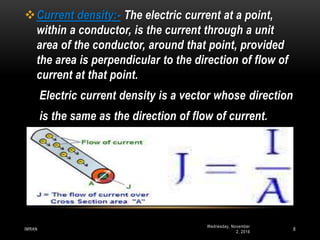
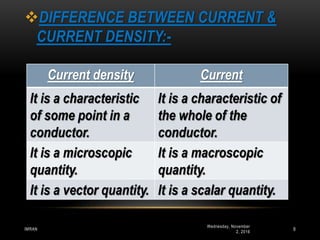
1) Current electricity deals with the motion of charges in conductors like electrons. Electric current is defined as the charge flowing through any cross-section of a conductor per second, with the standard unit being 1 ampere.
2) Materials can be classified as conductors, insulators, or semiconductors based on their conductivity. Conductors have high conductivity while insulators have very low conductivity.
3) Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in a conductor. It is measured in ohms and depends on factors like the material and dimensions of the conductor.