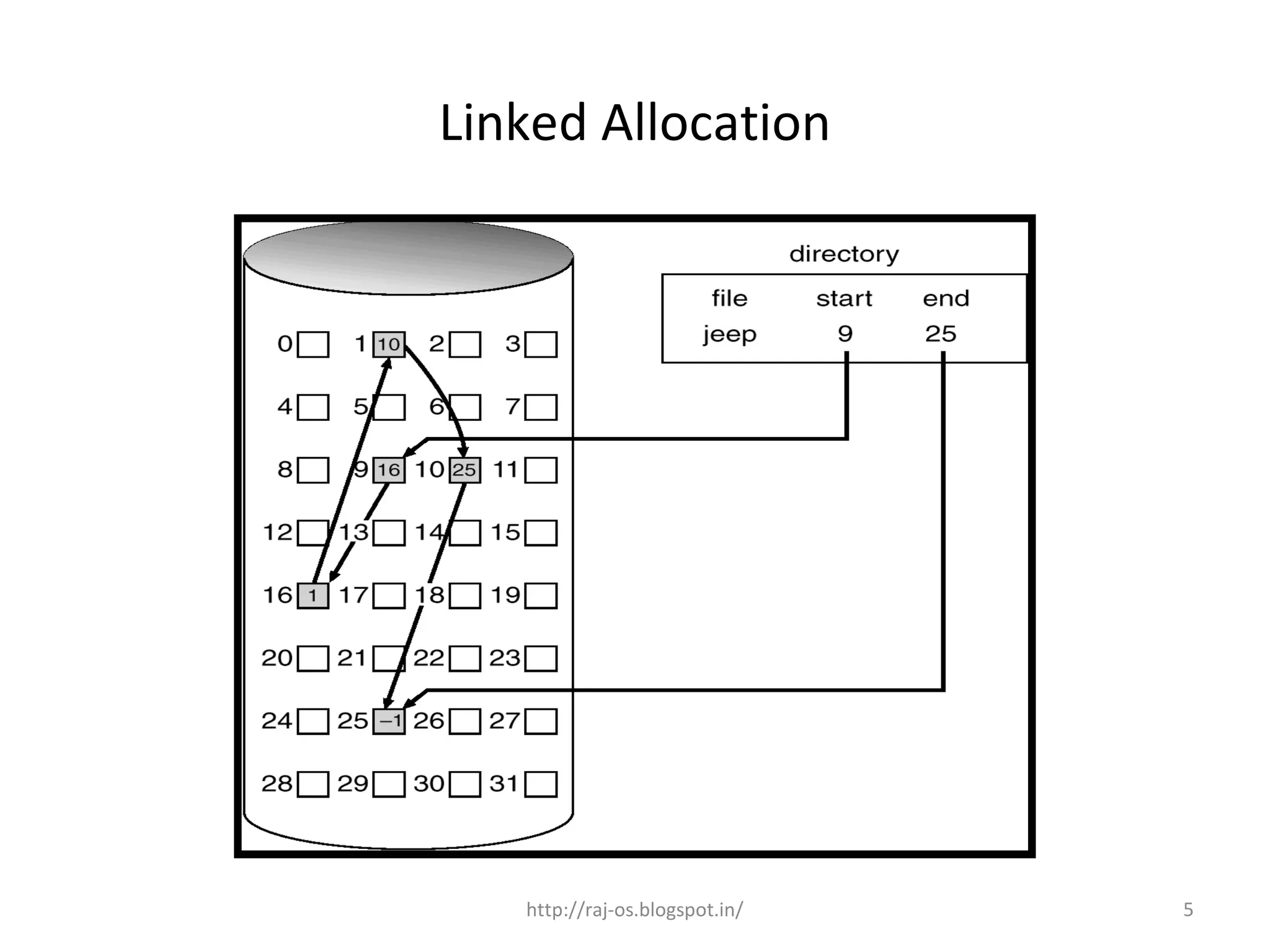
Linked allocation, also known as chained allocation, stores each file as a linked list of disk blocks where each block contains a pointer to the next block in the chain. This allows any free block to be added to the chain for a file. It is simple to implement as it only requires the starting address, but individual blocks cannot be randomly accessed and must be traced through the chain. A single damaged pointer can make many disk blocks inaccessible.