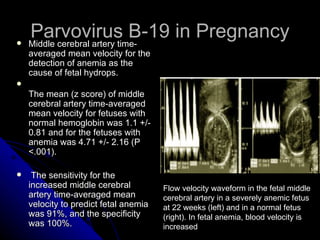
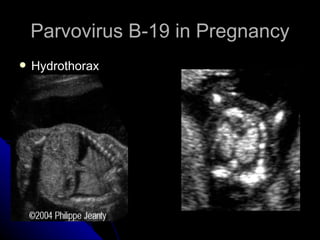
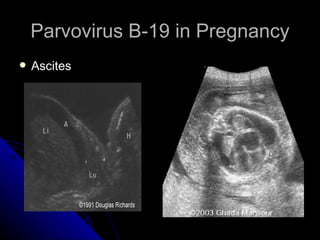
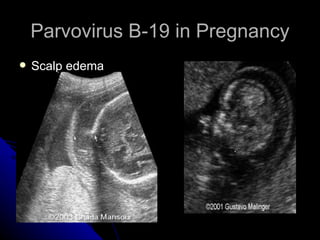
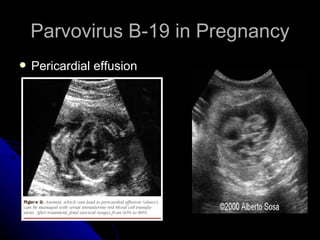
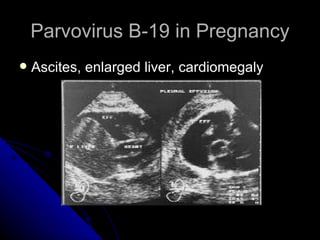
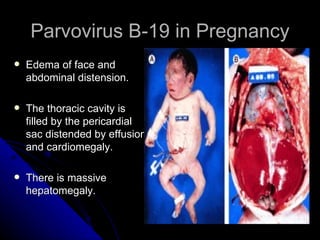
Parvovirus B-19 infection during pregnancy can pose risks to the fetus, including congenital infection, spontaneous abortion, and fetal anemia. Diagnosis typically involves serology testing to detect IgG and IgM antibodies, with further monitoring through ultrasounds if infection is confirmed. The management of affected pregnancies may require fetal surveillance, intrauterine transfusions, and close monitoring of maternal and fetal health to mitigate risks associated with the infection.









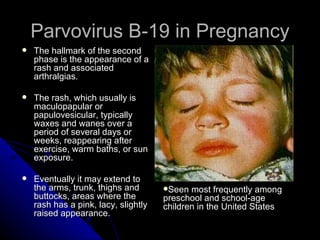







![Parvovirus B-19 in Pregnancy Monitoring and treating the infected fetus Women with documented seroconversion should undergo an initial targeted fetal ultrasound to identify or rule out congenital anomalies. Should perform weekly ultrasounds for 8 to 10 weeks after maternal infection. If the physician finds hydrops at sonography--the presence of which indicates that the fetus has parvovirus-induced anemia--cordocentesis (for B19-specific IgM). Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling [PUBS]) is indicated to assess fetal blood in preparation for intrauterine red blood cell transfusion to treat the anemia. Send fetal blood for IgG testing or for PCR (sensitivity, 100%) after 22 weeks, as IgG antibodies do not appear in the fetal circulation until this gestational age.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parvovirus-120205074935-phpapp01/85/Parvovirus-18-320.jpg)