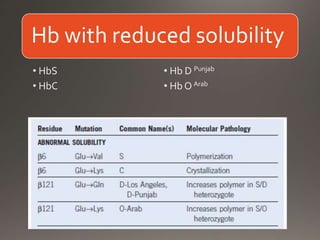
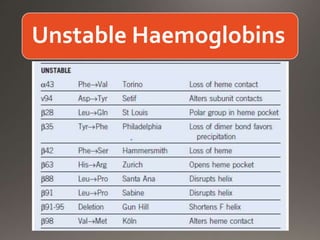
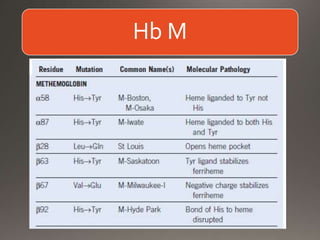
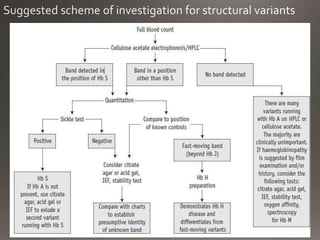
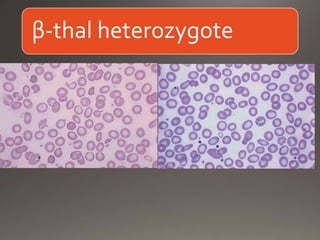
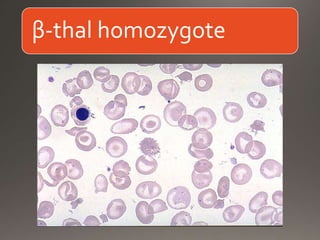
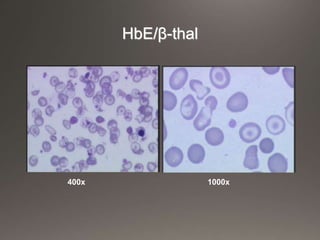
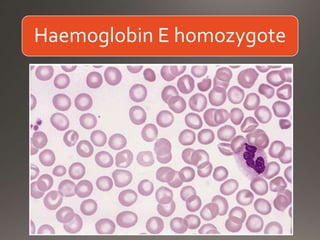
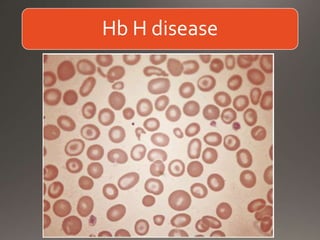
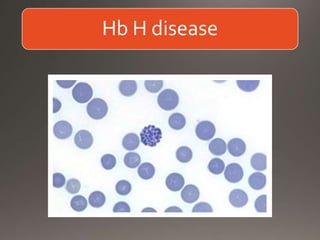
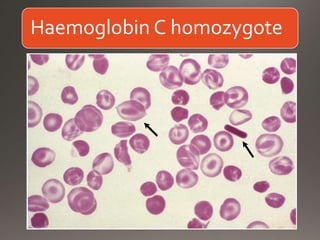
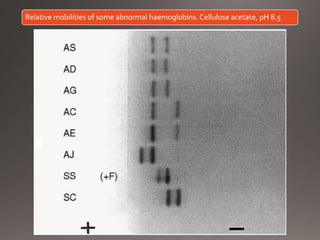
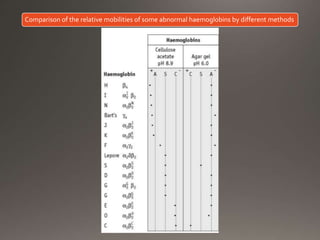
This document discusses the laboratory diagnosis of hemoglobinopathies. It covers the different types of hemoglobin variants including structural variants that cause reduced solubility or instability. It describes various laboratory techniques for detection such as peripheral blood smear examination, hemoglobin electrophoresis using cellulose acetate or agarose gel, and automated high-performance liquid chromatography. Diagnostic tests for specific variants like HbS and unstable hemoglobins are also outlined. Guidelines for investigation of suspected thalassemia including blood counts, HbA2 quantification and HbF analysis are provided.