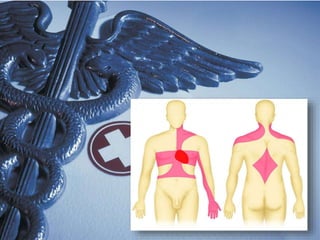
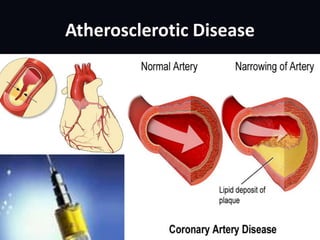
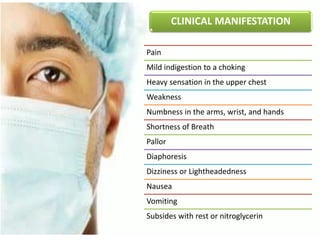
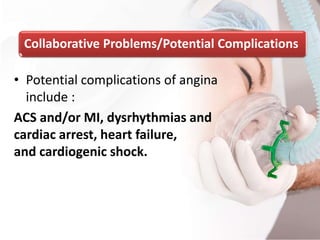
This document discusses angina pectoris, a clinical syndrome characterized by chest pain or pressure due to reduced blood flow to the heart. There are three main types of angina - stable, unstable, and variant. Risk factors include physical exertion, cold exposure, heavy meals, stress, and smoking. Diagnosis involves assessing symptoms, electrocardiograms, cardiac biomarkers, and imaging tests. Treatment focuses on relieving pain with nitroglycerin and preventing complications with beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiplatelets, and anticoagulants. Nursing priorities are to relieve pain, prevent myocardial complications, educate the patient, and support lifestyle changes.