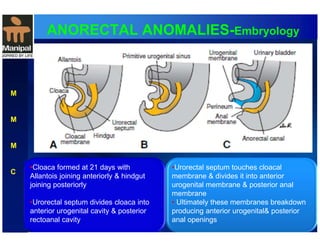
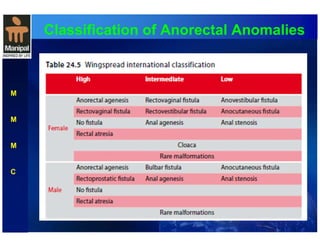
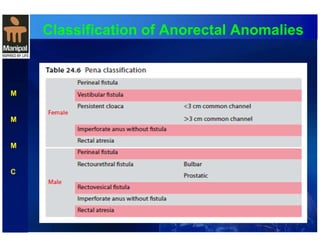
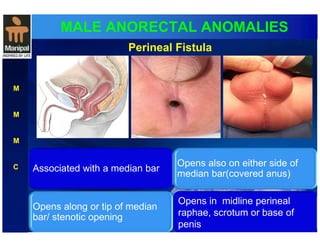
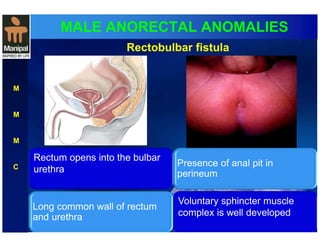
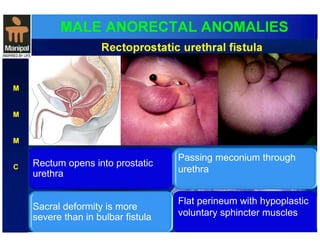
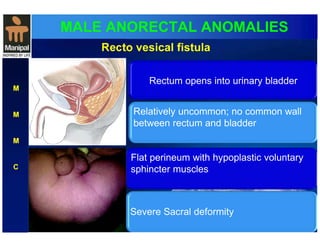
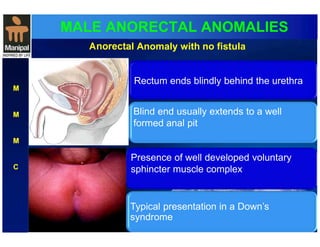
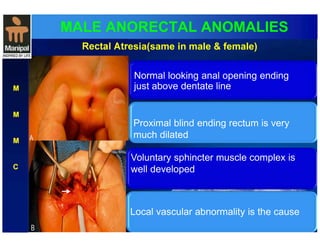
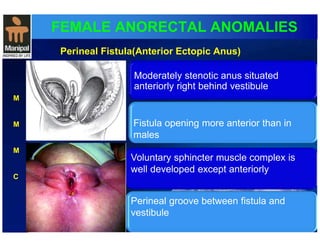
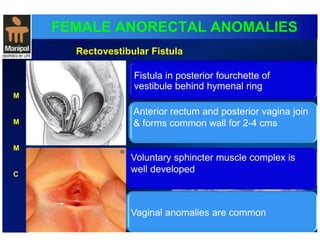
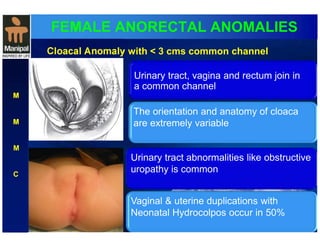
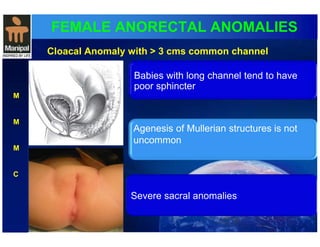
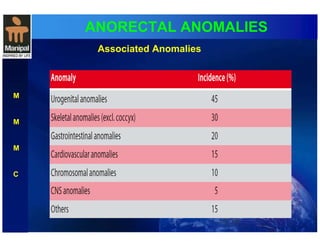
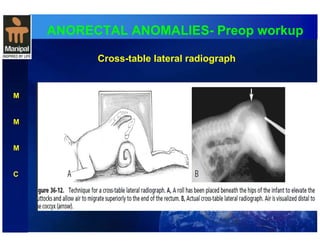
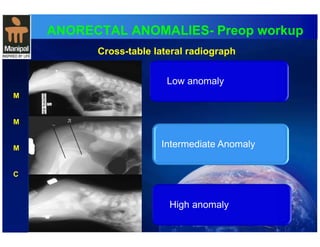
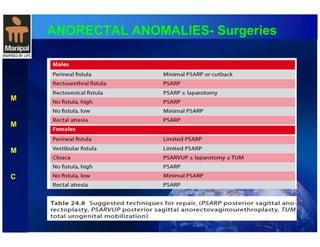
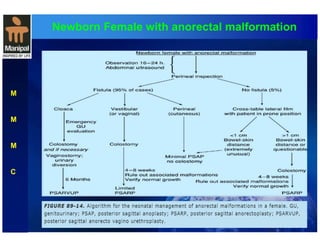
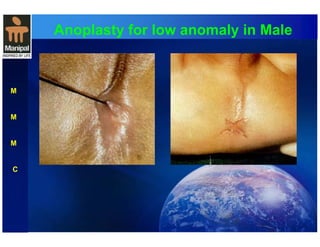
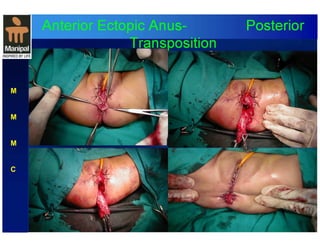
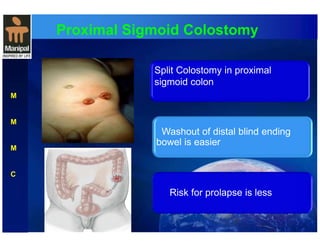
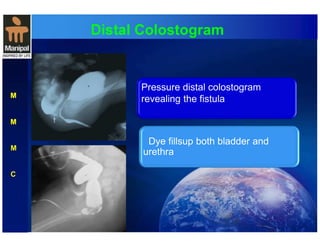
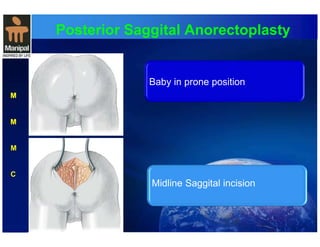
