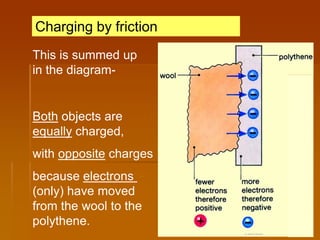
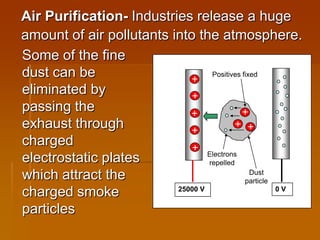
1) The document discusses static electricity and electric current. It explains how charging by friction can create static electricity and defines electric current as the rate of flow of electric charge.
2) Key concepts covered include the structure of atoms, charging by transferring electrons between materials, and how static charge is held on insulators while current involves the flow of electrons in conductors.
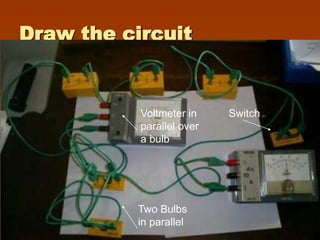
3) The document provides examples of current in series and parallel circuits, noting that current is the same everywhere in a series circuit while the total current entering a parallel junction equals the sum of the currents in the branches.