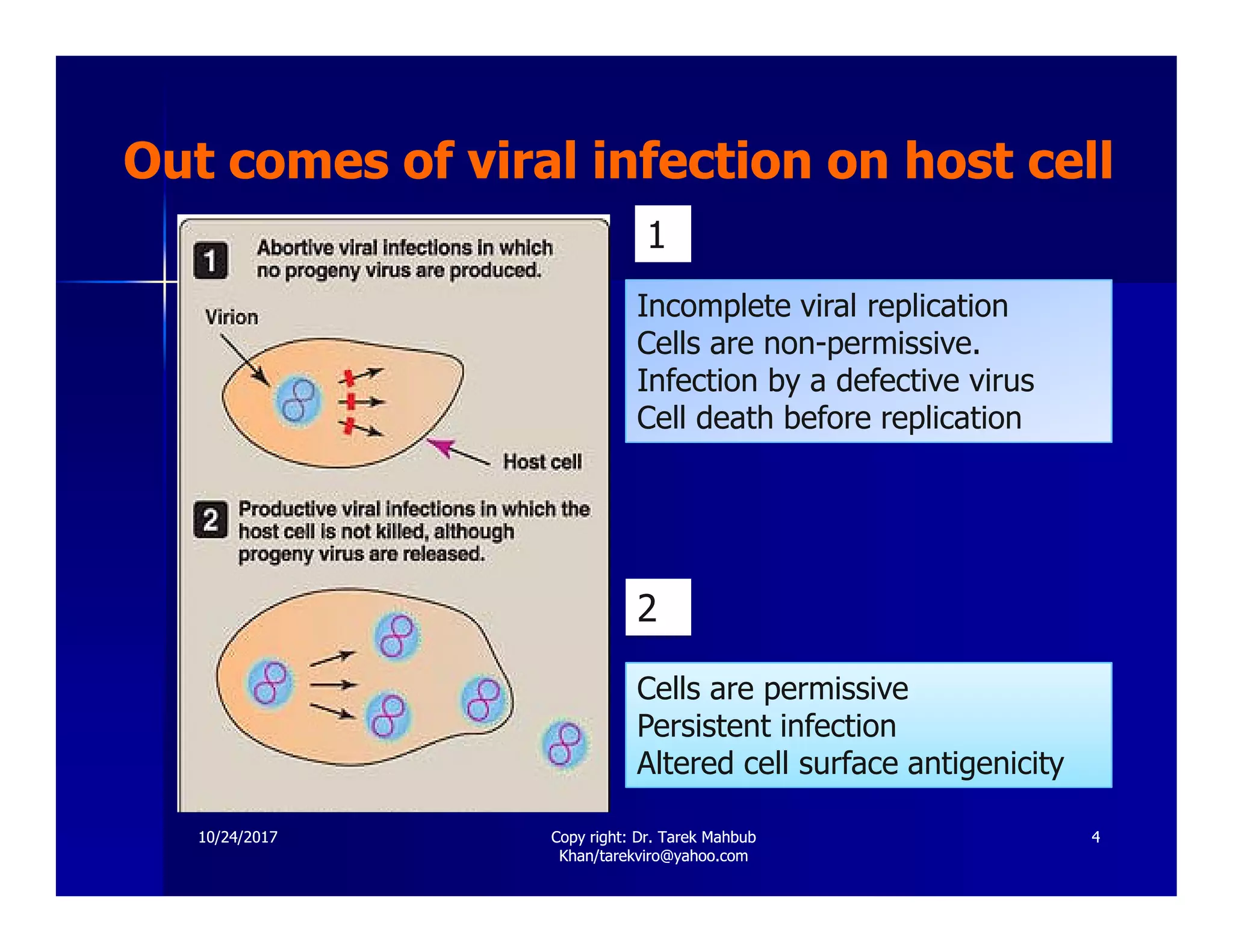
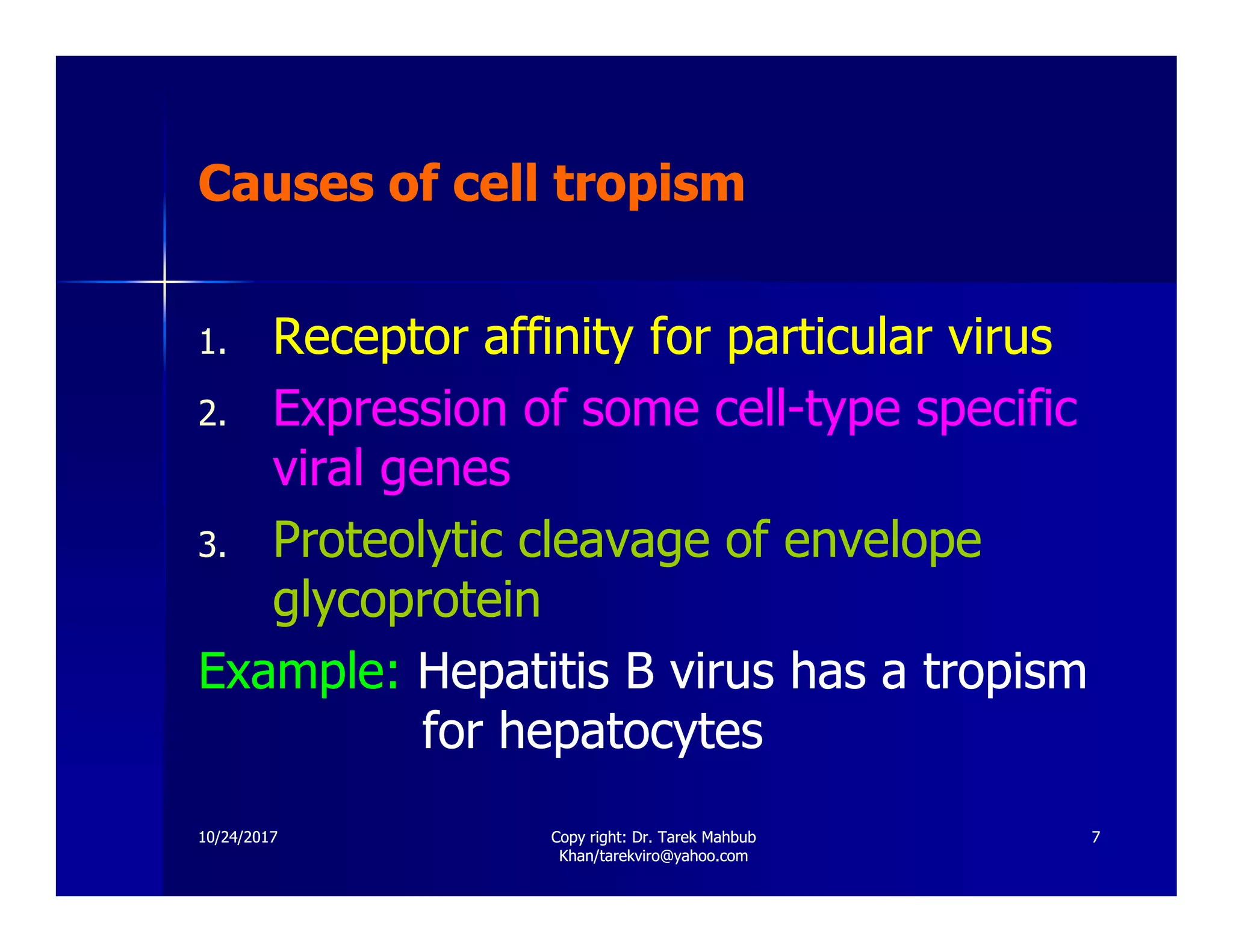
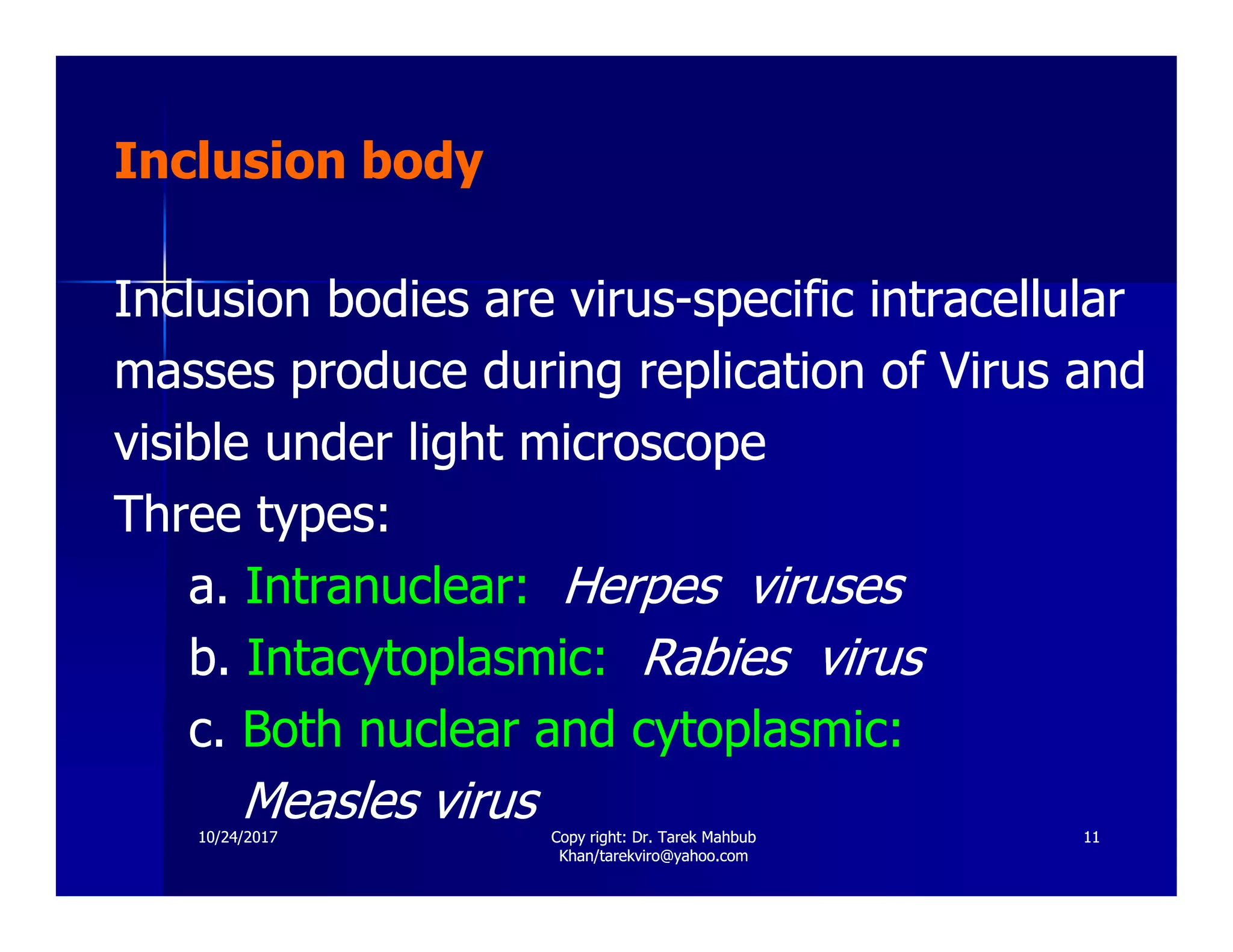
