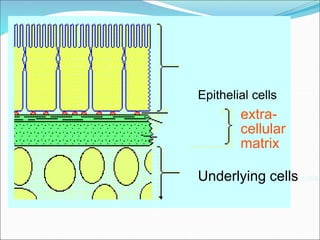
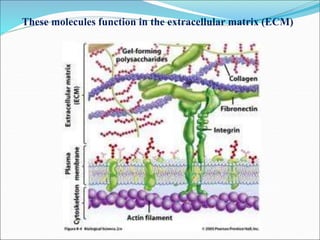
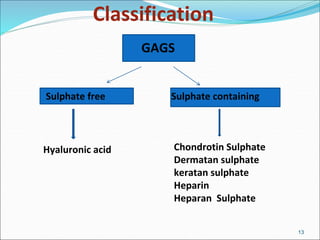
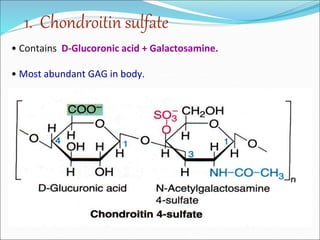
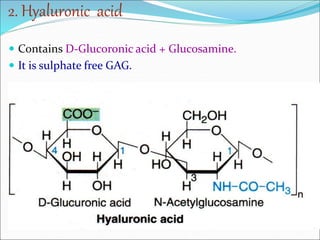
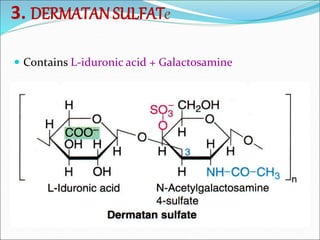
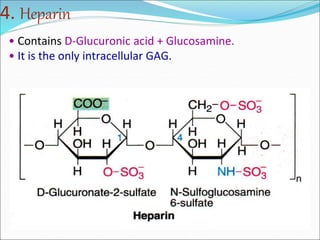
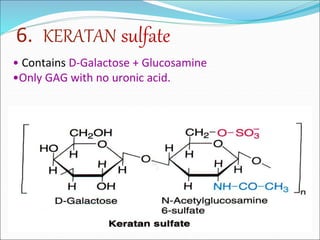
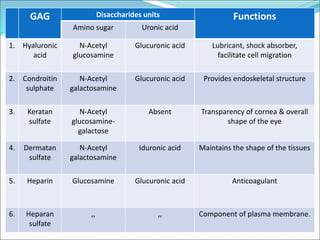
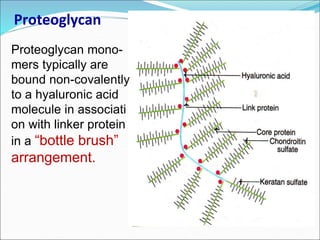
The document discusses the extracellular matrix (ECM) in mammalian tissues, highlighting its role in supporting cells and facilitating the diffusion of nutrients. It details the structure and function of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), their physiological significance, various types, and specific roles in tissues. Key GAGs covered include hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, and heparin, along with their functions in cartilage, lubrication, and anticoagulation.