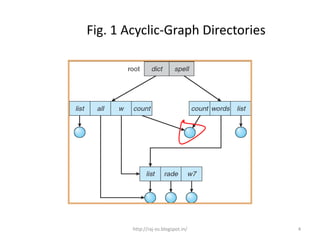
Acyclic-graph directories use a graph structure without cycles to allow shared files and subdirectories that can be accessed by multiple users, which is useful for collaboration. They implement shared resources by either creating link entries that reference the shared file, ignoring the links to preserve the acyclic structure, or by duplicating file information in all sharing directories and ensuring consistency when modified.