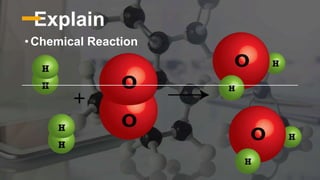
The document discusses chemical changes and reactions that occur during food processing. It defines a chemical reaction as a process where reactants are converted into products, and outlines the key parts of a chemical reaction including reactants, products, and signs that indicate a reaction occurred through the formation of new substances, evolution of gas or heat, color changes, etc. Common types of chemical reactions in food processing are described as single replacement, double replacement, synthesis, decomposition, and combustion.