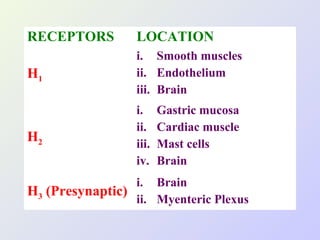
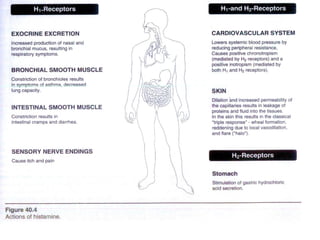
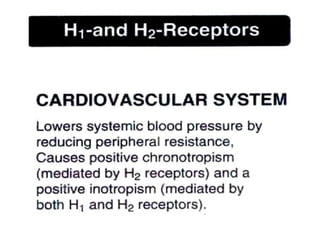
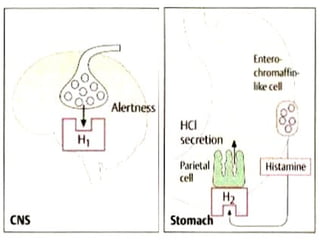
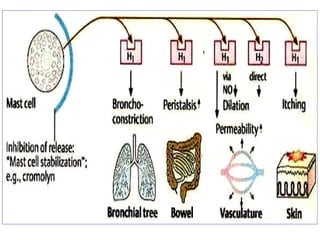
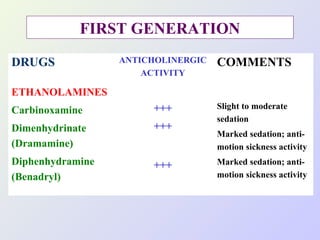
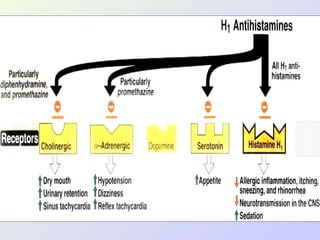
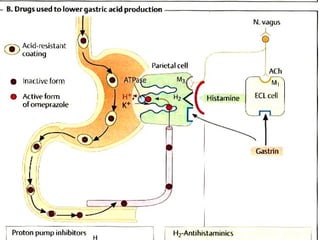
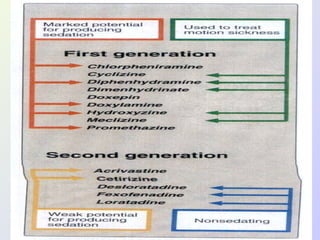
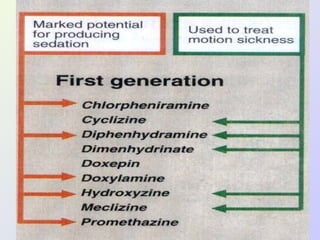
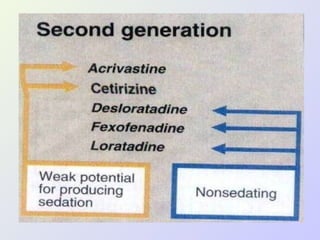
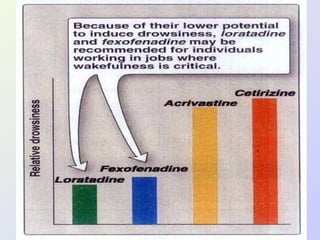
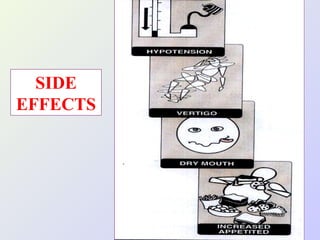
The document discusses autacoids and focuses on histamine and antihistamines. It notes that histamine is derived from the amino acid histidine and is found in tissues like lungs, skin, and the gastrointestinal tract. Histamine causes inflammatory and allergic reactions by binding to H1 and H2 receptors. Antihistamines work by blocking these histamine receptors. First generation antihistamines often have anticholinergic effects and sedation as side effects, while second generation antihistamines generally do not. Antihistamines are used to treat allergic disorders, motion sickness, nausea/vomiting, and anaphylaxis. Their side effects include dry mouth, urinary retention, sedation