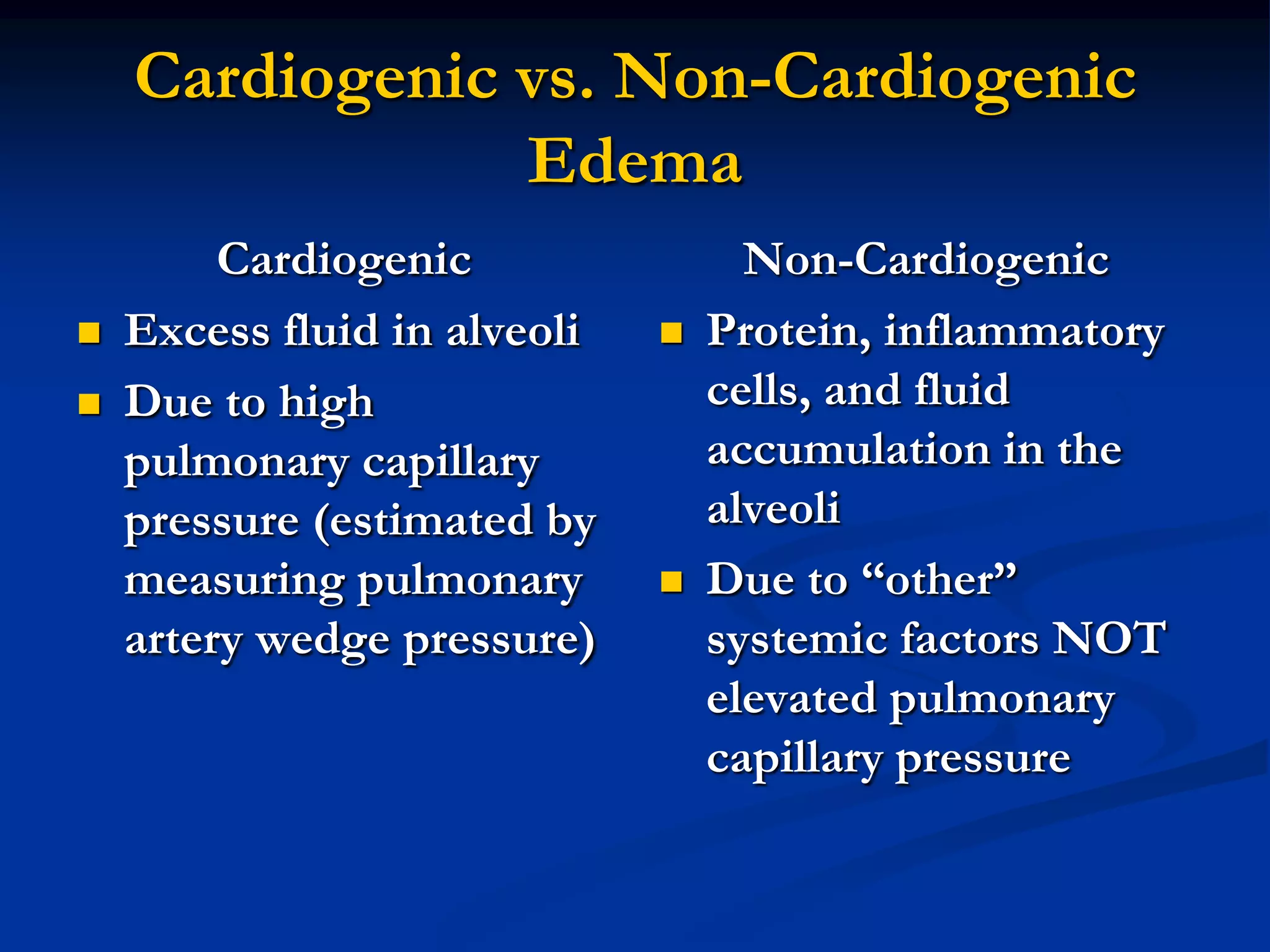
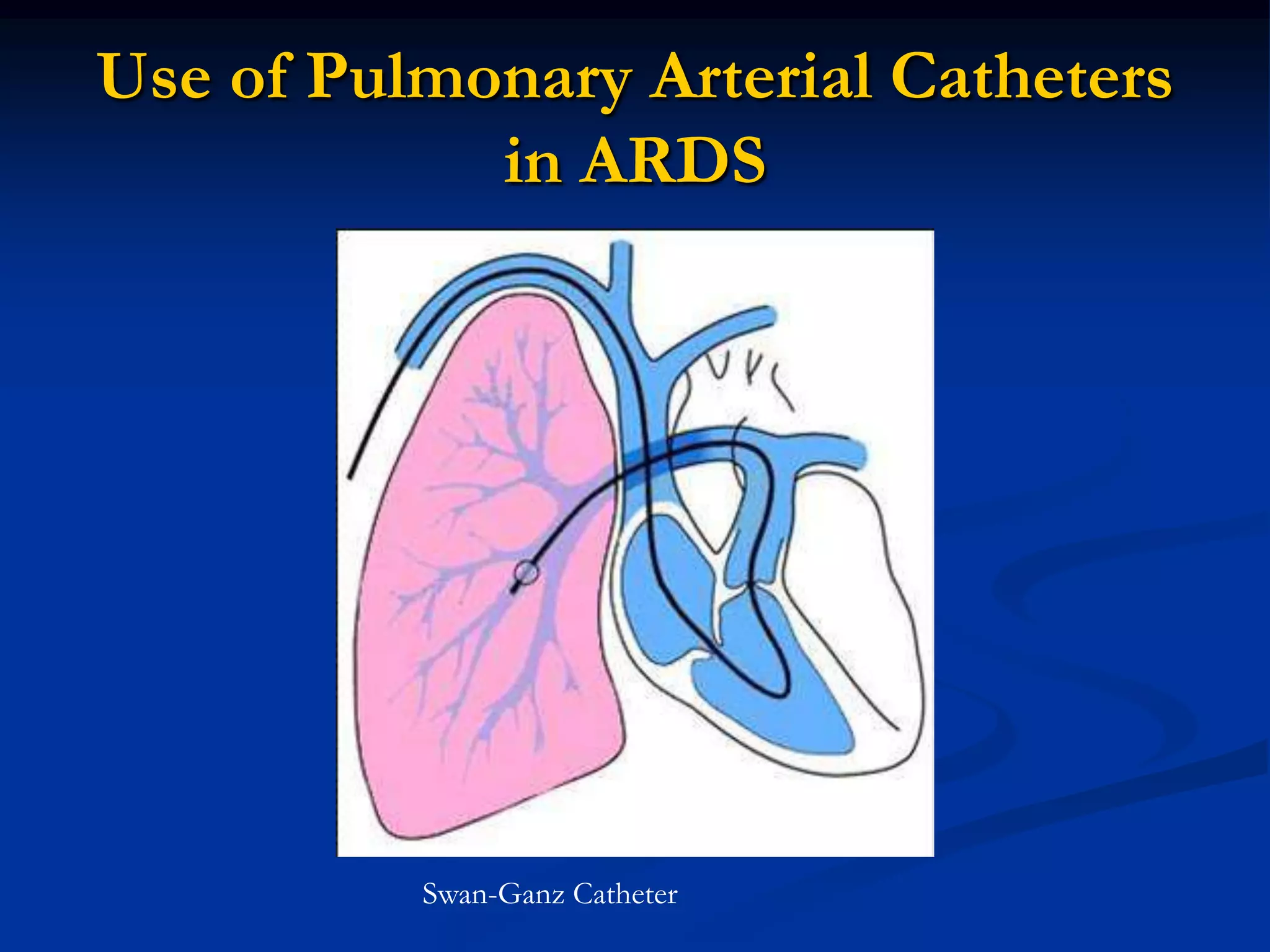
This document provides an overview of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). It defines ARDS and differentiates it from acute lung injury. The pathophysiology of ARDS involves diffuse lung inflammation from neutrophils and proteinaceous fluid in the alveoli, reducing gas exchange. Management focuses on low tidal volume ventilation to prevent further lung injury while allowing permissive hypercapnia. Diuretics may help lung function if used conservatively. Pulmonary artery catheters are no longer routinely recommended as they do not improve outcomes and carry risk of complications.