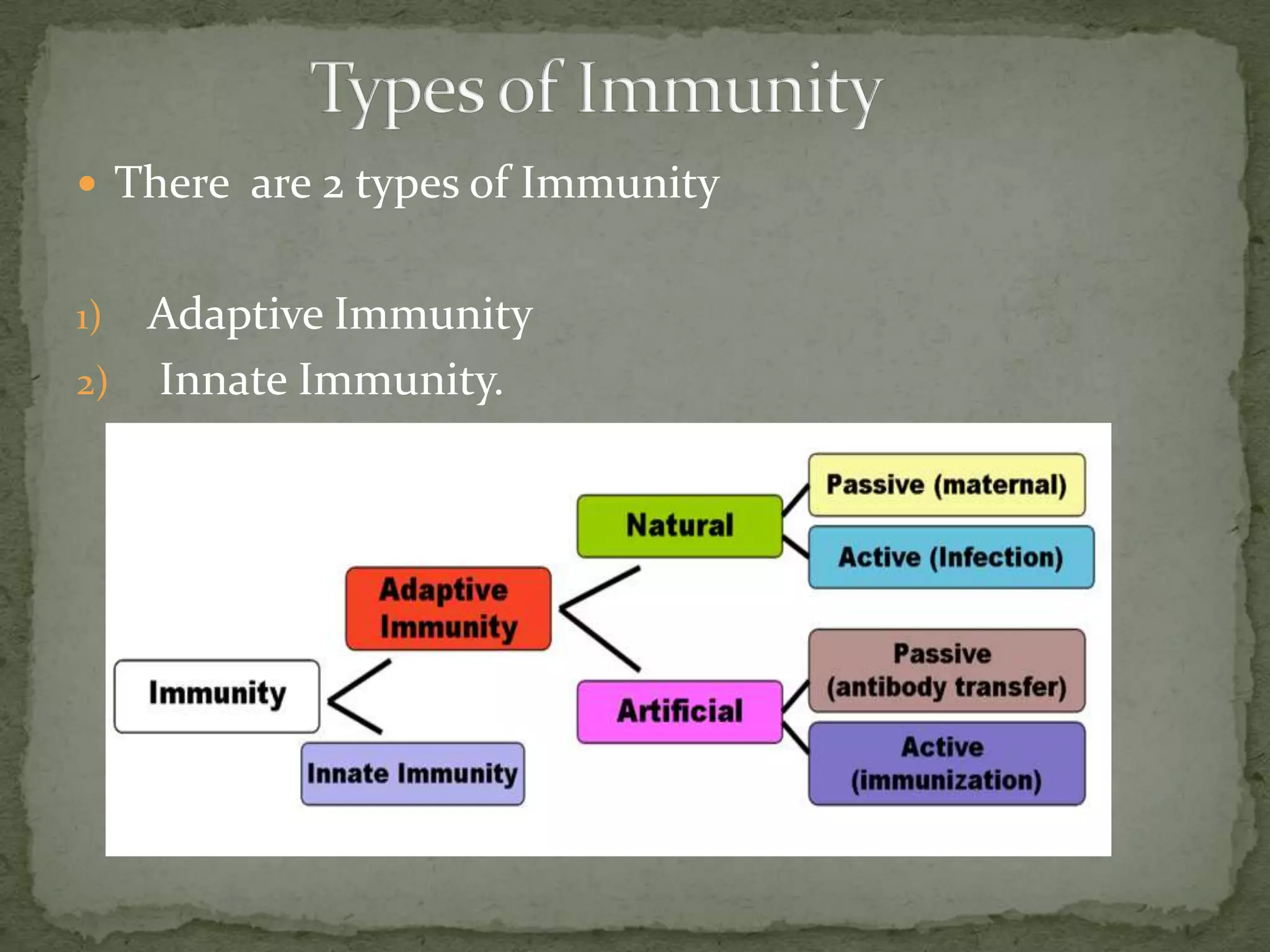
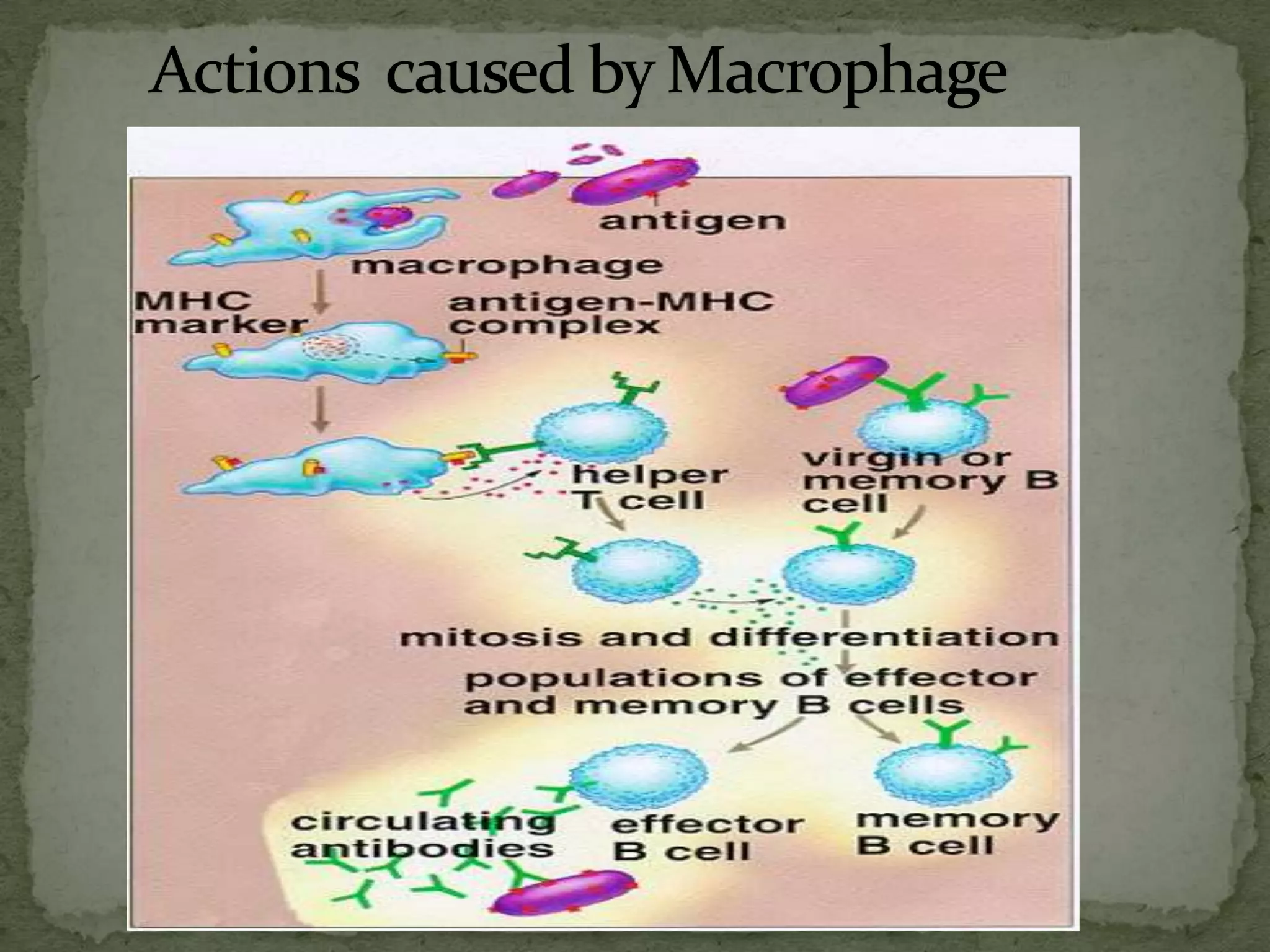
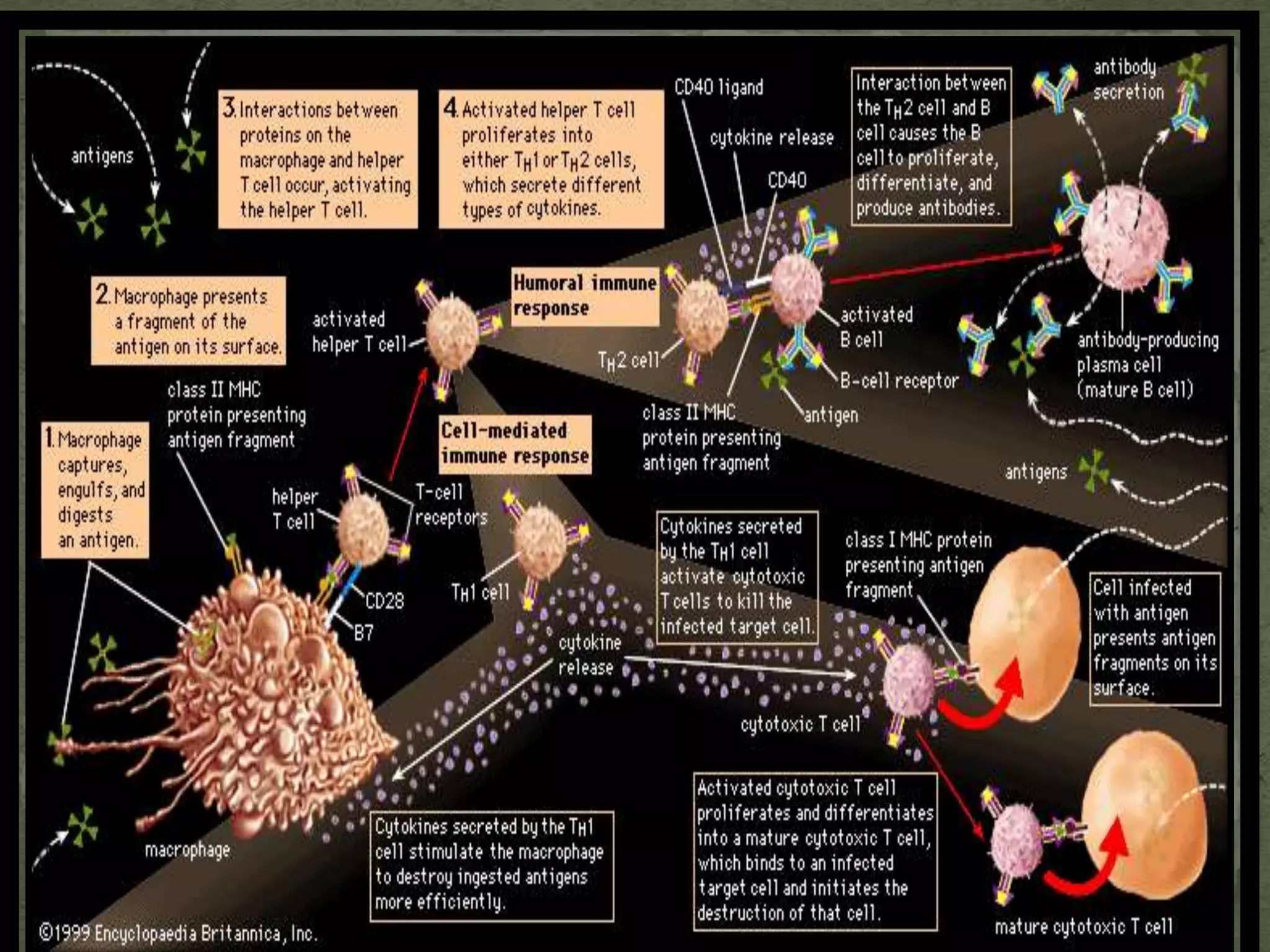
Immunity involves both specific and non-specific components of the immune system. The non-specific components act as barriers or eliminate a wide range of pathogens, while the specific components adapt to each new disease and generate pathogen-specific immunity. Cell-mediated immunity is mediated by activated macrophages, natural killer cells, cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and cytokines and does not involve antibodies. It is responsible for phagocytosing and killing intracellular pathogens and virus-infected cells. Memory T cells provide long-term immunity against past infections upon reexposure to the pathogen.