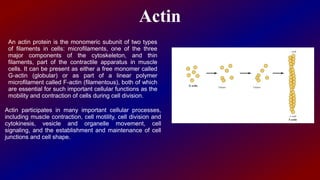
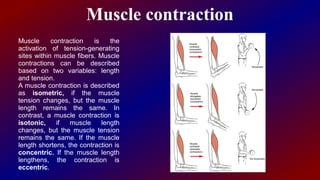
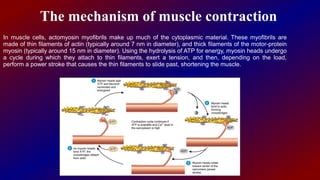
Actin and myosin are proteins that play important roles in muscle contraction. Actin exists as monomers called G-actin and polymers called F-actin that form microfilaments. Myosin has a head domain that binds to actin and uses ATP to generate force and move along actin filaments. During muscle contraction, myosin heads attach to actin, exert tension through a power stroke, causing actin filaments to slide and muscles to shorten. Precise interactions between actin and myosin are crucial for muscle function and movement.