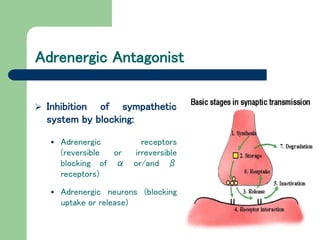
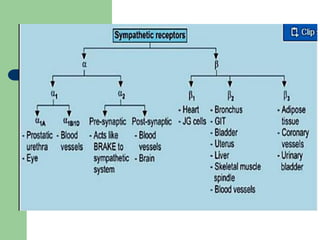
This document discusses adrenergic antagonists (sympatholytics) which inhibit the sympathetic nervous system by blocking adrenergic receptors or neurons. It describes different types of adrenergic blocking drugs that are selective for α and β receptors. Non-selective α-blockers like phenoxybenzamine cause irreversible blockade while phentolamine is competitive. Selective α1-blockers lower blood pressure with minimal effects on cardiac output. Orthostatic hypotension is a common side effect of α-blockers due to inhibition of venous vasoconstriction.






![ Actions:
Cardiovascular effects:
By blocking α1 receptors, phenoxybenzamine prevents
vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels by endogenous
catecholamines.
The decreased peripheral resistance provokes a reflex
tachycardia, arrhythmia, and even ischemic cardiac events.
Furthermore, the ability to block presynaptic inhibitory α2
receptors in the heart can contribute to an increased cardiac
output. [Note: These receptors when blocked will result in
more norepinephrine release, which stimulates β1 receptors
on the heart to increase cardiac output].
Thus, the drug has been unsuccessful in maintaining
lowered blood pressure in hypertension.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14313-190909055647-230829055034-21430f24/85/Pharmacology-9-320.jpg)

















