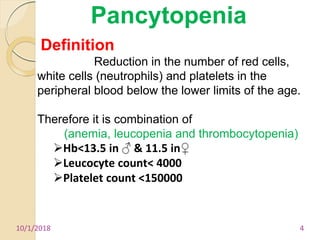
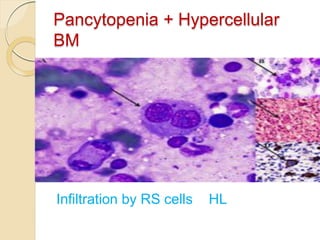
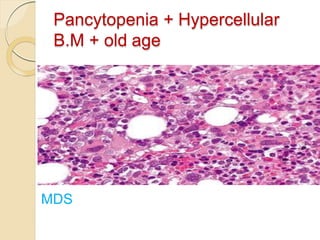
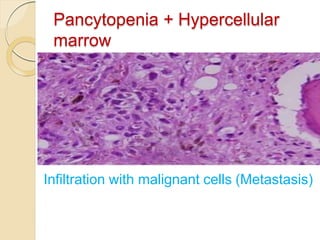
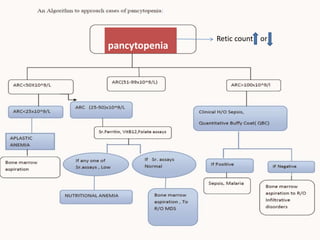
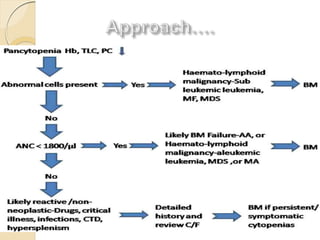
1. Pancytopenia is defined as a reduction in red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets below the normal range.
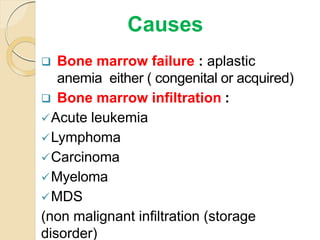
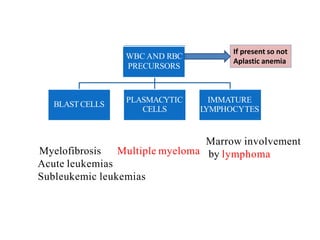
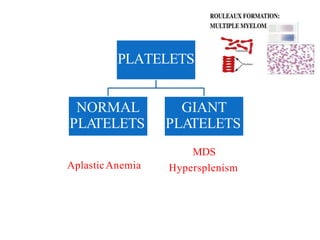
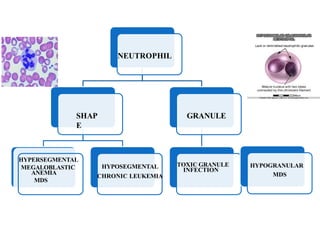
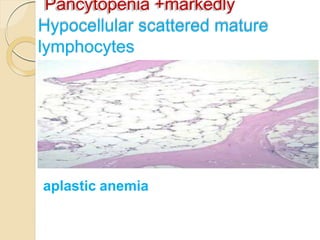
2. The most common causes of pancytopenia include megaloblastic anemia, infections, hypersplenism, aplastic anemia, drug-induced pancytopenia, and acute myeloid leukemia.
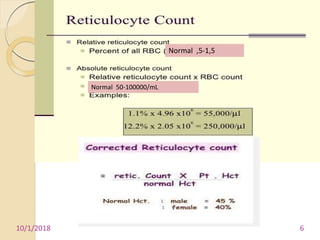
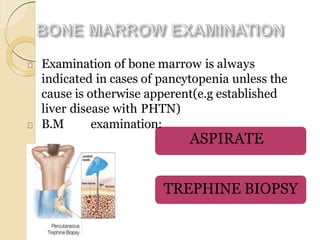
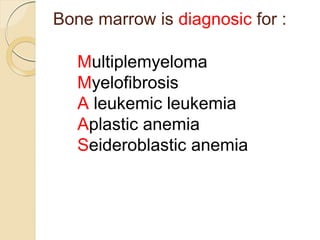
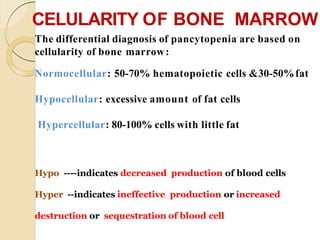
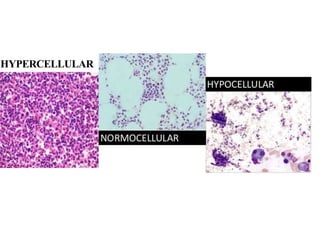
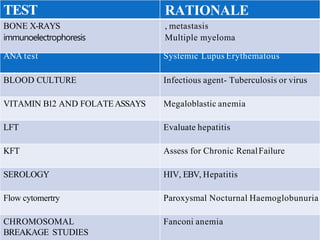
3. Evaluation of pancytopenia involves a complete blood count, peripheral smear, bone marrow aspiration and biopsy to determine if the bone marrow is aplastic, infiltrated, or displaying dysplastic changes which can help identify the underlying cause.