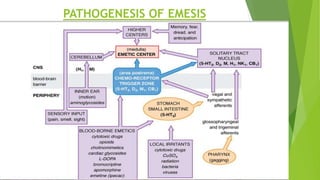
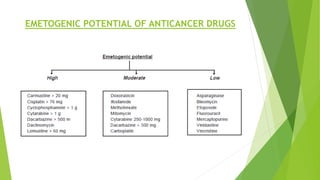
Aprepitant is an NK1 receptor antagonist approved for preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. It works by blocking substance P in the brain, which is involved in the final common pathway leading to vomiting. Aprepitant significantly increases the effectiveness of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists and corticosteroids for CINV prevention. It has a good safety profile but requires monitoring for potential drug interactions due to being metabolized by CYP3A4.