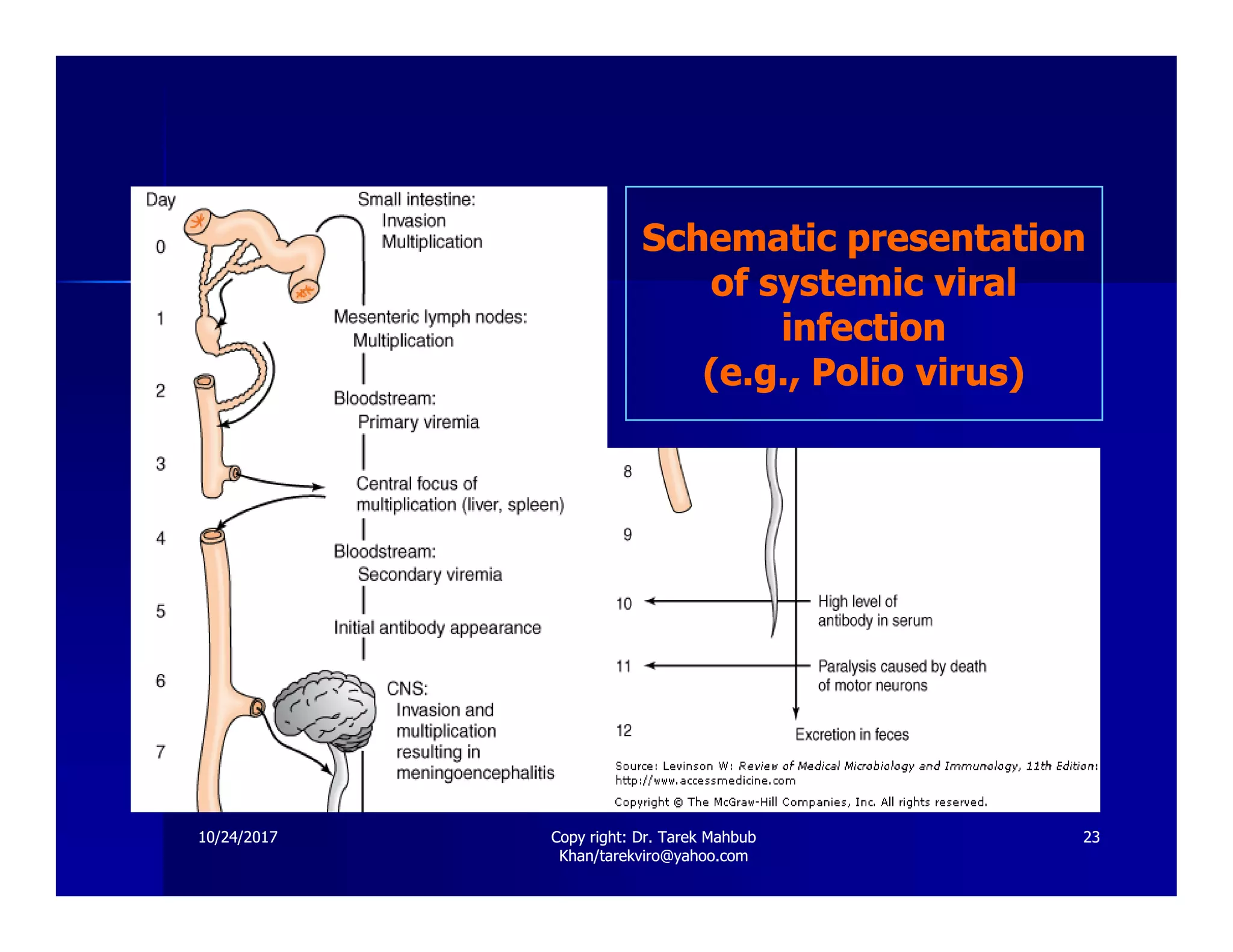
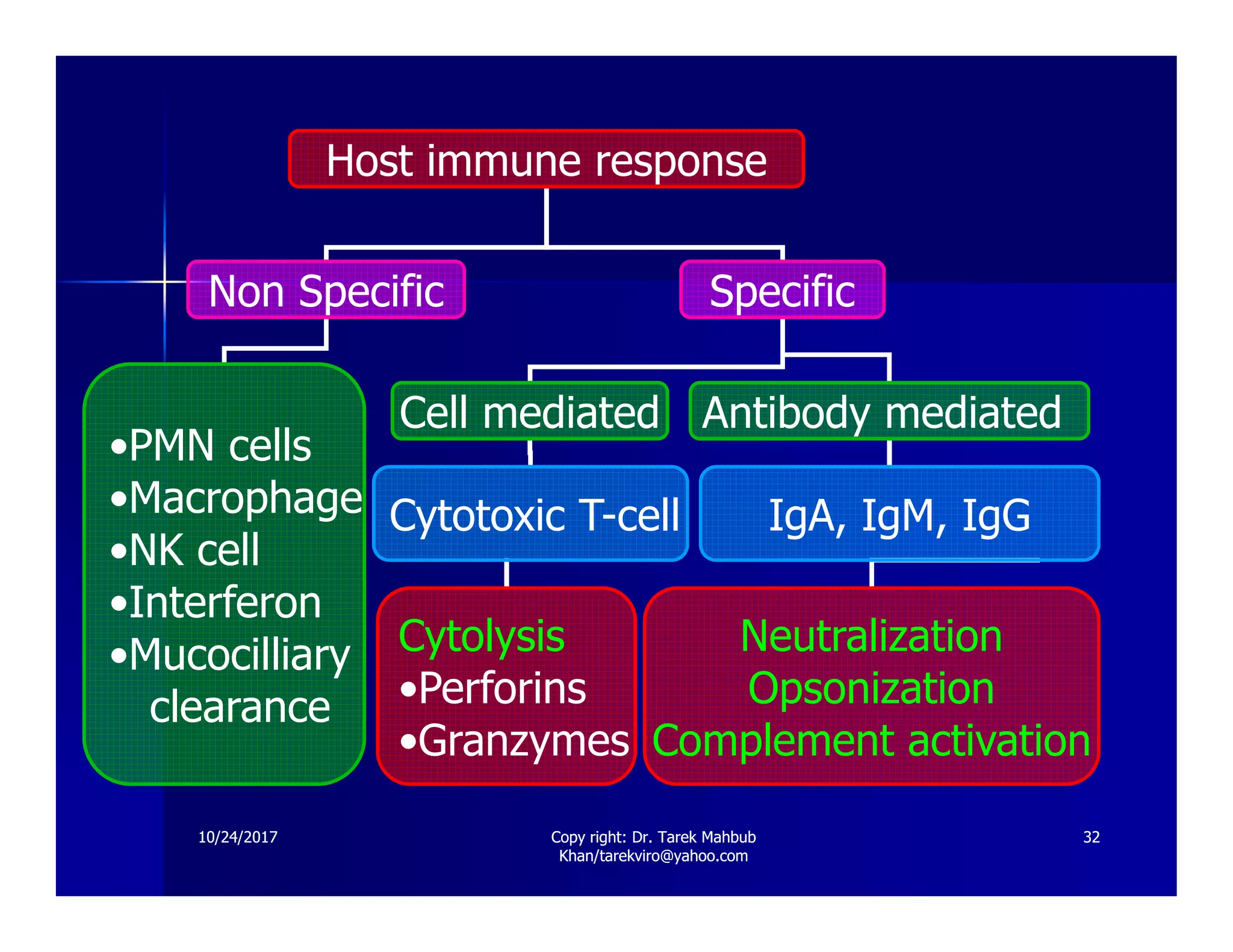
The document discusses the effects of viruses on host cells, including cytopathic effects, viral pathogenesis, and host immune responses. It outlines various types of viral infections, mechanisms of infection, and the concept of viral persistence, highlighting how viruses can evade the immune system. Key learning objectives for students cover understanding viral impacts, cellular interactions, and routes of transmission.