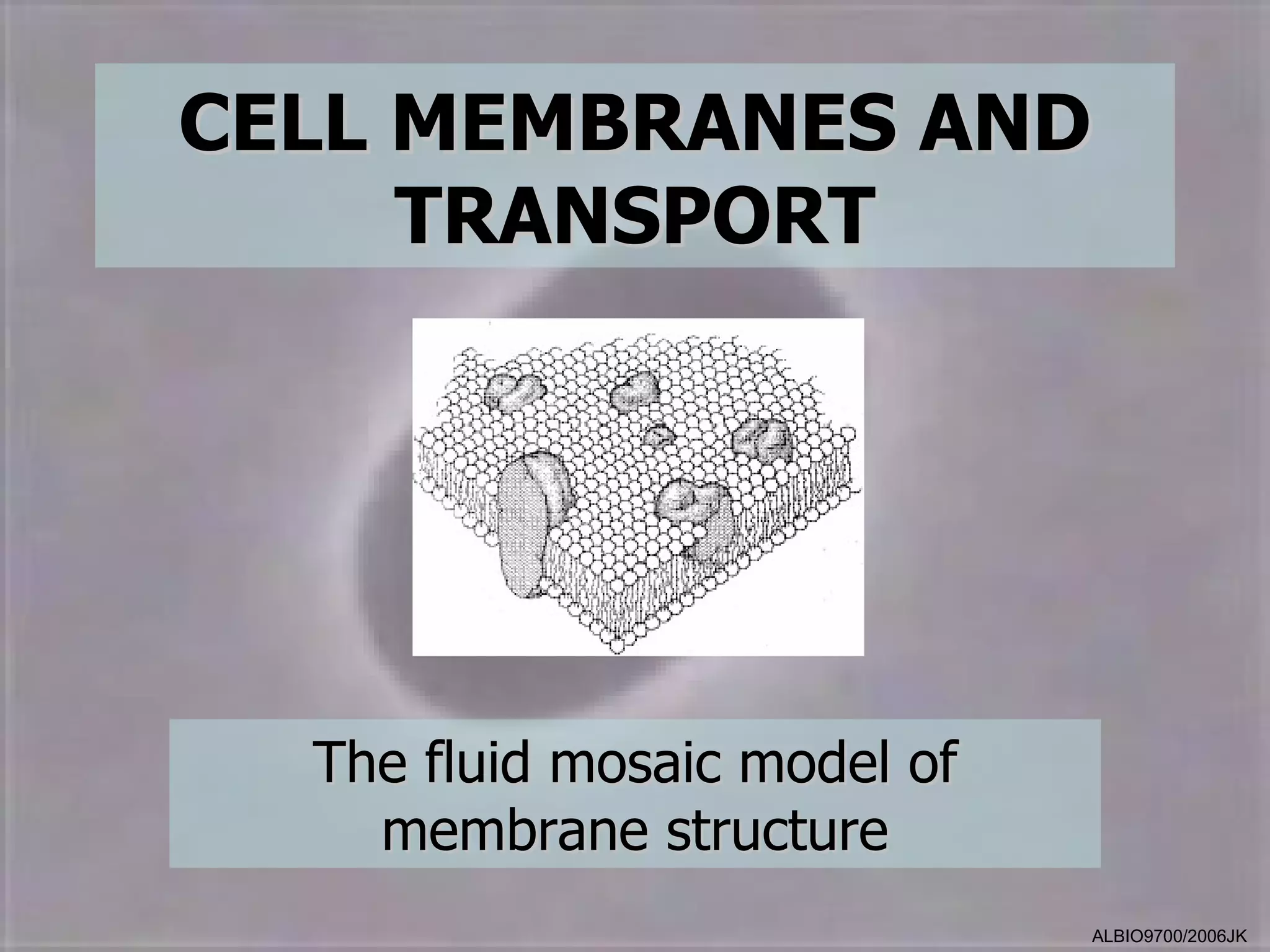
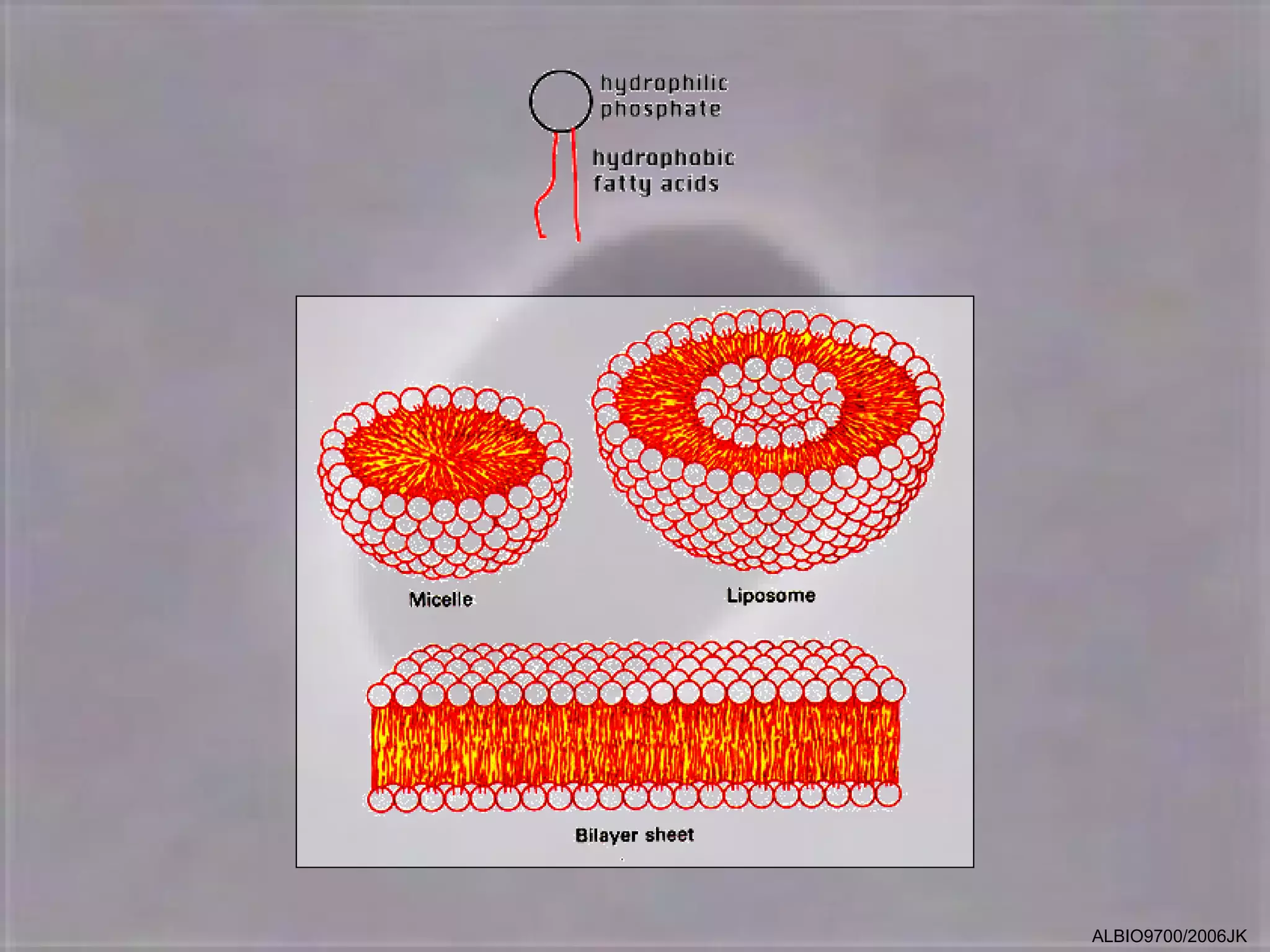
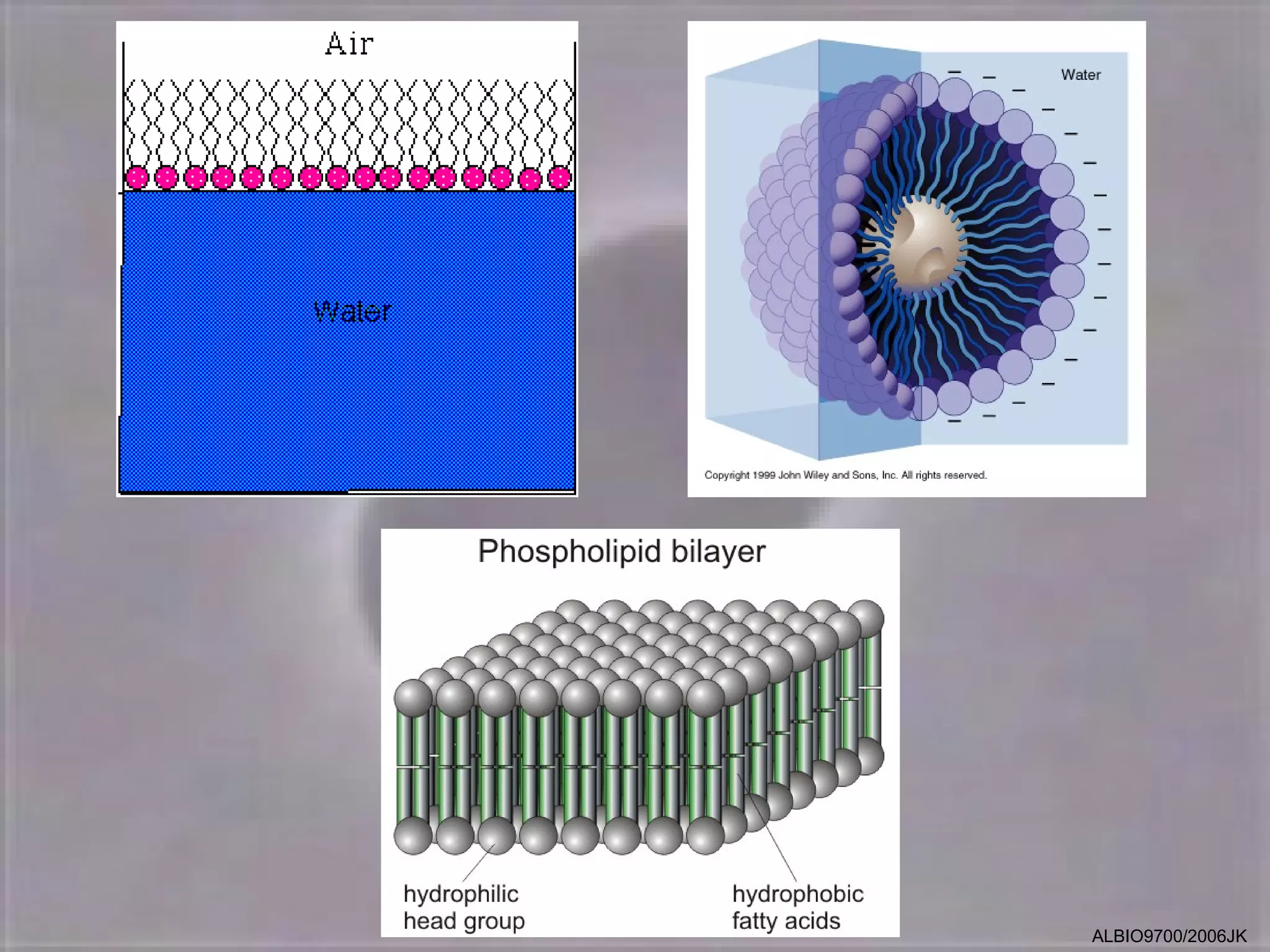
