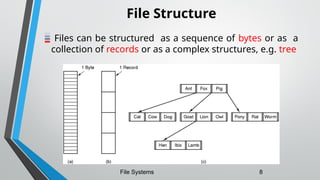
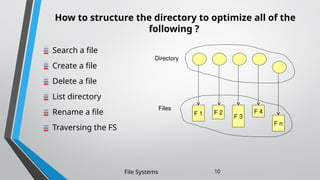
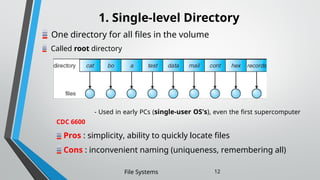
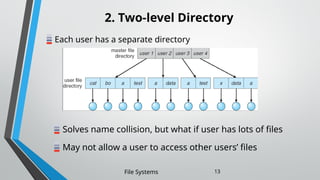
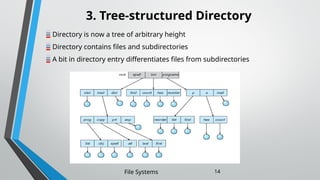
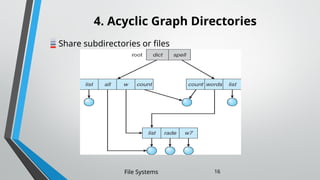
The document outlines the essential components and properties of file systems, explaining how files are organized, accessed, and protected on secondary storage. It covers file attributes, basic operations like read and write, file structuring, and directory organization methods. Additionally, it discusses access methods and the importance of file protection against unauthorized access and physical damage.