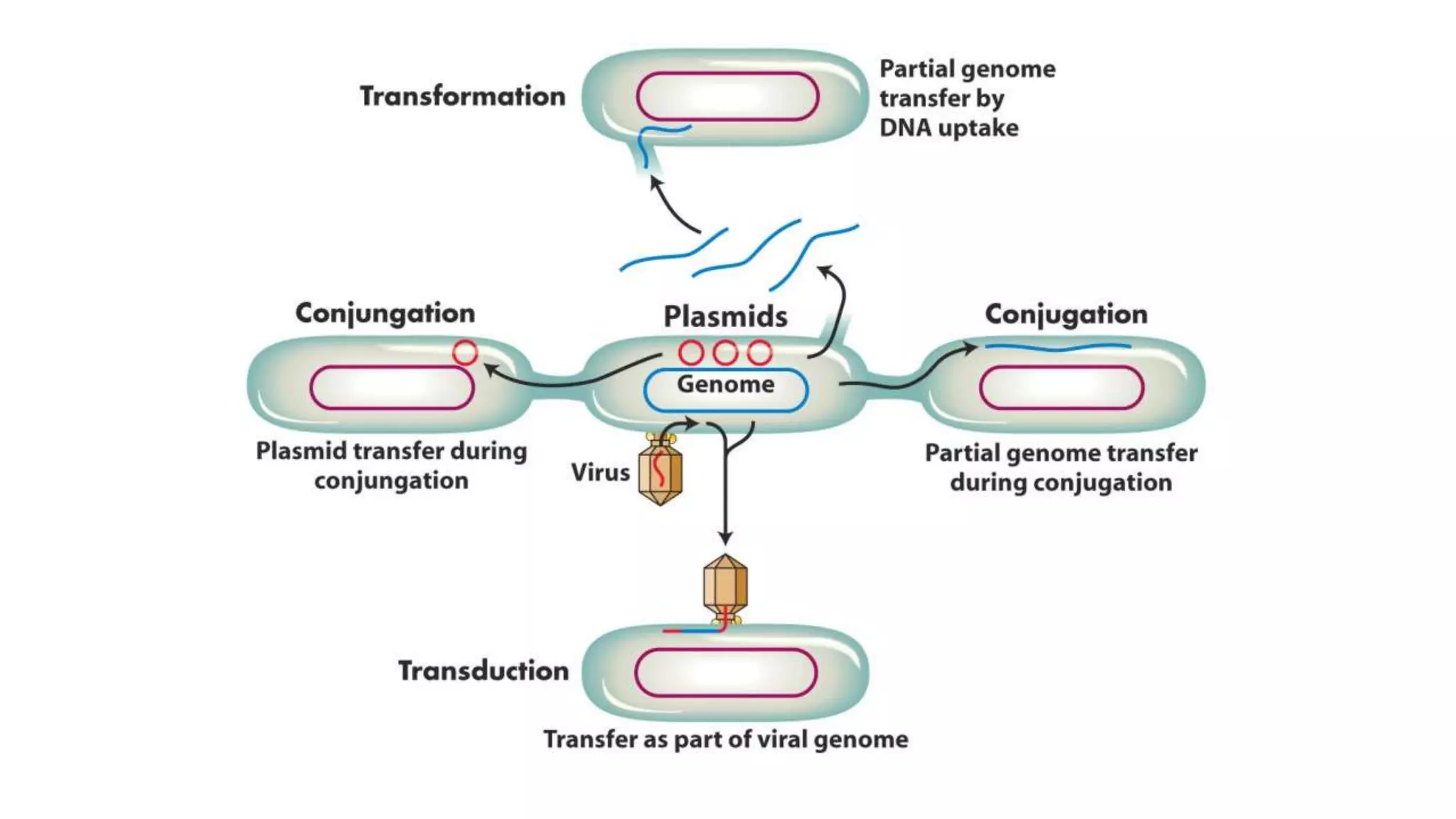
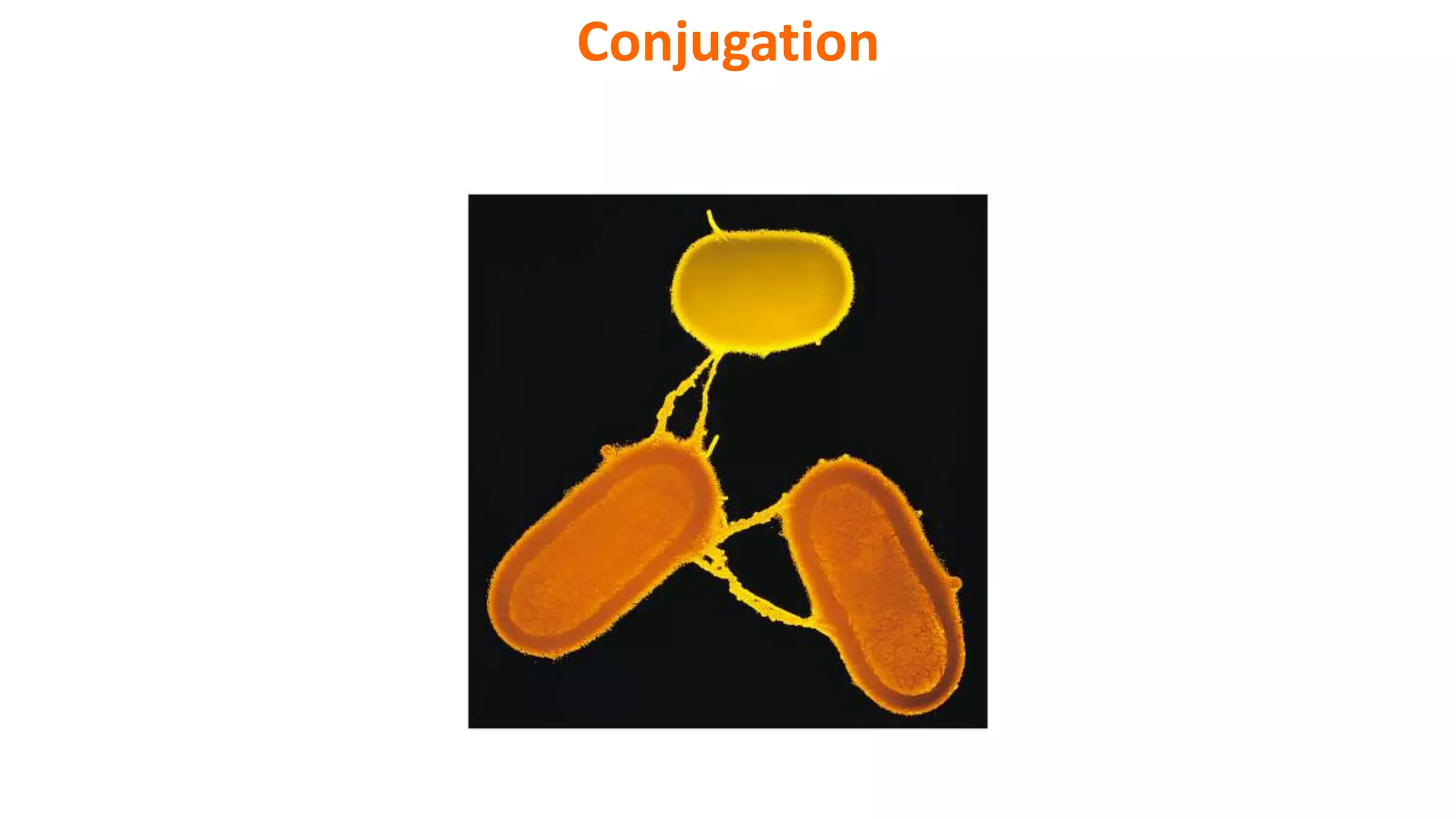
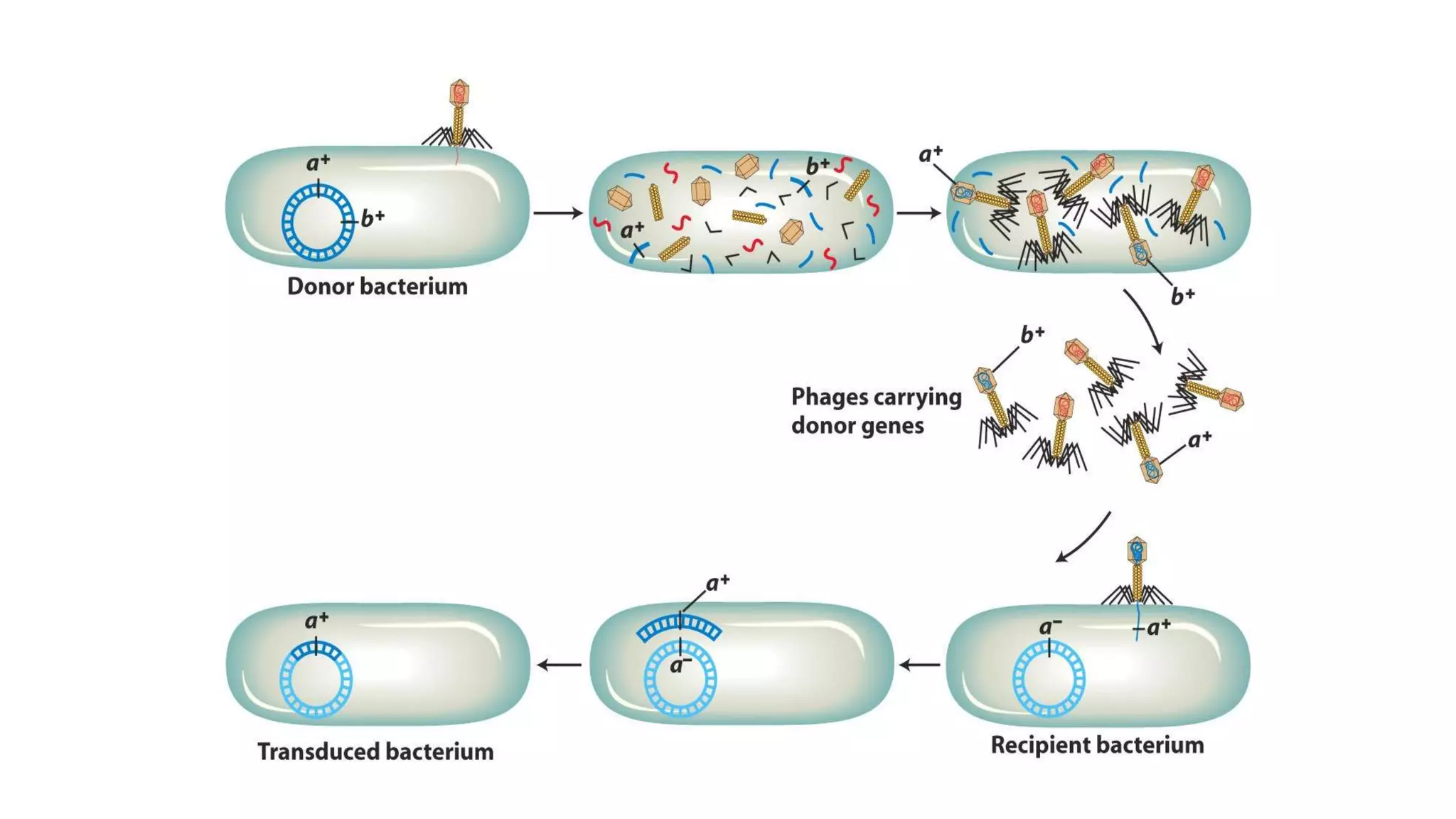
This document discusses three mechanisms of gene transfer in bacteria: conjugation, transformation, and transduction. Conjugation involves the direct transfer of DNA via a connection tube from a donor to recipient cell. Transformation occurs when environmental DNA is taken up by a competent cell. Transduction is when a bacteriophage transfers DNA from one bacterial cell to another. All three mechanisms are unidirectional and involve recombination of the transferred DNA into the recipient genome.