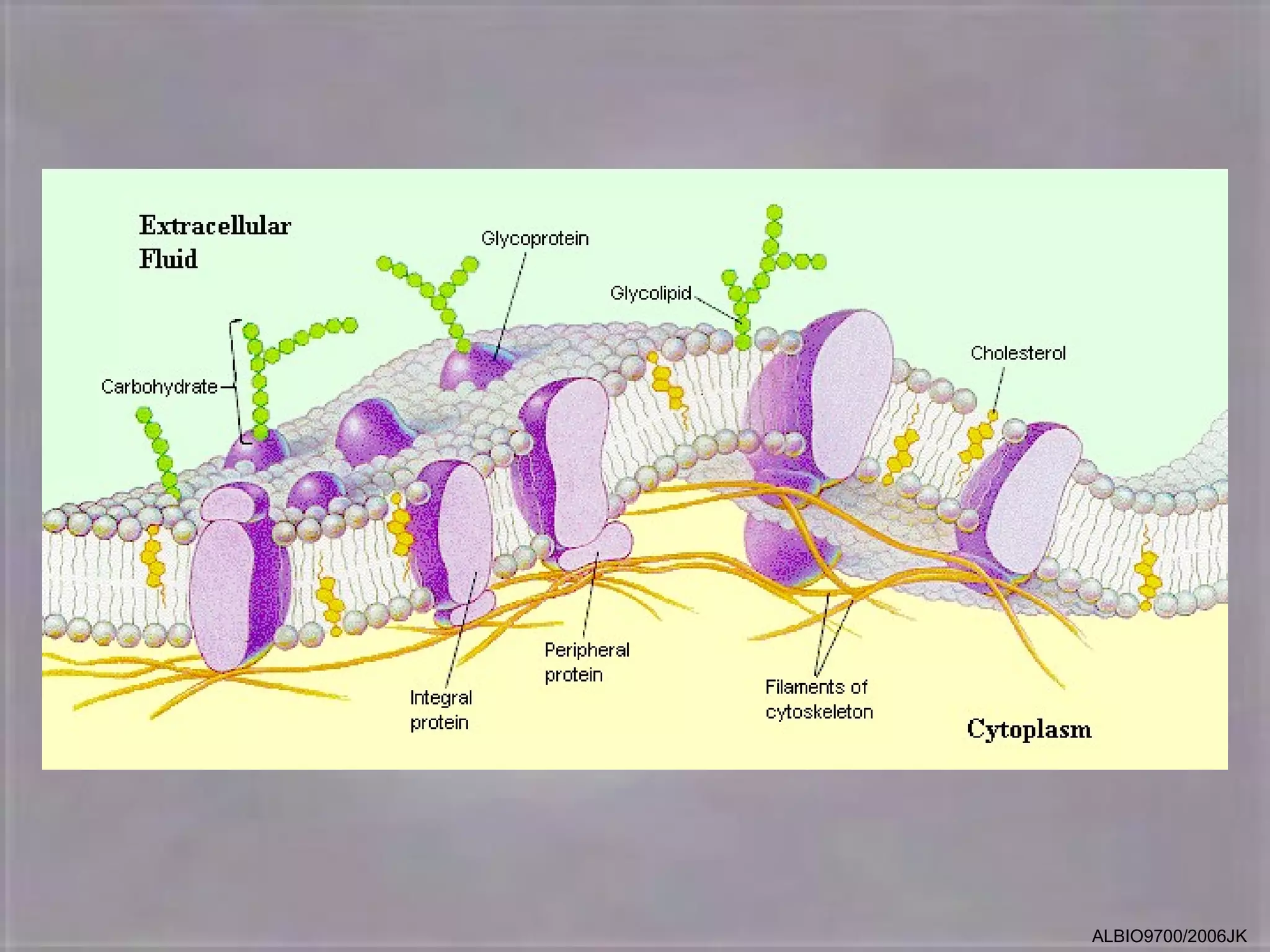
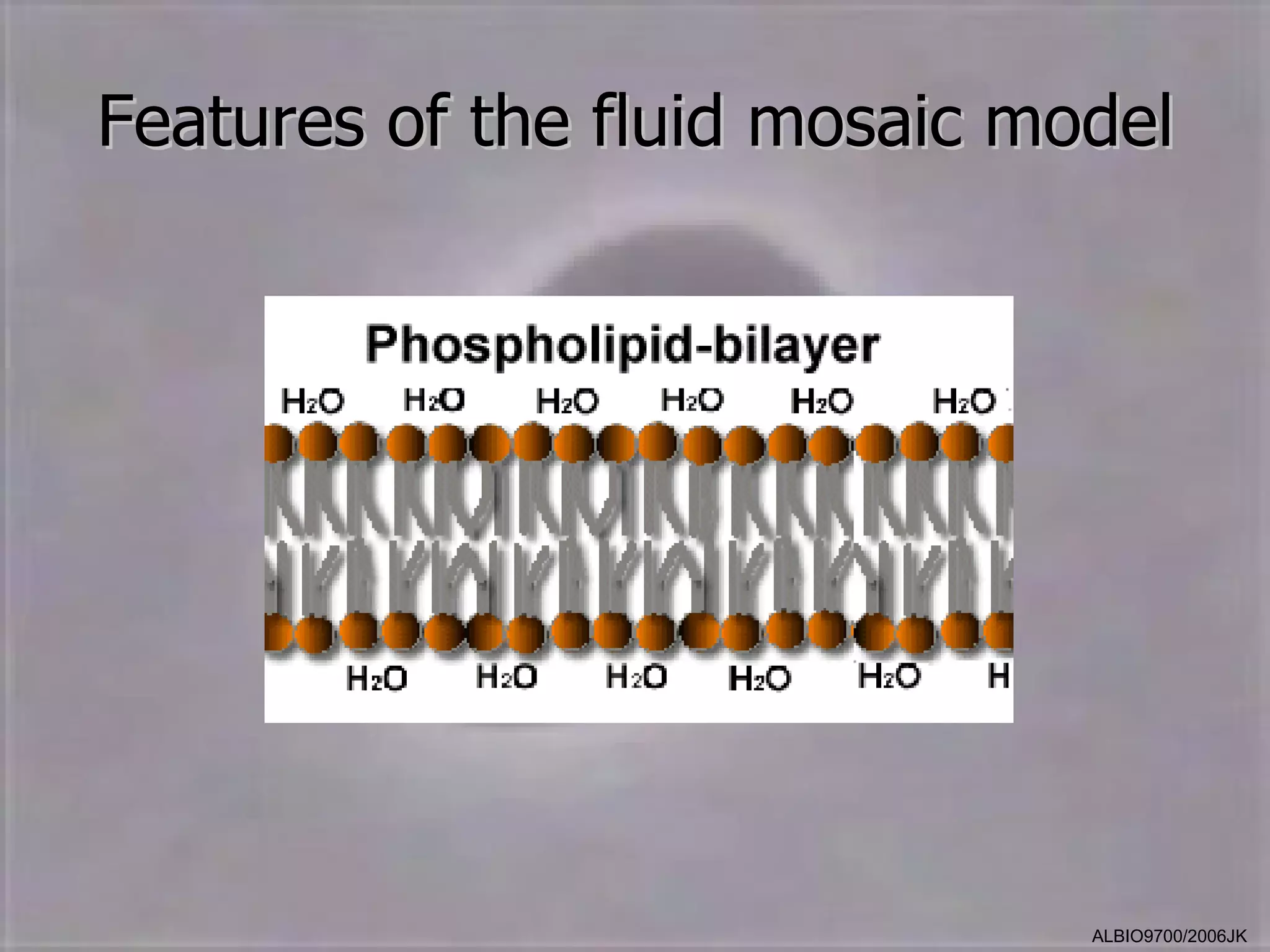
