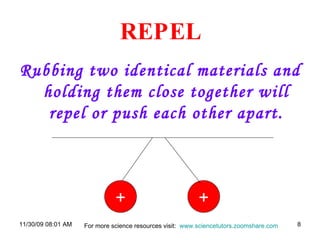
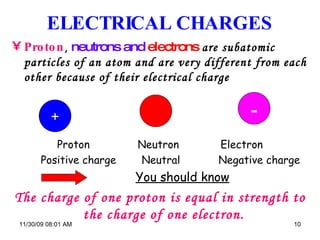
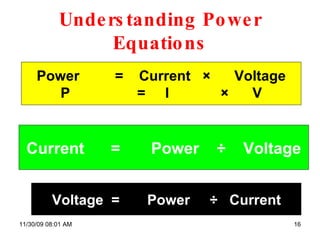
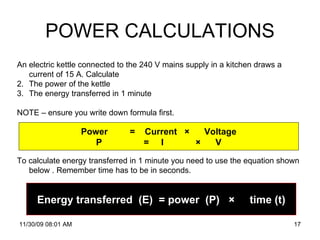
The document provides an overview of static and current electricity, detailing the concepts of electric charge, electric current, voltage, and resistance. It explains how static electricity develops through the movement of electrons in insulators, and how electrical current is defined as the flow of electric charge in a complete circuit. Additionally, it covers the calculation of electrical power and energy transfer in household appliances, as well as the operation of transformers in electricity distribution.