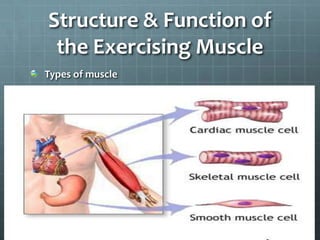
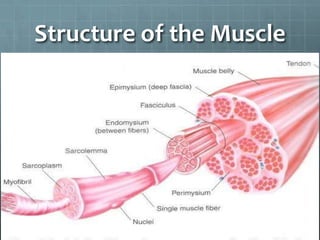
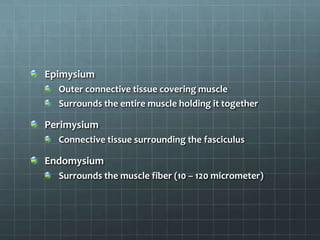
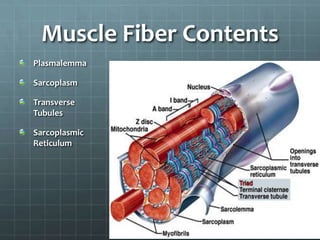
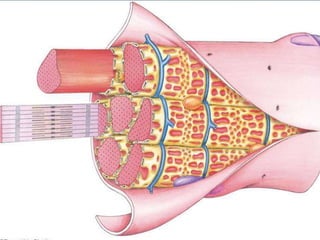
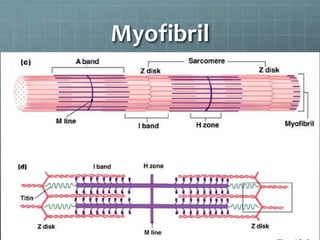
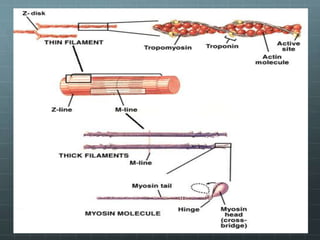
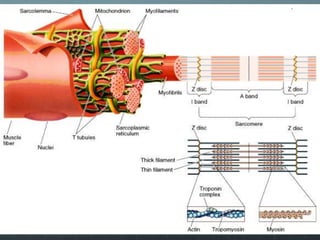
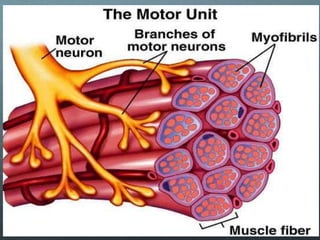
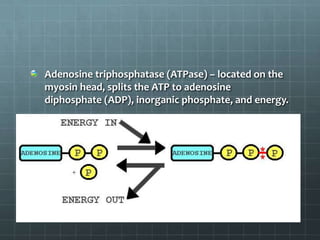
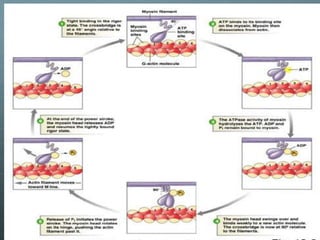
This document discusses exercise physiology and the structure and function of exercising muscle. It begins by defining anatomy, physiology, exercise physiology, and sports physiology. It then describes the structure of muscle including the epimysium, perimysium, endomysium, plasmalemma, sarcoplasm, transverse tubules, and sarcoplasmic reticulum. It explains the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction which is driven by the hydrolysis of ATP and the release and reuptake of calcium. It concludes by describing the roles of the neuromuscular junction, action potentials, and calcium in initiating and ending muscle contraction.