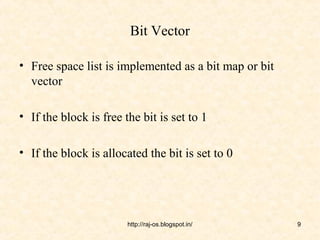
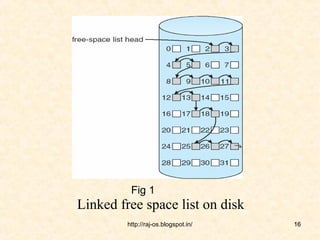
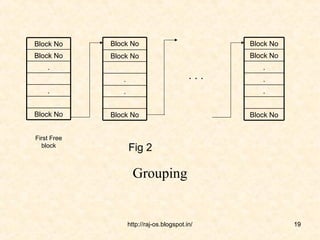
This document discusses free space management techniques in operating systems. It explains the need to track free disk space and reuse it from deleted files. Various free space list implementations are described, including bit vector, linked list, grouping, and counting. Bit vector uses a bitmap to track free blocks, linked list links free blocks, grouping stores addresses of free blocks in blocks, and counting tracks free block runs with an address and count.









![Bit Vector (n blocks)
0 1 2 n-1
…
0 ⇒ block[i] free
bit[i] =
1 ⇒ block[i] occupied
Block number calculation
(number of bits per word) *
(number of 0-value words) +
offset of first 1 bit
http://raj-os.blogspot.in/ 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespacemanagment46-130319070257-phpapp02/85/Free-space-managment46-11-320.jpg)













![Quiz
• To keep track of disk space the system maintains
Free space list
• Bit map requires extra space [T/F]
True
http://raj-os.blogspot.in/ 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespacemanagment46-130319070257-phpapp02/85/Free-space-managment46-27-320.jpg)
![Quiz
• In Linked allocation it is easy to get the contiguous space
[T/F]
False
• In Counting it is easy to get the contiguous space [T/F]
True
http://raj-os.blogspot.in/ 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespacemanagment46-130319070257-phpapp02/85/Free-space-managment46-28-320.jpg)
