Embed presentation
Downloaded 136 times




![Top Hat Function
Using this the Top Hat Function may
be expressed as:
F(t) = f1(t) [H(t) – H(t-t1)] + f2(t)[H(t-t1) –
H(t-t2)] + f3(t)[H(t1-t2)]
= f1(t)H(t) + [f2(t) – f1(t)]H(t-t1) +
[f3(t) – f2(t)]H(t-t2)
which is same as that of Heaviside
Step Function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1302101070392130002-160222141034/85/Applications-Of-Laplace-Transforms-9-320.jpg)

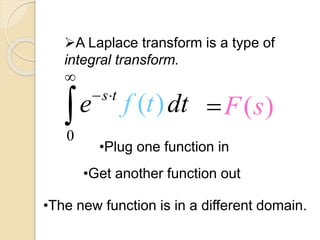
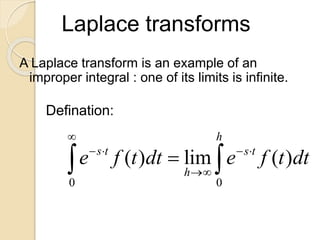
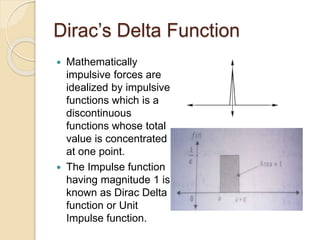
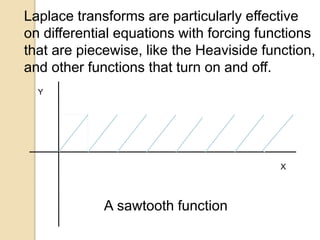
Laplace transforms convert a function of time into a function of complex variables. They are useful for solving differential equations with discontinuous forcing functions like the Heaviside step function and Dirac delta function. The Laplace transform of a top hat function, which is 1 between two times and 0 otherwise, can be expressed as a combination of Heaviside step functions multiplied by the values of the function before and after the transitions.








![Top Hat Function
Using this the Top Hat Function may
be expressed as:
F(t) = f1(t) [H(t) – H(t-t1)] + f2(t)[H(t-t1) –
H(t-t2)] + f3(t)[H(t1-t2)]
= f1(t)H(t) + [f2(t) – f1(t)]H(t-t1) +
[f3(t) – f2(t)]H(t-t2)
which is same as that of Heaviside
Step Function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1302101070392130002-160222141034/85/Applications-Of-Laplace-Transforms-9-320.jpg)
