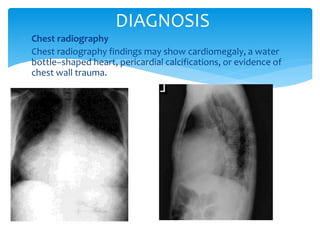
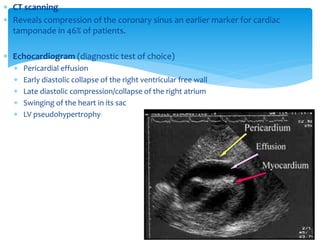
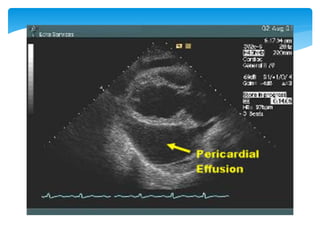
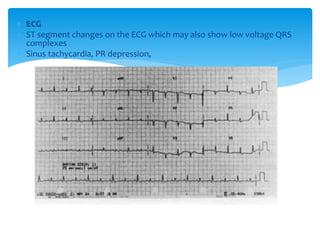
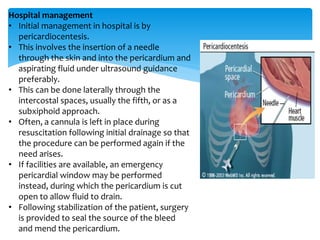
Cardiac tamponade is caused by fluid accumulating in the pericardial space, putting pressure on the heart and reducing ventricular filling. Common causes include malignant diseases, infections like tuberculosis, and recent cardiovascular procedures. Symptoms include dyspnea, tachycardia, and muffled heart sounds. Diagnosis is made through echocardiogram showing pericardial effusion and ventricular collapse. Treatment involves pericardiocentesis to drain fluid followed by surgery to address the underlying cause and prevent reaccumulation. Complications can include cardiogenic shock if not treated promptly.