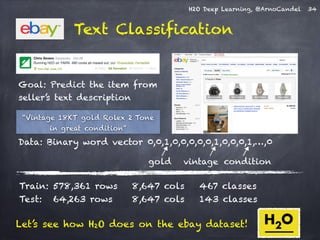
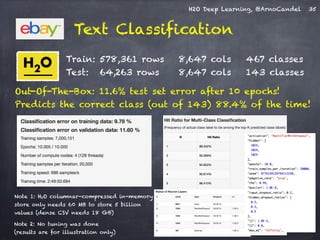
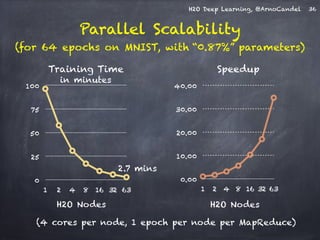
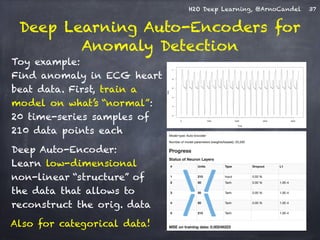
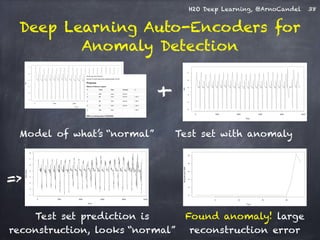
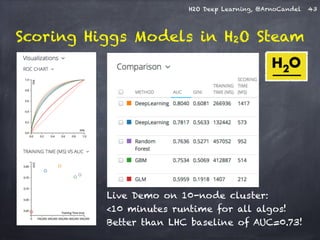
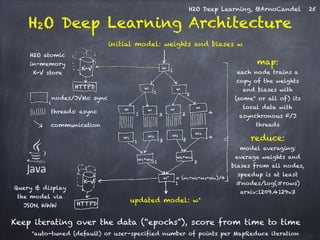
The document presents a detailed overview of deep learning techniques and the capabilities of H2O.ai's machine learning platform, including live demos and practical applications like Higgs boson detection and handwritten digit classification. It highlights the architecture, training methodologies, and performance metrics of H2O's deep learning models, emphasizing their efficiency with big data. Additionally, the document discusses various algorithms, adaptive learning rates, and dropout regularization to improve accuracy in predictions.





 // will be implicit in the future
// Validate prediction
validatePrediction( predictionRDD.collect().map (_.predict.getOrElse(Double.NaN)), validationData)
}
Brand-Sparkling-New Sneak Preview!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/h2odeeplearningarnocandel090314-140904005857-phpapp02/85/Deep-Learning-through-Examples-9-320.jpg)

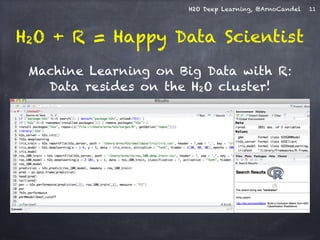

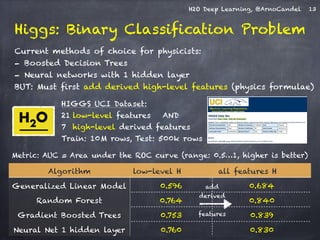





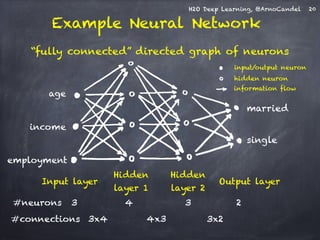
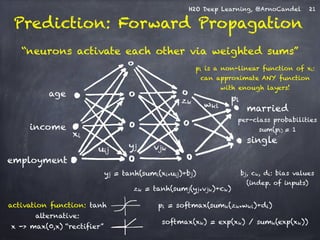
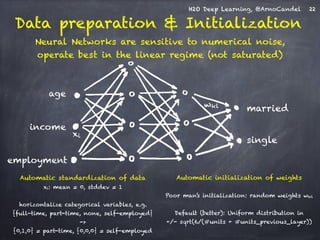

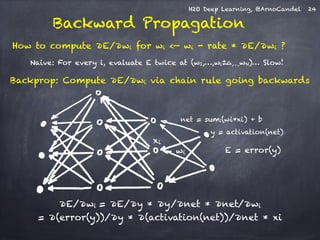

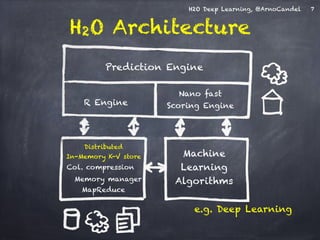
![H2O Deep Learning, @ArnoCandel
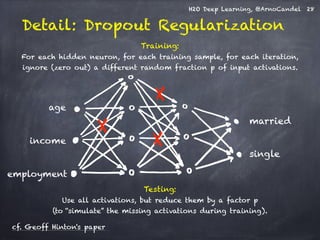
Detail: Adaptive Learning Rate
!
Compute moving average of Δwi2 at time t for window length rho:
!
E[Δwi2]t = rho * E[Δwi2]t-1 + (1-rho) * Δwi2
!
Compute RMS of Δwi at time t with smoothing epsilon:
!
RMS[Δwi]t = sqrt( E[Δwi2]t + epsilon )
Adaptive acceleration / momentum:
accumulate previous weight updates,
but over a window of time
Adaptive annealing / progress:
Gradient-dependent learning rate,
moving window prevents “freezing”
(unlike ADAGRAD: no window)
Do the same for ∂E/∂wi, then
obtain per-weight learning rate:
RMS[Δwi]t-1
RMS[∂E/∂wi]t
rate(wi, t) =
cf. ADADELTA paper
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/h2odeeplearningarnocandel090314-140904005857-phpapp02/85/Deep-Learning-through-Examples-27-320.jpg)