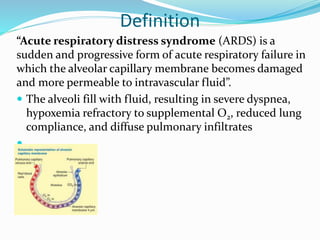
The document provides information on acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), including its definition, etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, diagnostic findings, and collaborative therapy. ARDS is defined as acute respiratory failure caused by damage to the alveolar-capillary membrane, resulting in fluid-filled alveoli. It has three pathophysiology phases: injury/exudative, reparative/proliferative, and fibrotic. Clinical features include hypoxemia, reduced lung compliance, and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates on chest imaging. Treatment involves mechanical ventilation with low tidal volumes, application of PEEP, and prone positioning to improve oxygenation.
























![ Physiologic Stress Ulcers.
Critically ill patients with acute respiratory failure are at
high risk for stress ulcers.
Bleeding from stress ulcers occurs in 30% of patients
with ARDS who require PPV, a higher incidence than
other causes of acute respiratory failure.
Management strategies include correction of
predisposing conditions such as hypotension, shock, and
acidosis.
Prophylactic management includes antiulcer agents
such as H2-histamine receptor antagonists (e.g.,
ranitidine [Zantac]), as well as proton pump inhibitors
(e.g., pantoprazole [Protonix]) and mucosal-protecting
agents (e.g., sucralfate [Carafate]).
Early initiation of enteral nutrition also helps prevent
mucosal damage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ards-230220035206-3eb572a7/85/ARDS-pptx-27-320.jpg)






