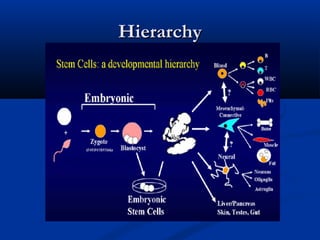
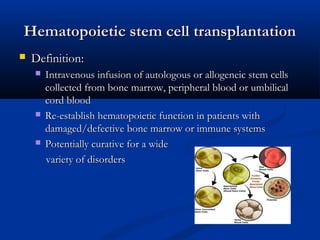
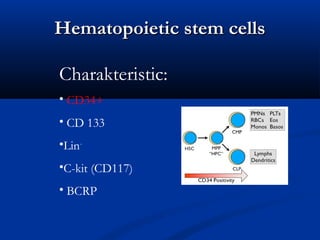
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation involves intravenous infusion of stem cells collected from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood to reestablish hematopoietic function in patients with damaged bone marrow or immune systems. It is potentially curative for various disorders. Stem cells are collected via bone marrow harvest or apheresis and may be manipulated before infusion. Complications can include mucositis, sinusoidal obstructive syndrome, and graft-versus-host disease.