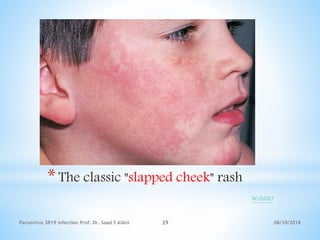
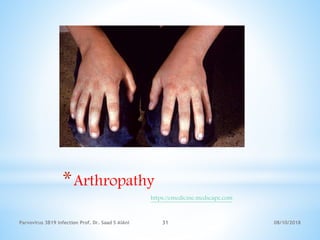
Parvovirus B19 is a single-stranded DNA virus that primarily infects humans and is associated with several clinical conditions, including fifth disease, aplastic crisis, and papular-purpuric 'gloves-and-socks' syndrome. Transmission occurs through respiratory secretions, vertical transmission, and exposure to infected blood, with symptoms typically manifesting 4-14 days post-infection. While infectious morbidity is generally low, severe complications such as hydrops fetalis can occur, especially if a nonimmune woman contracts the virus during early pregnancy.


































![08/10/2018Parvovirus 3B19 infection Prof. Dr. Saad S AlAni 39
*Laboratory Studies
1. Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA)
2. Radioimmunoassay
3. Immunofluorescence
Can be used to determine parvovirus serology
(anti–parvovirus B19 immunoglobulin M [IgM]
and immunoglobulin G [IgG] antibodies)
Bredl S, Plentz A, Wenzel JJ, Pfister H, Möst J, Modrow S. False-negative serology in
patients with acute parvovirus B19 infection. J Clin Virol. 2011 Jun. 51(2):115-20.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parvovirusb19infection-181027173525/85/Parvovirus-b19-infection-39-320.jpg)









