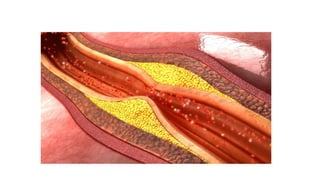
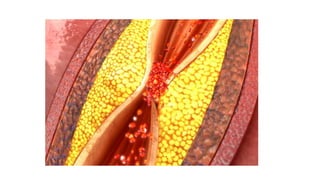
This document discusses angina pectoris, also known as angina, which is a temporary chest pain or discomfort due to an imbalance between the heart's oxygen supply and demand. There are three main types of angina: stable angina, which is the most common and occurs during physical exertion; unstable angina, which occurs at rest and is more severe and dangerous; and Prinzmetal's angina, which results from coronary artery spasms, especially during the night. Angina is caused by conditions that reduce blood flow to the heart such as atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes. Diagnosis involves tests like electrocardiograms, stress tests, and angiography. Treatment