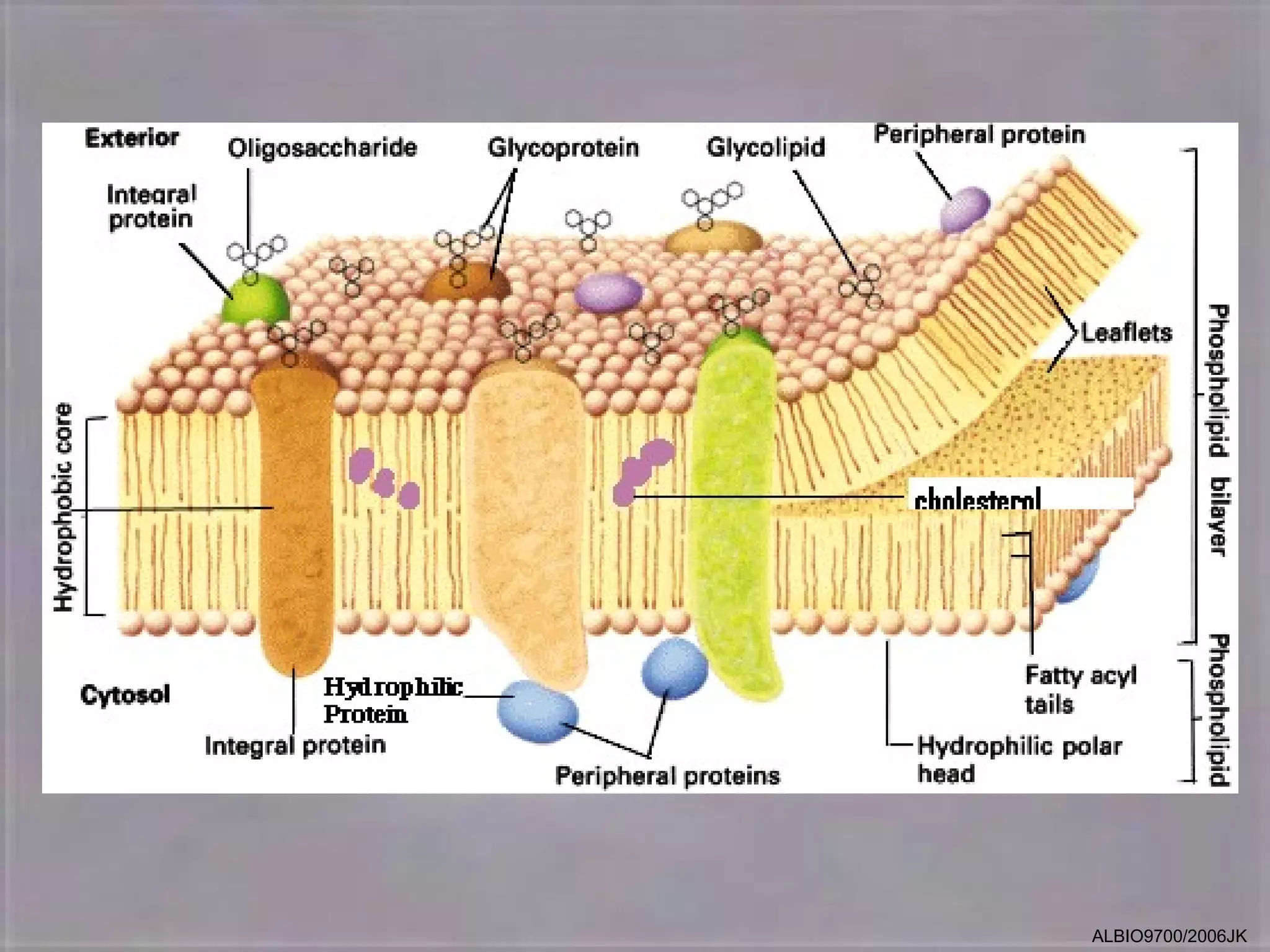
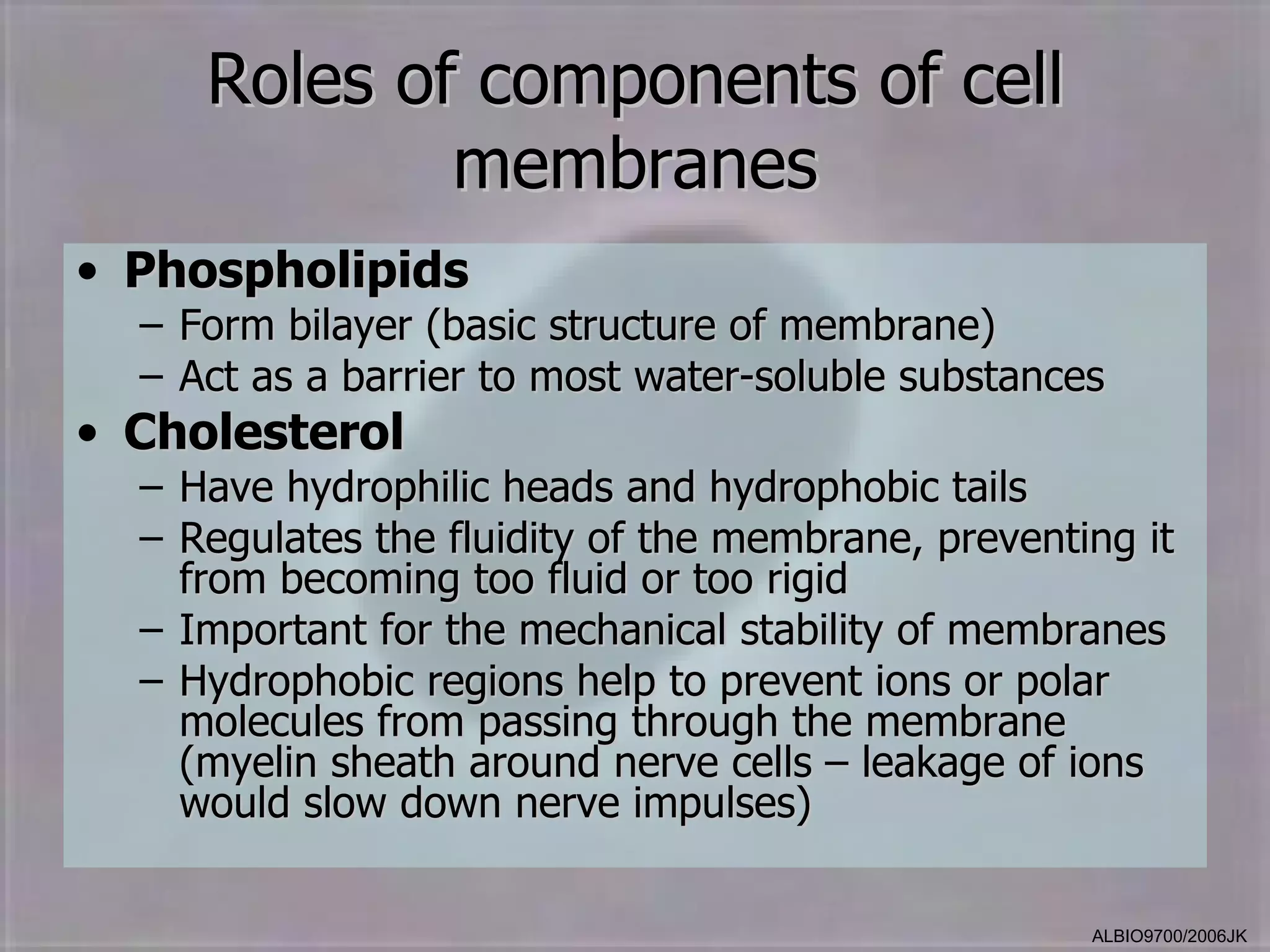
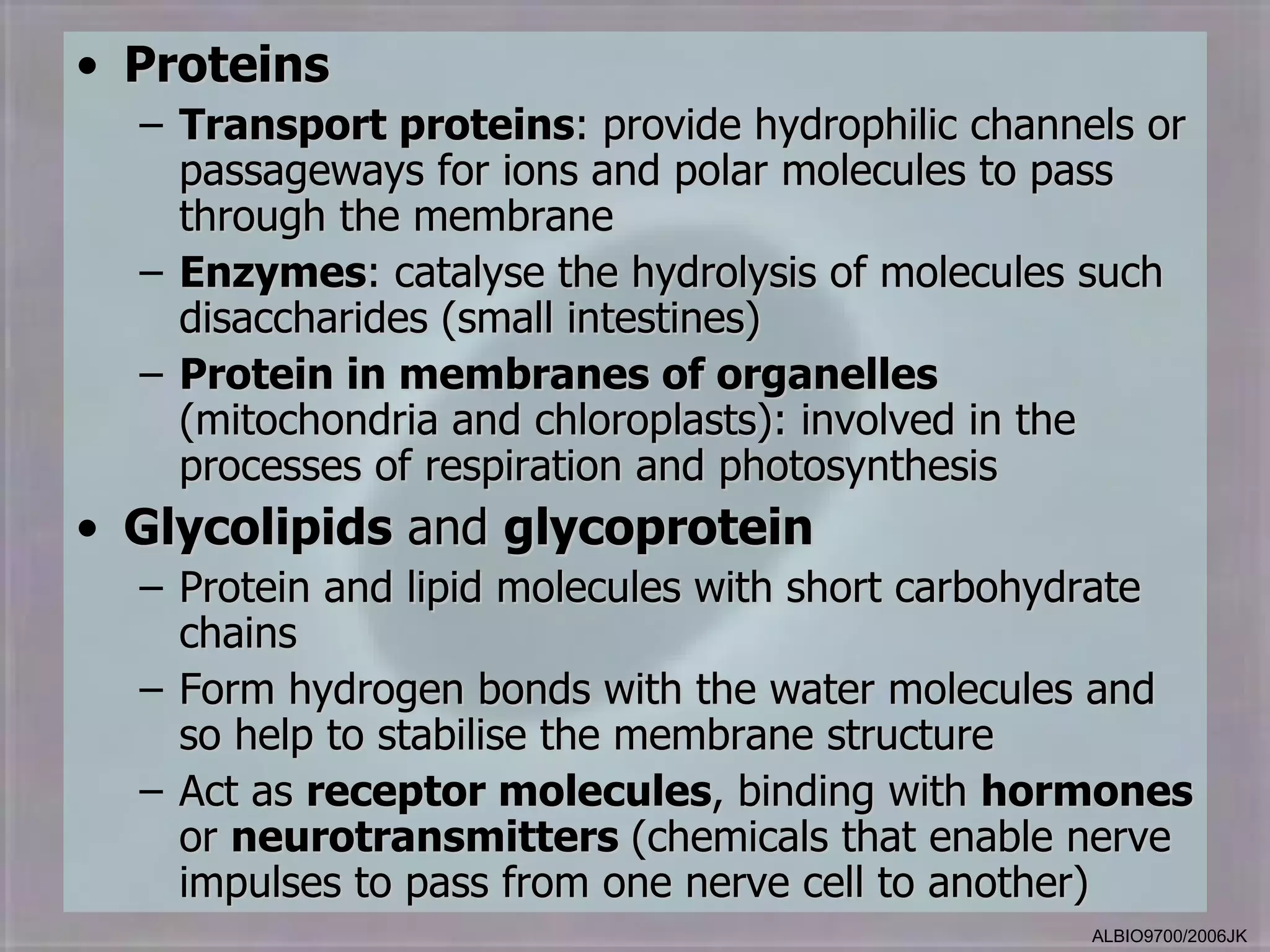
