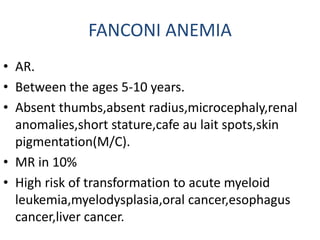
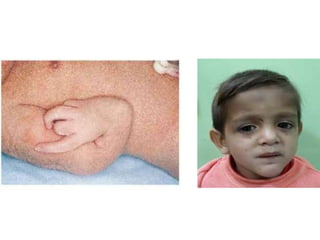
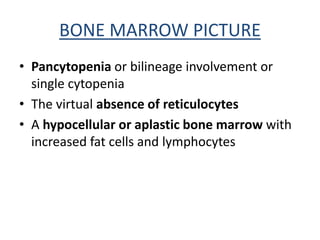
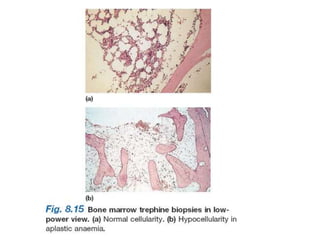
Aplastic anemia comprises disorders of hematopoietic stem cells resulting in suppression of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It can be inherited or acquired from viruses, toxins, chemicals, or immune-mediated causes. Clinically, it presents as pancytopenia and bone marrow hypocellularity. Definitive treatment is hematopoietic stem cell transplant, which has better outcomes when using cells from an HLA-identical sibling donor. Without treatment, prognosis depends on severity of cytopenias and presence of risk factors.