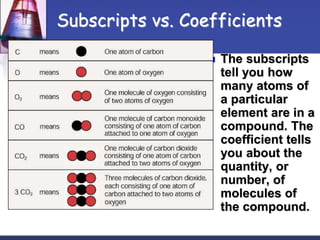
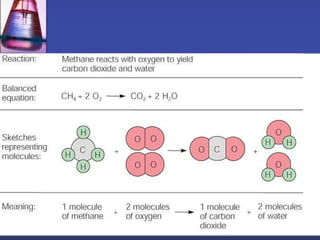
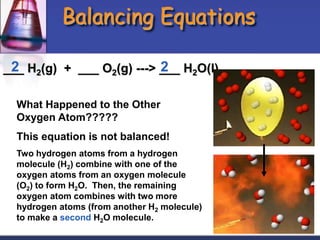
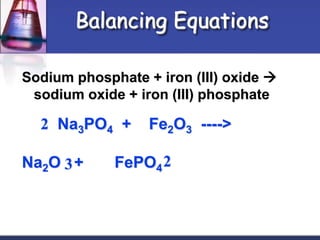
Chemical equations are used to represent chemical reactions. They show the reactants and products, including the types of atoms and molecules involved and their relative quantities. For a chemical equation to be valid, it must be balanced so that the same number of each type of atom is on both sides of the reaction. To balance equations, coefficients are placed in front of formulas as needed to make the number of atoms of each element equal on both sides without changing the subscripts in the formulas. The basic steps to balance equations are to write the correct formulas, identify the atoms on each side, insert coefficients as needed, and check that all elements are balanced.