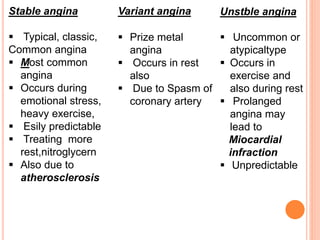
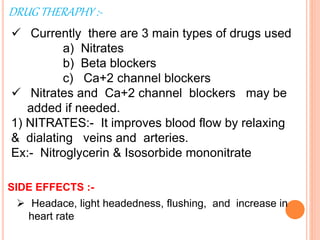
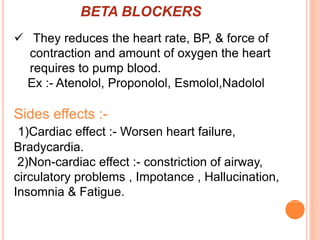
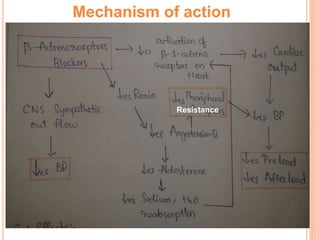
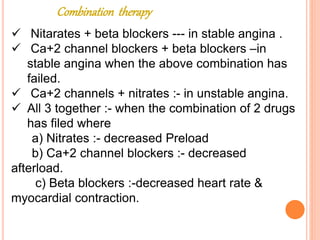
Angina pectoris is chest pain due to an imbalance between the heart's oxygen demand and supply. There are three types: stable angina occurs during exercise and is relieved by rest; variant angina occurs at rest due to coronary artery spasm; unstable angina is unpredictable and may lead to heart attack. Risk factors include age, sex, smoking, diabetes, and hypertension. Treatment includes nitrates, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers to reduce symptoms and mortality from coronary artery disease progression.