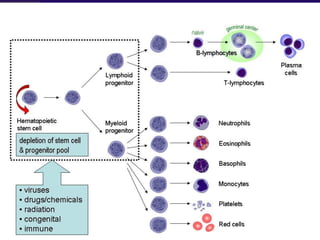
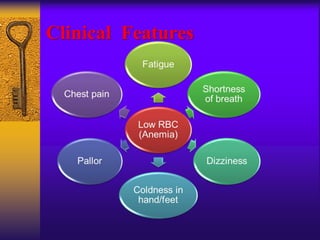
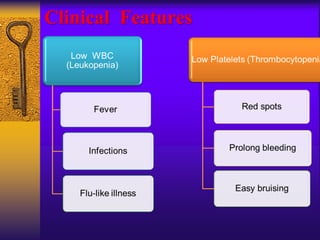
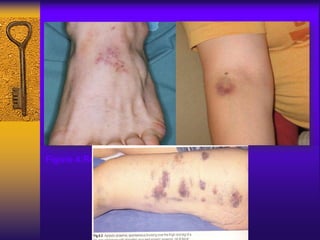
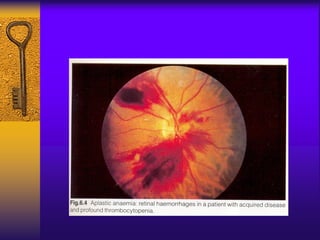
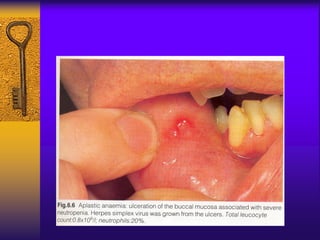
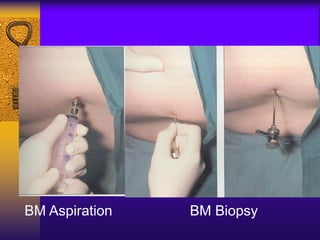
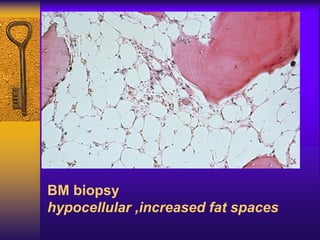
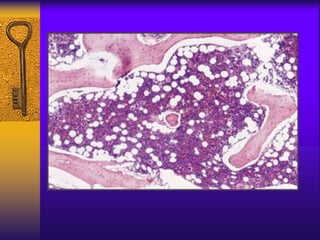
This document discusses aplastic anemia, which is a condition characterized by pancytopenia (low red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets) due to bone marrow failure. It can be acquired through exposure to drugs, radiation, chemicals, or viruses, or inherited through conditions like Fanconi anemia. Clinically, it presents with anemia, bruising, and increased infection risk. The bone marrow appears hypocellular on biopsy. Treatment involves managing symptoms, stopping any triggers, and attempts to restore bone marrow function through transplantation, immunosuppression, or growth factors.