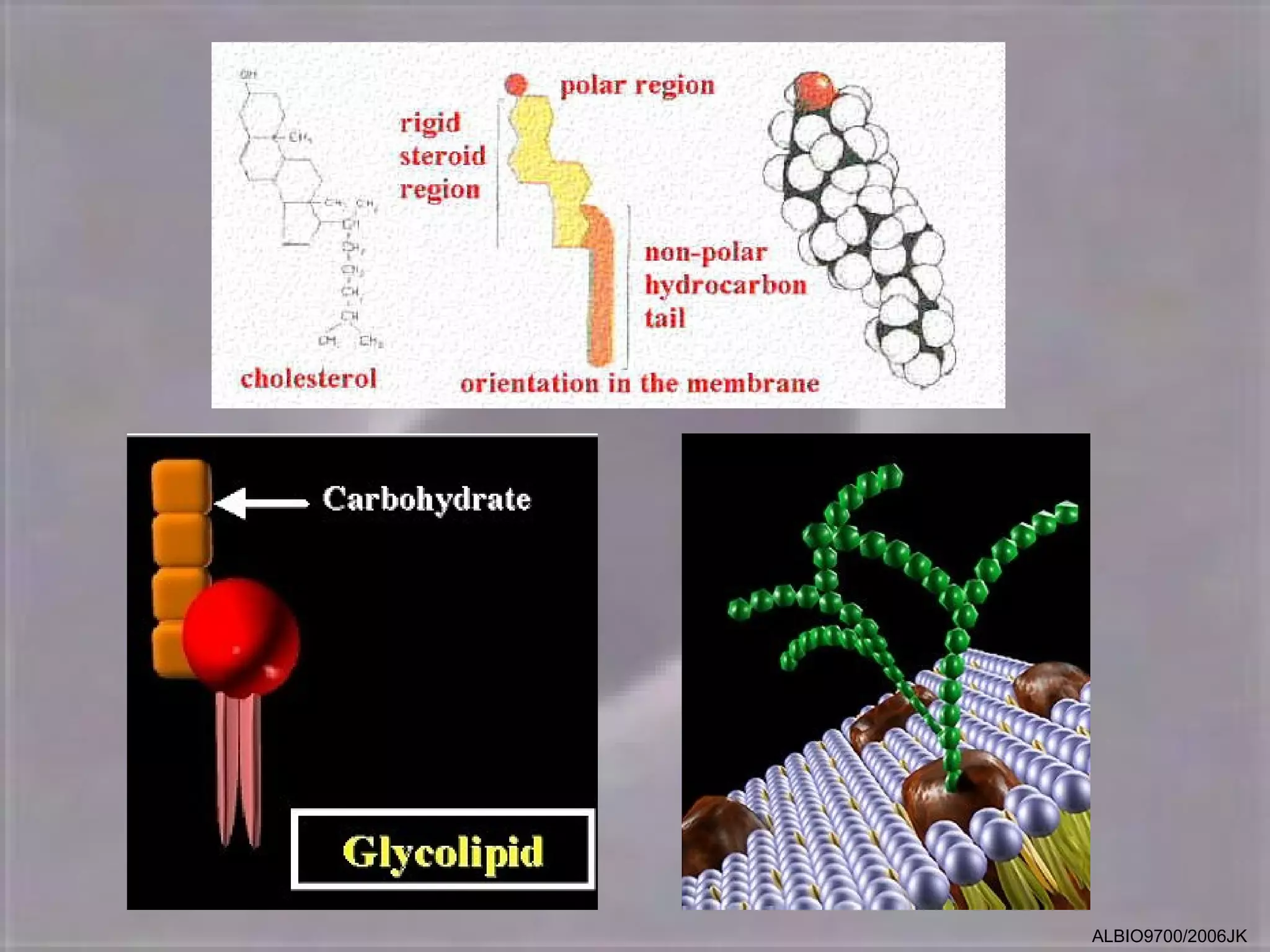
The cell membrane is made up of a fluid mosaic of phospholipids and proteins. Phospholipids form a bilayer with hydrophobic tails pointing inward and hydrophilic heads facing out. This structure acts as a selective barrier. Embedded and integral proteins carry out important functions like transporting molecules and catalyzing reactions. The fluid mosaic model accounts for the membrane's fluidity and ability to allow movement of components while maintaining selective permeability.