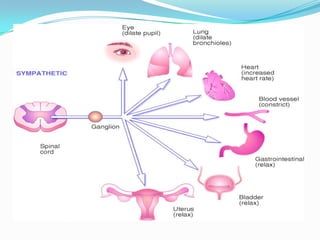
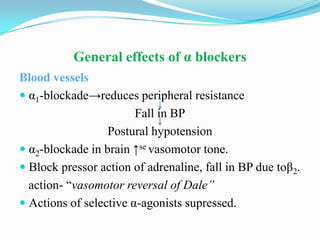
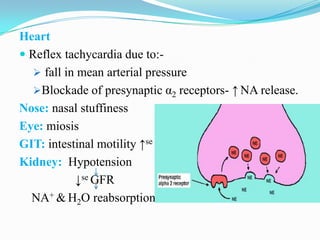
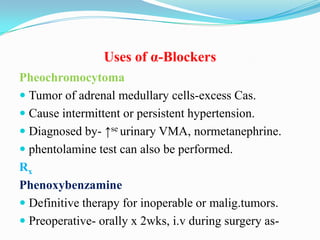
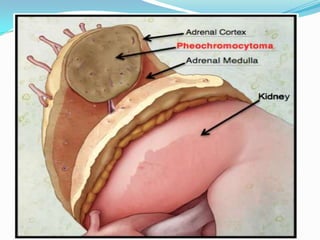
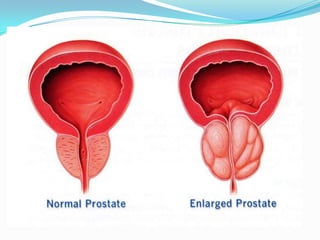
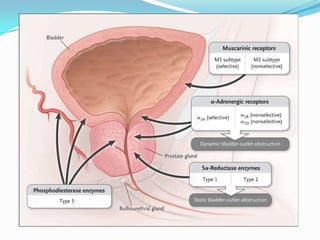
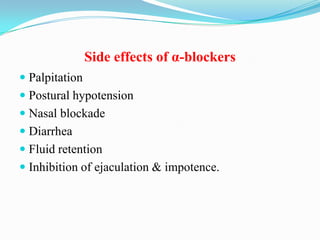
This document summarizes the classification, mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, and clinical uses of α-adrenergic receptor antagonists (α-blockers). It discusses non-selective α-blockers that block both α1 and α2 receptors like phentolamine and phenoxybenzamine, as well as selective α1-blockers like prazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, and selective α2-blockers like yohimbine. The major uses of α-blockers include treatment of pheochromocytoma, hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, benign prostatic hyperplasia, migraine, and congestive heart failure. Common side effects include hypotension