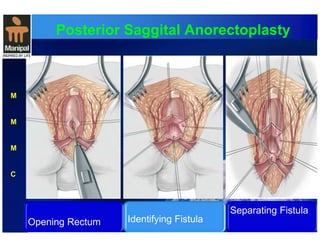
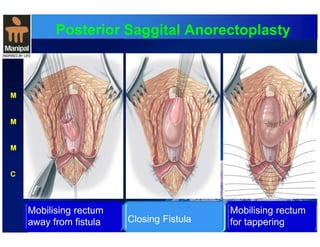
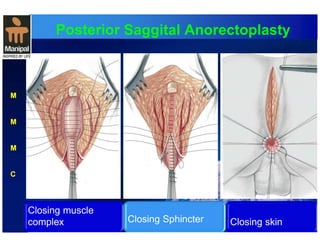
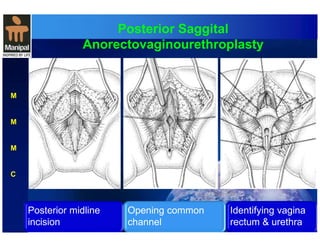
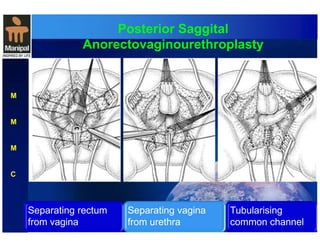
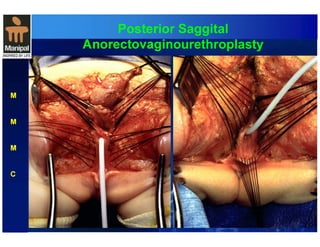
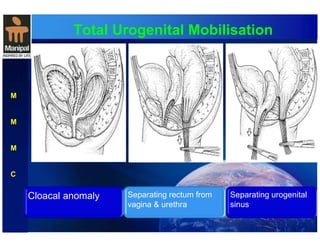
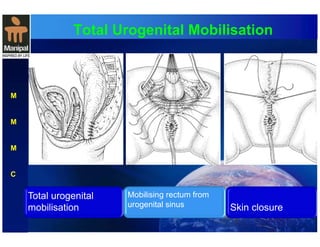
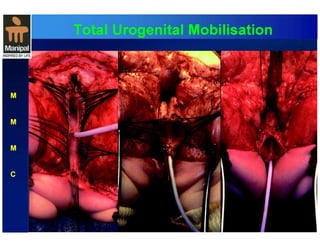
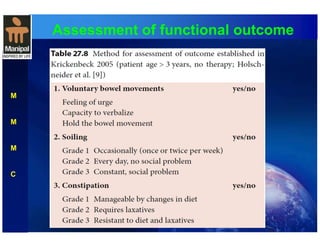
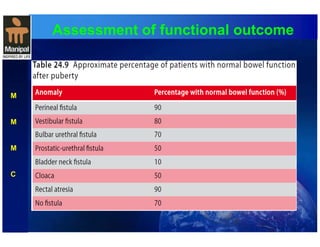
The document discusses anorectal anomalies, their embryological development, classification, and surgical management. It highlights the significance of recognizing these anomalies in neonatal patients for effective surgical treatment and outlines associated conditions and preoperative workup methods. The document emphasizes the variability in presentation, diagnosis, and surgical approaches for different anorectal anomalies in both males and females.