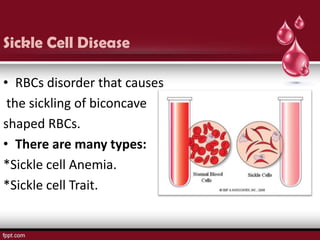
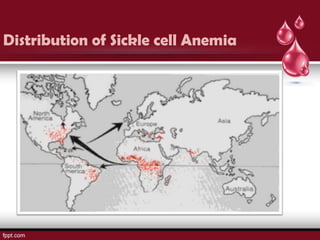
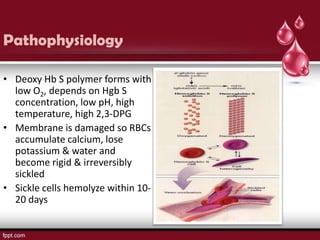
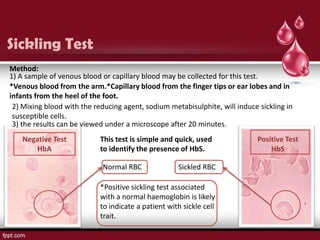
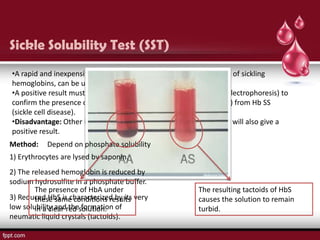
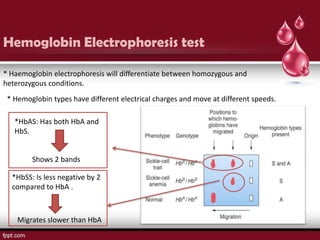
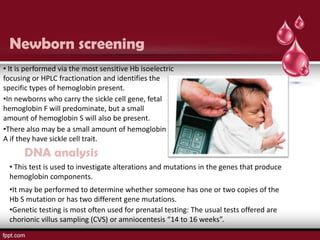
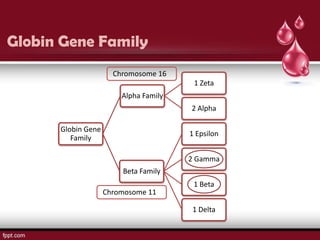
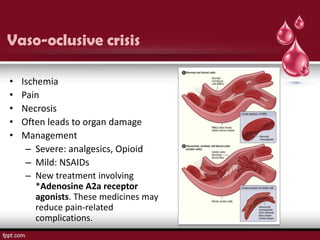
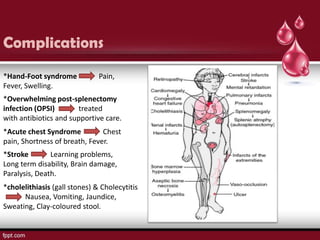
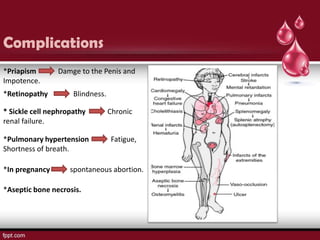
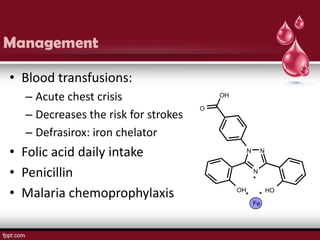
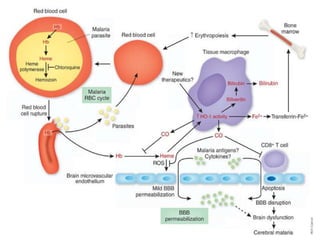
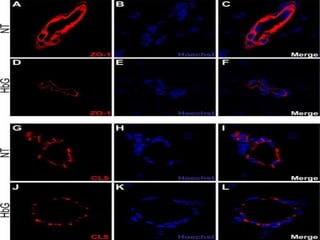
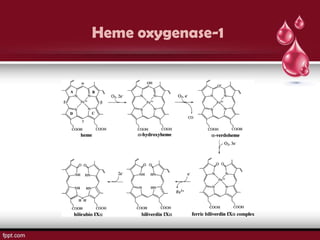
Sickle cell disease is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the hemoglobin beta gene, leading to the sickling of red blood cells, with major types including sickle cell anemia and sickle cell trait. Key symptoms arise from complications such as vaso-occlusive crises and infections, and the condition is diagnosed through tests like hemoglobin electrophoresis and DNA analysis. Current treatments focus on managing symptoms, promoting fetal hemoglobin production, and preventing complications, with genetic counseling recommended for affected families.