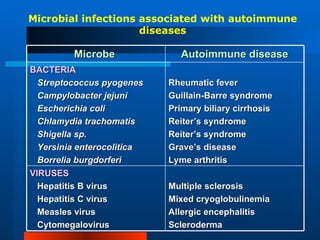
This document discusses immunological tolerance and autoimmunity. It defines central and peripheral tolerance as mechanisms by which the immune system learns to distinguish self from non-self. Central tolerance involves deletion of self-reactive lymphocytes in the thymus and bone marrow. Peripheral tolerance mechanisms include clonal deletion, anergy, and suppression. Failure of tolerance can lead to autoimmune diseases, which are influenced by genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Common triggers include molecular mimicry between microbial and self-antigens.