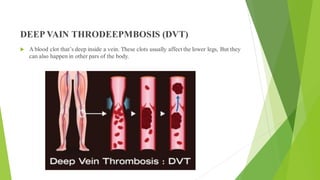
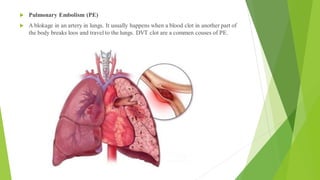
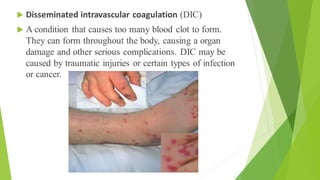
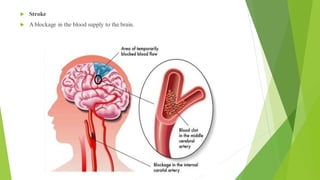
The D-dimer test measures levels of D-dimer in the blood, which is a fragment produced when a blood clot dissolves. An elevated D-dimer level may indicate the presence of a blood clotting disorder such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, disseminated intravascular coagulation, or stroke. The D-dimer test is used to help diagnose these conditions in patients experiencing related symptoms or who have risk factors for blood clots. While an elevated D-dimer suggests a clotting disorder, additional imaging tests are needed to locate any clots.