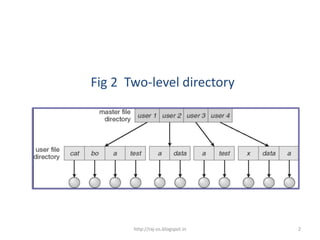
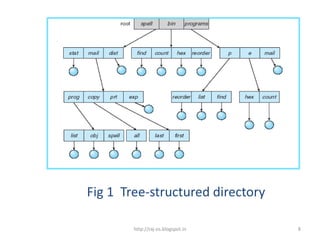
The document discusses different directory structures in operating systems, including single-level, two-level, and tree-structured directories. A two-level directory structure has a master file directory (MFD) that contains pointers to individual user file directories (UFDs) for each user. This solves the name collision problem of single-level directories by isolating each user's files. Tree-structured directories extend the two-level approach recursively to allow subdirectories within subdirectories. Path names then specify the directory tree path to a given file.