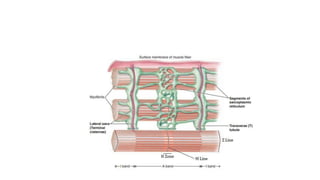
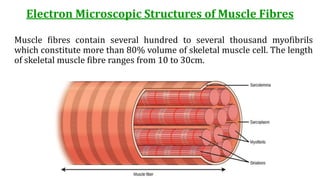
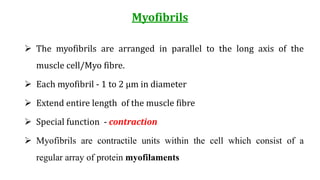
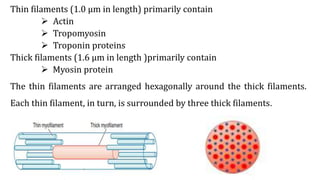
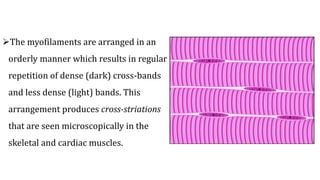
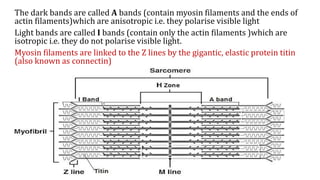
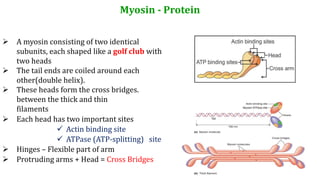
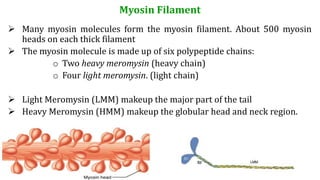
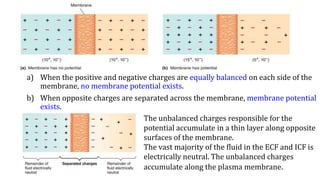
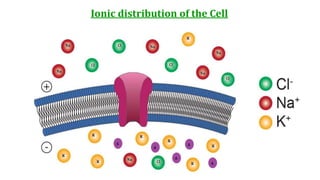
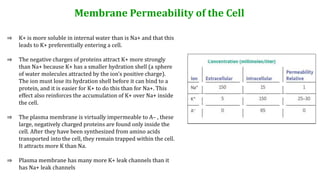
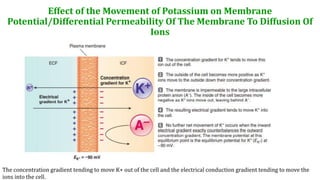
This document provides information about muscle physiology and the structure of muscle fibers at the microscopic level. It discusses the basic units of muscles including myofibrils, myofilaments, sarcomeres, and the proteins actin and myosin that make up the thin and thick filaments. It describes the striated banding pattern visible in muscle fibers due to the organized arrangement of these contractile proteins. It also covers concepts related to muscle membrane potential including ion gradients and the role of the sodium-potassium pump in establishing the resting potential.