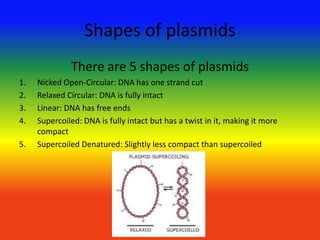
Plasmids are DNA molecules that can transfer genes between organisms. There are three types of plasmids: conjugative plasmids which can transfer themselves, non-conjugative plasmids which cannot transfer, and intermediate plasmids which rely on conjugative plasmids for transfer. Plasmids serve several functions including carrying antibiotic resistance genes, producing toxins that kill bacteria, and aiding in the breakdown of unusual substances. They come in various shapes like circular, supercoiled, or linear. In genetic engineering, genes are inserted into plasmids which are then put into bacteria to mass produce the genes. Plasmids are also used in gene therapy to deliver therapeutic genes to specific chromosomal sites.