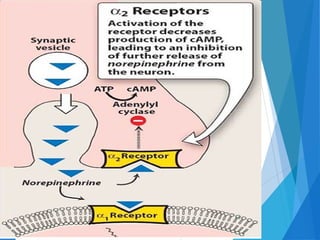
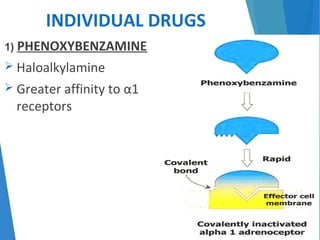
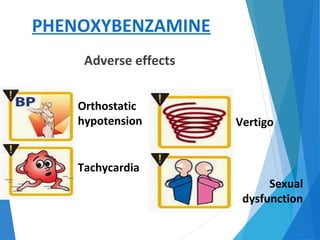
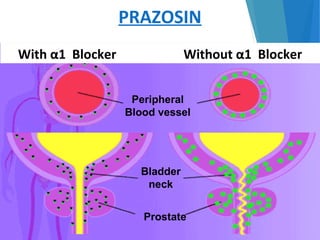
This document discusses alpha blockers, which are drugs that inhibit the interaction of hormones like norepinephrine with alpha receptors. It describes their classification as selective or non-selective, their functions in relaxing smooth muscle and reducing vasoconstriction, and individual drugs like prazosin, terazosin, and doxazosin. These drugs are important in managing conditions like pheochromocytoma, benign prostatic hyperplasia, hypertension, and peripheral vascular disease, but can cause adverse effects like postural hypotension and reflex tachycardia.