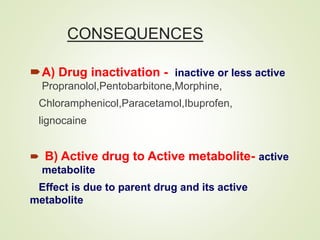
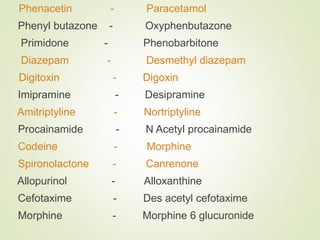
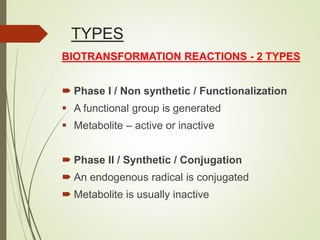
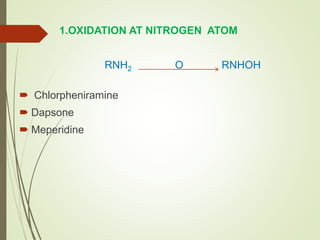
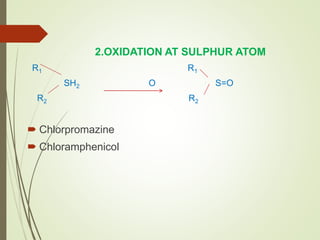
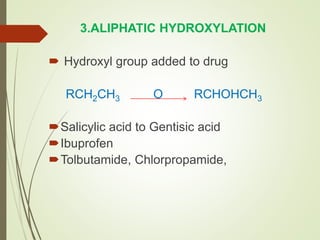
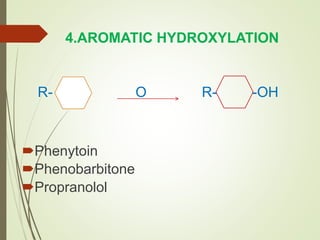
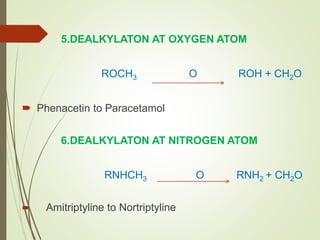
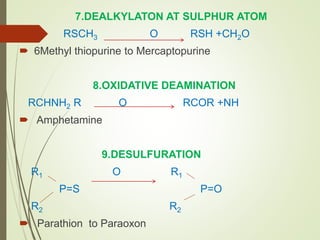
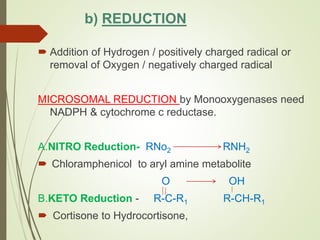
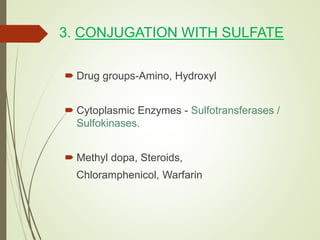
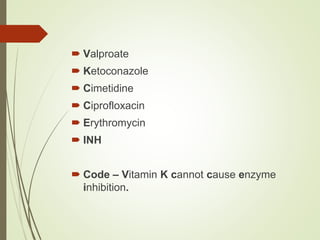
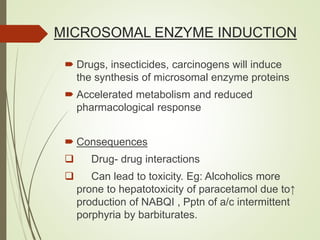
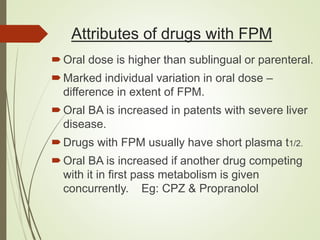
The document provides an overview of biotransformation, defining it as the chemical alteration of drugs in the body primarily to promote detoxification and enhance excretion. It details the types of biotransformation reactions—Phase I (functionalization) and Phase II (conjugation)—along with their respective metabolic processes, enzymes involved, and consequences for drug action. Additionally, it discusses factors influencing drug metabolism, such as first-pass metabolism and drug interactions, highlighting the importance of these processes in pharmacology.