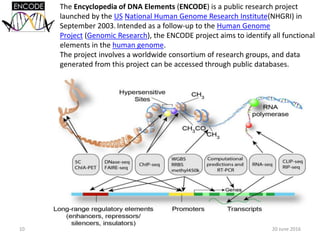
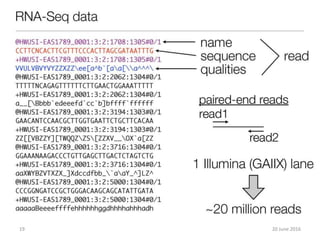
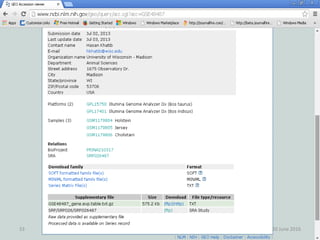
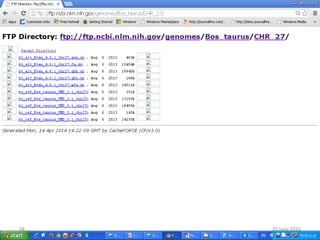
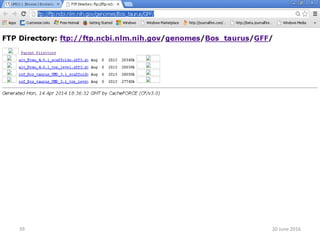
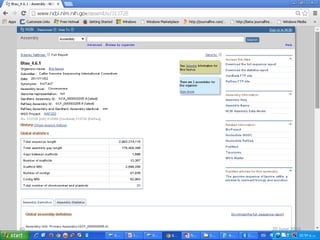
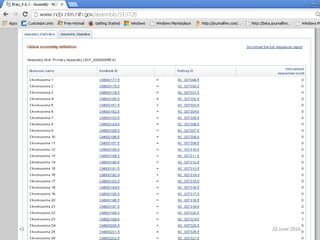
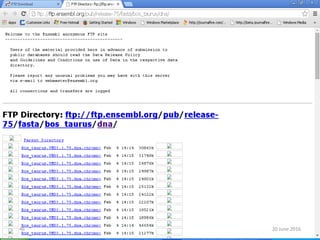
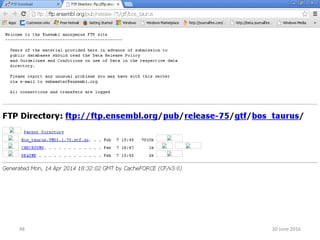
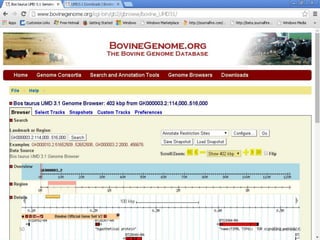
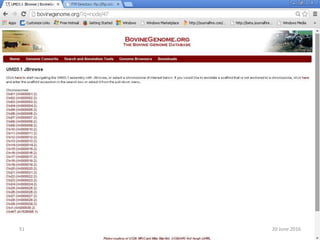
The document outlines a workshop on next-generation sequencing (RNA-seq), emphasizing its role in transcriptome analysis and the principles underlying systems biology and bioinformatics. It highlights the significance of the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project, which reshapes the understanding of gene function and regulation. RNA-seq is presented as a more comprehensive method compared to traditional microarrays, allowing for a detailed examination of transcript levels and variations.