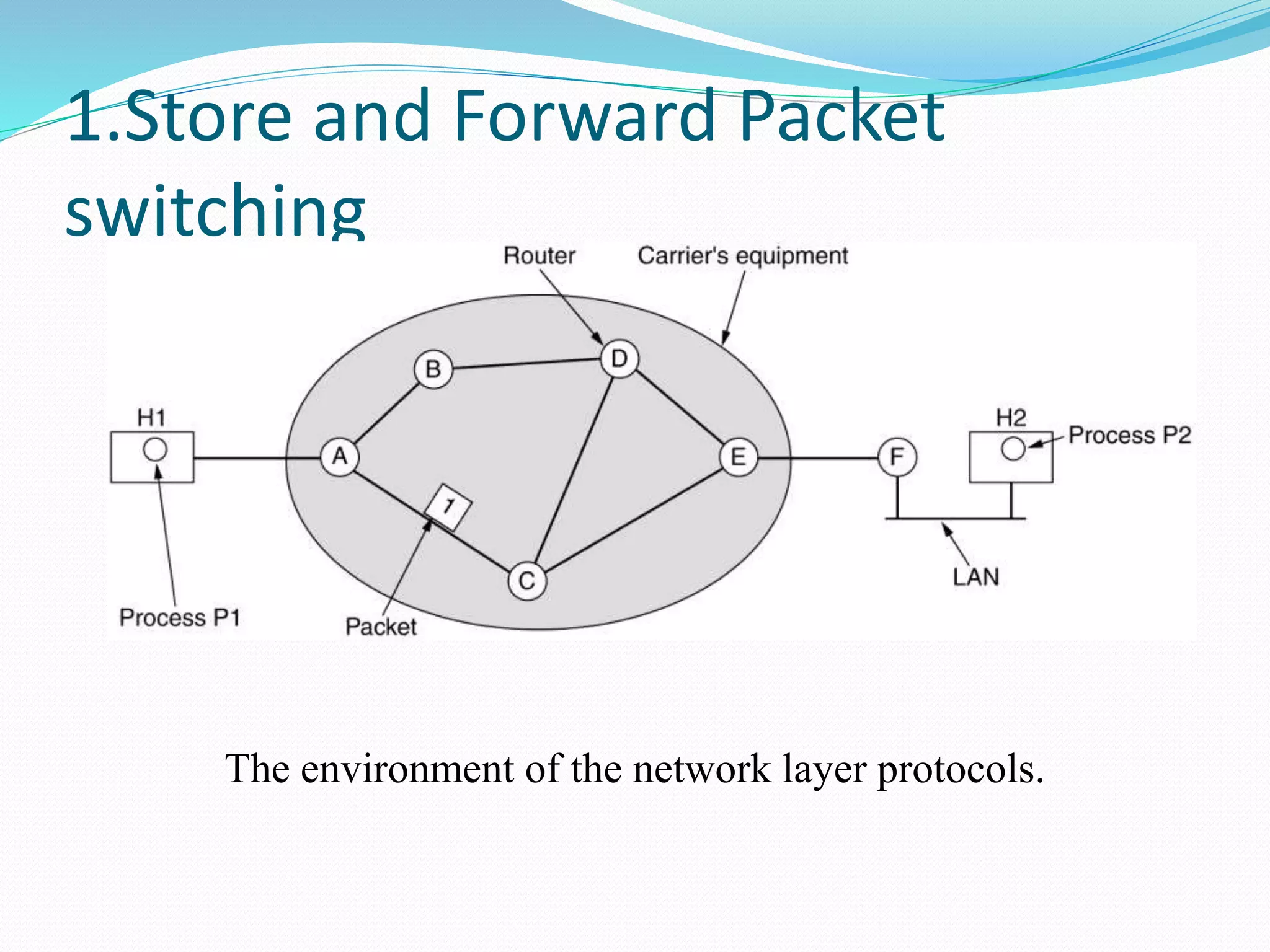
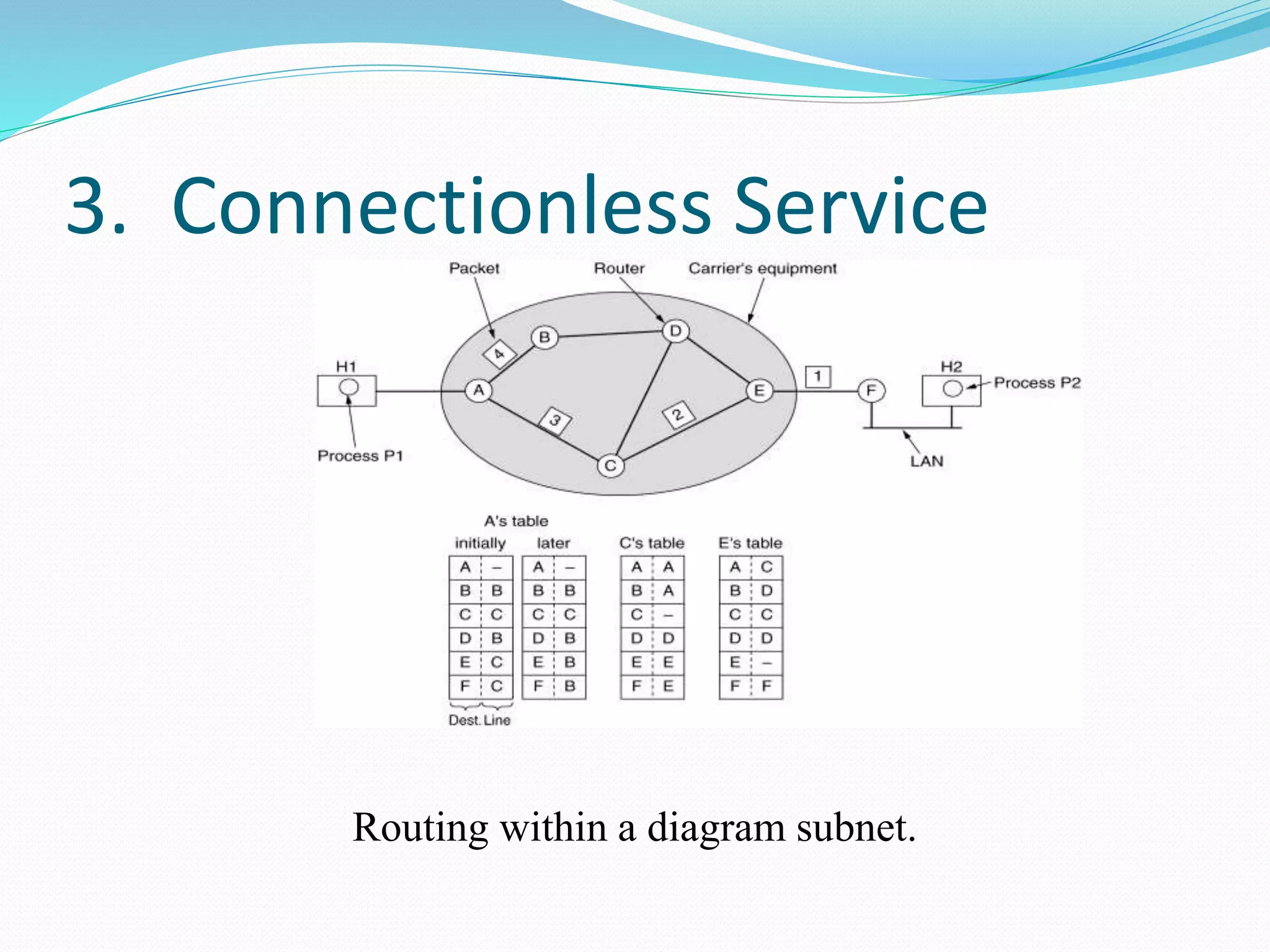
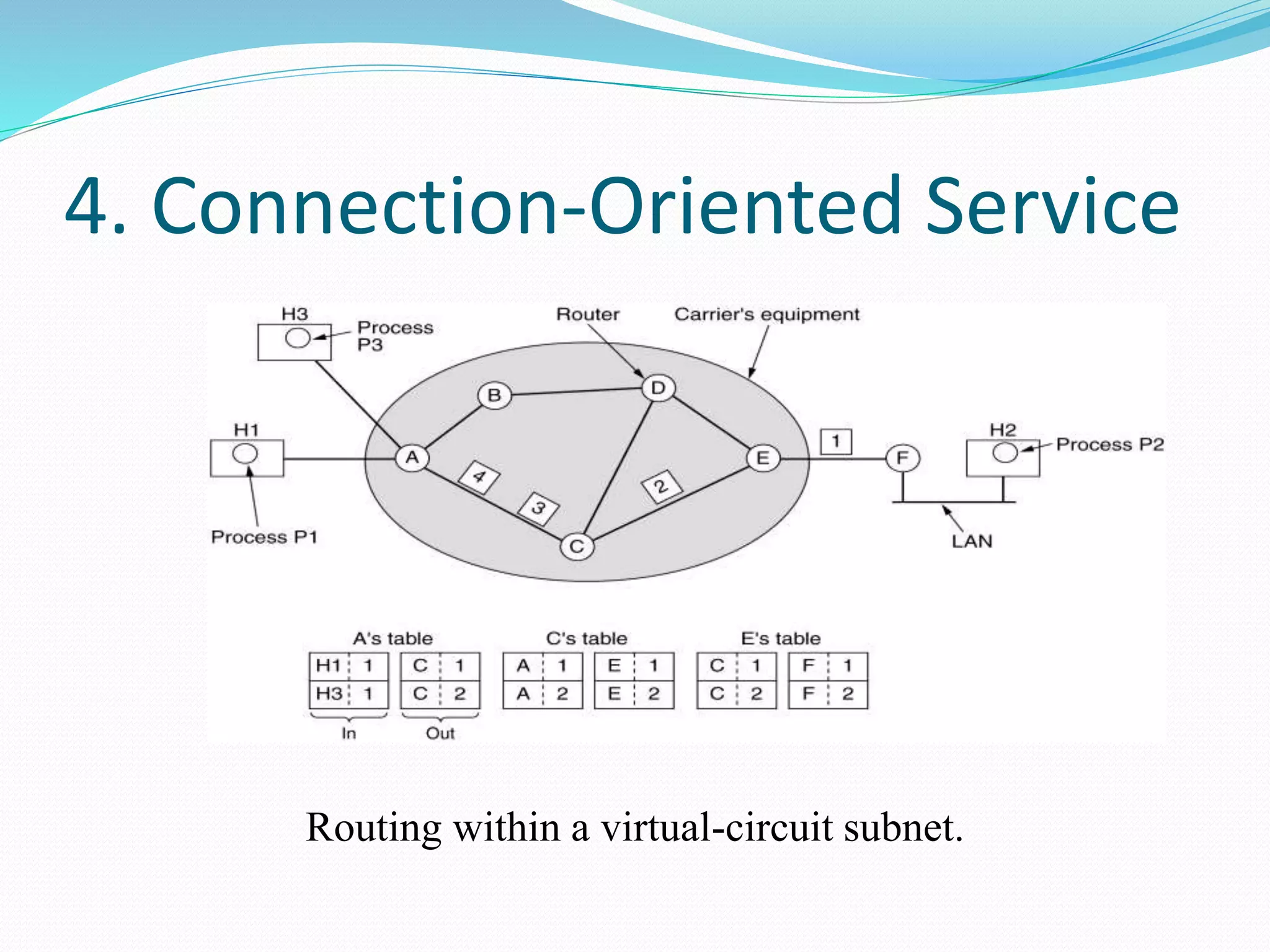
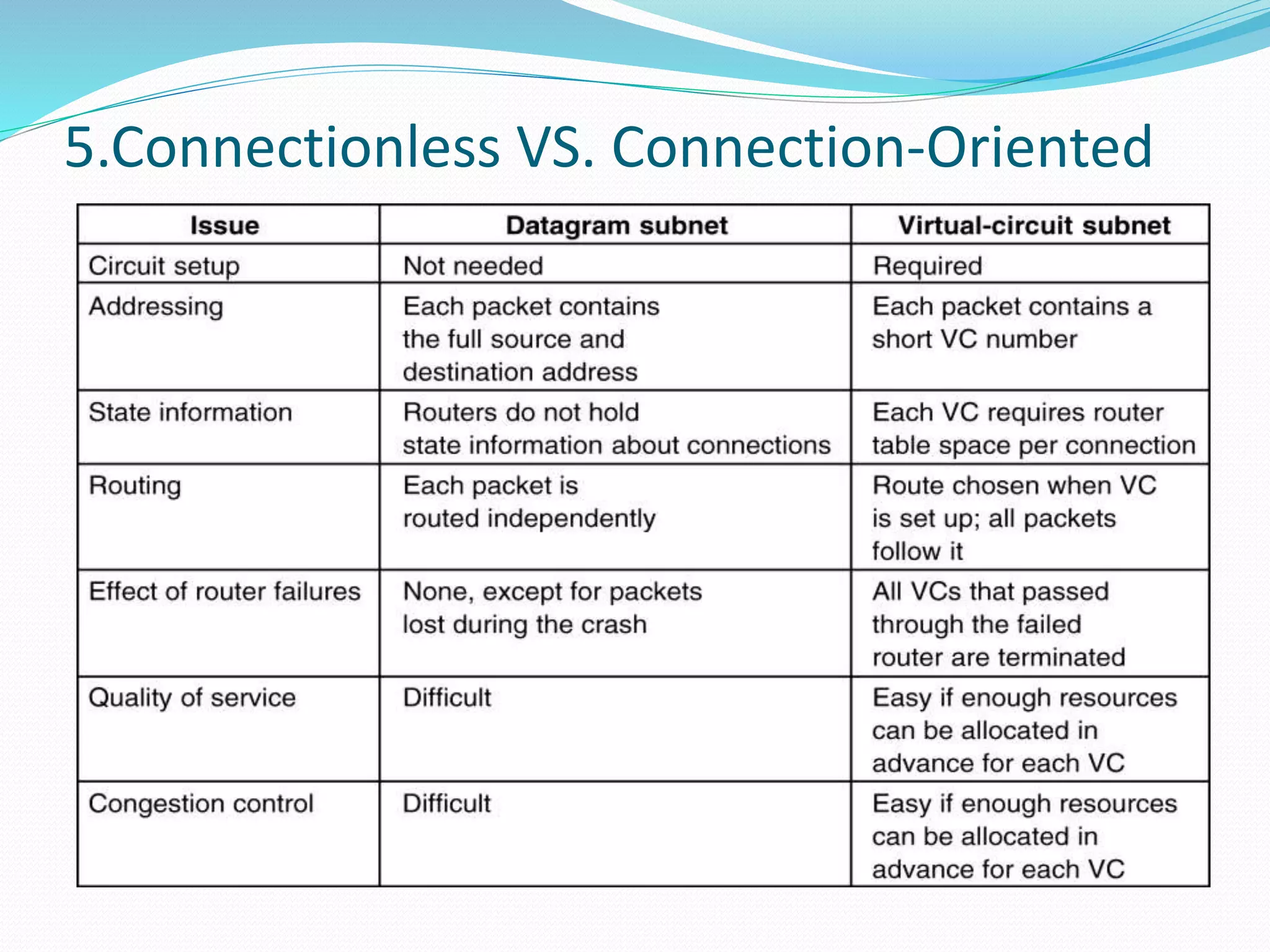
The network layer provides two main services: connectionless and connection-oriented. Connectionless service routes packets independently through routers using destination addresses and routing tables. Connection-oriented service establishes a virtual circuit between source and destination, routing all related traffic along the pre-determined path. The document also discusses store-and-forward packet switching, where packets are stored until fully received before being forwarded, and services provided to the transport layer like uniform addressing.