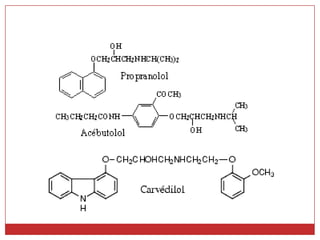
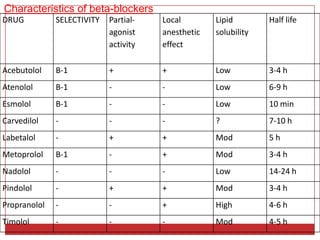
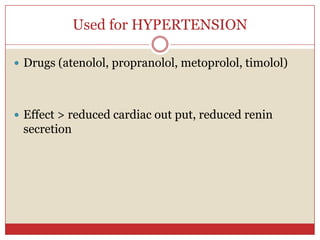
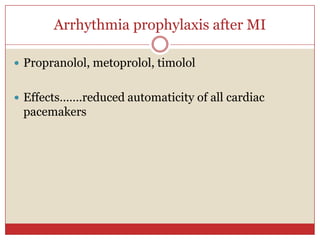
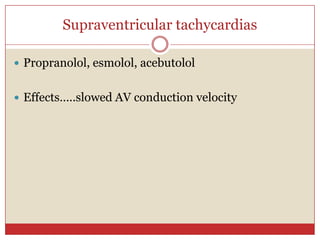
Beta blockers are a class of drugs that are used to treat high blood pressure and heart conditions by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors. There are several types of beta blockers that are categorized based on their selectivity and other properties. Some are cardioselective, meaning they mainly affect the heart, while others are non-selective. Beta blockers have various therapeutic uses for conditions like hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, and migraine prevention. Their effects are primarily cardiovascular in nature by slowing the heart rate and reducing blood pressure. Common adverse effects include worsening heart failure and bronchospasm.