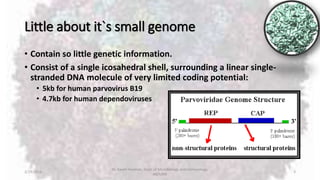
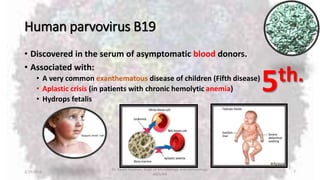
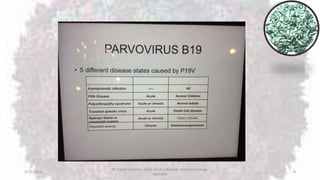
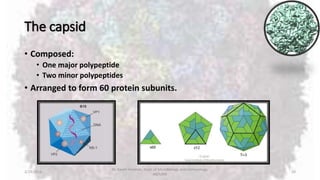
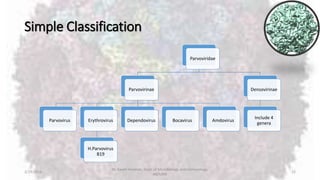
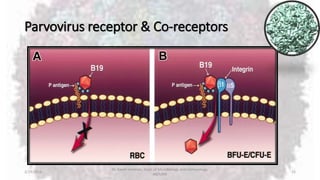
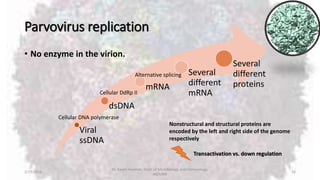
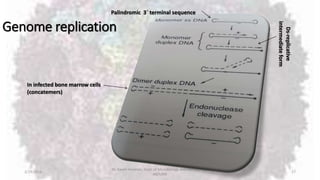
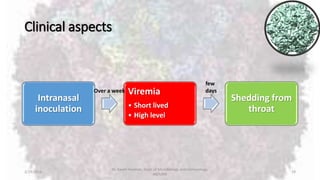
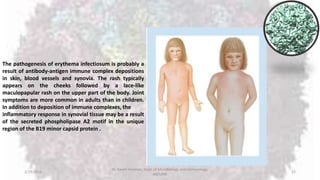
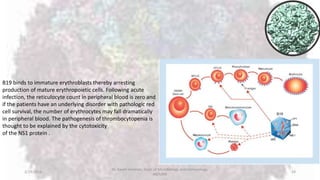
Parvoviruses are the smallest known human viruses. They require actively dividing host cells to replicate and can cause a range of diseases. Human Parvovirus B19 commonly causes Fifth disease in children, characterized by a rash on the cheeks and limbs. It can also result in transient aplastic crisis in patients with chronic hemolytic anemias, as well as hydrops fetalis if acquired vertically during pregnancy. Laboratory diagnosis involves cell culture, serology to detect antibodies, and molecular detection methods like PCR to detect the virus.